Comprehensive Guide to Managing Atopic Dermatitis Through Dietary Choices
This comprehensive guide explores how dietary choices impact atopic dermatitis management. It highlights foods to include, such as omega-3 rich fish, probiotics, and antioxidants, and foods to avoid, like dairy, citrus, and eggs, which may trigger flare-ups. Combining proper diet with skincare and medical treatments can significantly improve symptoms and quality of life for individuals suffering from eczema. Learn effective strategies for managing this chronic skin condition through informed nutrition and lifestyle adjustments.

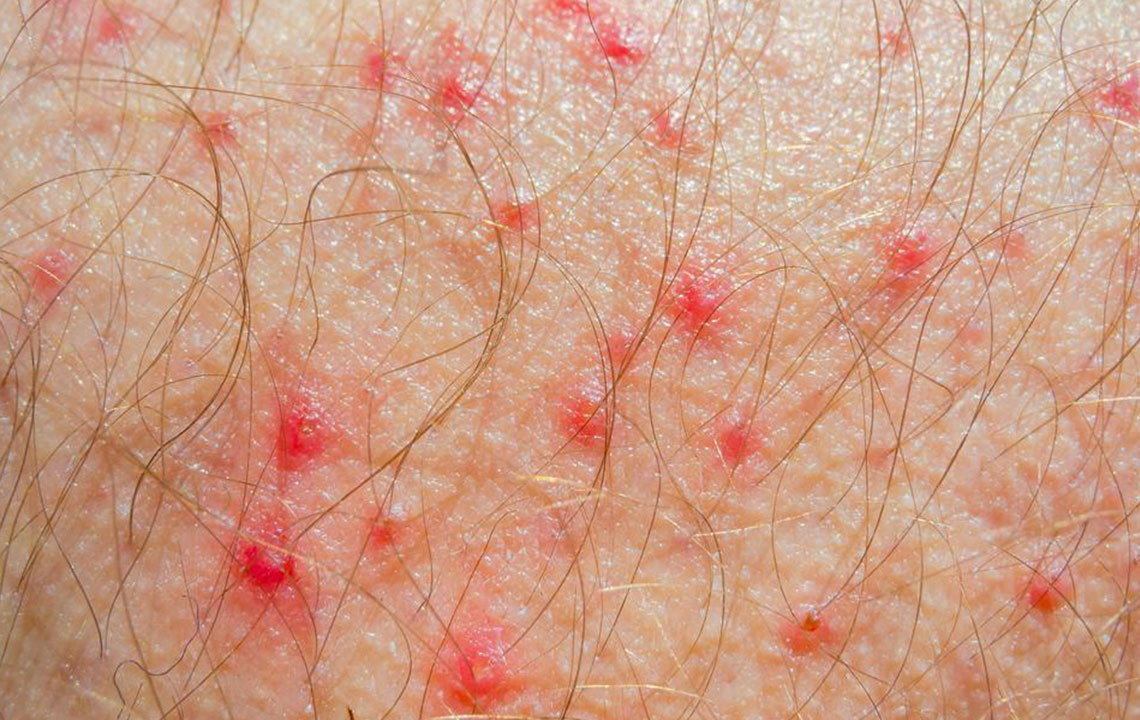
Atopic dermatitis, commonly referred to as eczema, is a complex chronic skin condition characterized by inflammation, dryness, itching, and irritation. It affects individuals across all age groups, with a higher incidence observed in young children. Proper management of atopic dermatitis often involves a multifaceted approach that includes skincare routines, medical treatments, and importantly, dietary modifications. Understanding which foods can help alleviate symptoms and which ones may trigger flare-ups is essential for patients seeking relief and improved quality of life.
Atopic dermatitis is recognized for its recurring episodes of skin inflammation that often manifest early in life. Many children exhibit initial signs before reaching the age of five, including visibly dry, itchy skin, small bumps, and patches that appear red or grayish. These symptoms tend to surface on the face, arms, legs, and other areas prone to friction, often resulting in significant discomfort and affecting daily activities. While the exact cause remains unknown, genetic factors combined with environmental triggers are believed to play a substantial role.
Understanding the Role of Diet in Managing Atopic Dermatitis
Emerging scientific research suggests that diet significantly influences the severity and frequency of atopic dermatitis flare-ups. An anti-inflammatory diet, rich in specific nutrients, can help reduce skin inflammation and alleviate symptoms. Conversely, certain foods are known to trigger allergic reactions or exacerbate inflammation in sensitive individuals, leading to worsened skin conditions.
Foods to Include for Symptom Relief
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found abundantly in fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and anchovies, omega-3 fatty acids possess potent anti-inflammatory properties. Regular consumption of these fish can help modulate immune responses and decrease skin inflammation on a cellular level.
Probiotic-Rich Foods: Introducing probiotics through foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi supports a healthy gut microbiome. A balanced gut flora is linked to improved immune function and may reduce allergic responses that contribute to eczema outbreaks.
Antioxidant-Rich Fruits: Berries such as blueberries, strawberries, and blackberries contain high levels of antioxidants, which combat oxidative stress involved in skin inflammation. These fruits also provide vitamins and minerals essential for skin healing.
Healthy Fats and Oils: Incorporating sources of healthy fats like avocados, nuts, and seeds can support skin barrier function and decrease dryness.
Vitamin D: Adequate levels of vitamin D, obtained from fatty fish, fortified foods, or supplements, have been associated with reduced inflammation and improved skin condition in atopic dermatitis patients.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
Cow's Milk and Dairy Products: Some studies indicate that dairy products may trigger allergic reactions in certain individuals with eczema, leading to increased flare-ups. Monitoring dairy intake can help identify personal triggers.
Citrus Fruits: Oranges, lemons, limes, and grapefruits contain acids that can irritate sensitive skin and cause itching or redness in some eczema sufferers.
Eggs: Eggs are common food allergens and have been linked to exacerbating eczema symptoms in sensitive individuals.
Processed Foods and Sugary Snacks: High intake of processed foods, fast food, and sweets can promote systemic inflammation and worsen skin conditions.
Food Additives and Preservatives: Artificial colorants, flavorings, and preservatives found in many packaged foods may act as irritants or allergens.
Additional Dietary Tips for Managing Atopic Dermatitis
Besides choosing appropriate foods, adopting a few simple dietary habits can make a significant difference:
Maintain a food diary to track potential trigger foods.
Eat a variety of nutrient-dense fruits and vegetables to support overall skin health.
Stay well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
Consult a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized dietary guidance and to rule out any food allergies.
Incorporate supplements like fish oil or vitamin D under medical supervision if necessary.
Integrating Diet with Other Management Strategies
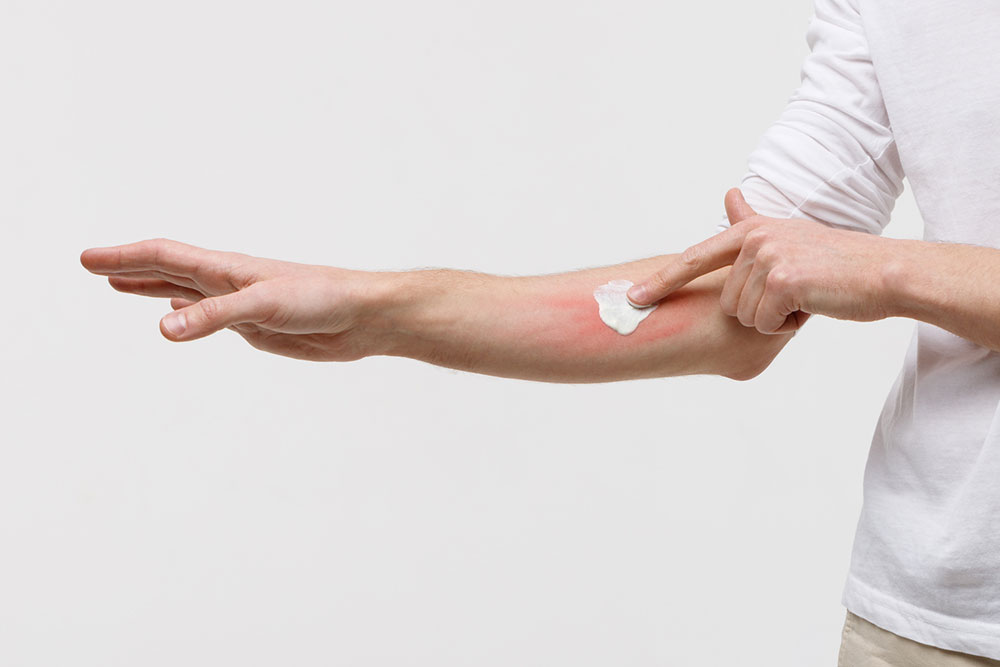
While diet plays a critical role, comprehensive management of atopic dermatitis includes skin hydration, avoiding irritants, and medical treatments prescribed by dermatologists. Regular moisturizing with emollients helps restore the skin barrier, reducing dryness and itchiness. Identifying and avoiding specific triggers—whether environmental or dietary—is key to minimizing flare-ups. Medicinal therapies, including topical steroids or antihistamines, complement lifestyle modifications for effective disease control.
Conclusion
Managing atopic dermatitis requires a holistic approach that integrates proper skincare, medical intervention, and targeted dietary choices. By focusing on anti-inflammatory foods such as omega-3 rich fish, probiotics, and antioxidant-laden fruits while avoiding common triggers like dairy, citrus, and eggs, individuals can better control their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Remember to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized management plan that suits your specific needs.