The Complete Guide to Effectively Managing Type 1 Diabetes
This comprehensive guide explores the essential aspects of managing type 1 diabetes, including early signs, treatment options, lifestyle changes, and strategies to prevent complications. With expert insights, it provides practical advice to help individuals live healthier lives despite the condition.

Understanding, Detecting, and Managing Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune condition that primarily affects children and young adults, though it can occur at any age. This disease arises when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing beta cells within the pancreas, leading to an absolute deficiency of insulin. Insulin is a vital hormone responsible for regulating blood glucose levels by facilitating the entry of sugar into our cells for energy, and its absence results in dangerous increases in blood sugar, known as hyperglycemia. Proper management and early diagnosis are essential to prevent life-threatening complications and to maintain a good quality of life.
Understanding the complexities of type 1 diabetes is key to effective management. The exact triggers for autoimmune destruction of pancreatic cells remain unclear, but genetic predisposition combined with environmental factors, such as viral infections, may play significant roles. Additionally, the presence of other autoimmune disorders, such as vitiligo (depigmentation of the skin) and Grave's disease (an autoimmune thyroid disorder), sometimes coexist in individuals with type 1 diabetes, indicating shared autoimmune mechanisms.
Recognizing the early symptoms is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment. Common signs include an insatiable thirst, dry mouth, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss. Patients may also experience severe fatigue, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, and recurrent infections like urinary tract infections or skin infections. These symptoms often appear suddenly and require immediate medical attention to prevent acute complications like diabetic ketoacidosis, which can be life-threatening.
While there is no known method to prevent type 1 diabetes entirely, maintaining vigilant blood sugar control and routine health screenings are vital strategies for early detection and effective management. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol helps prevent or delay the onset of secondary complications. Adopting a healthy lifestyle—avoiding smoking, limiting alcohol intake, and ensuring vaccinations are up-to-date—further reduces risks associated with the disease.
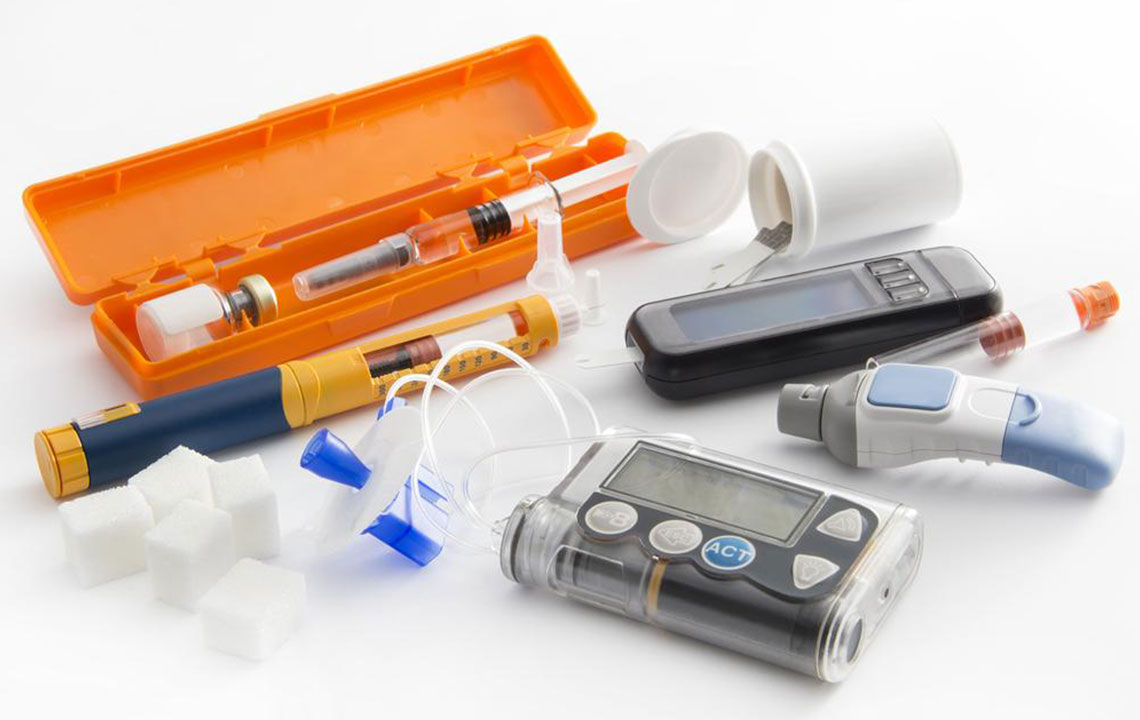
Effective management of type 1 diabetes hinges on a comprehensive treatment plan involving insulin therapy, lifestyle modifications, and dietary adjustments. Insulin therapy remains the cornerstone of treatment, with options including multiple daily injections or continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion via an insulin pump. The choice depends on individual needs, lifestyle, and medical advice. Proper carbohydrate counting and meal planning are essential to balance insulin doses and prevent high or low blood sugar episodes.
Beyond insulin, adopting a healthy diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and non-starchy vegetables supports stable blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity enhances insulin sensitivity and overall well-being, but must be carefully managed with blood glucose monitoring to avoid hypoglycemia. Using devices such as continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) can provide real-time glucose data, enabling more precise insulin dosing and dietary adjustments.
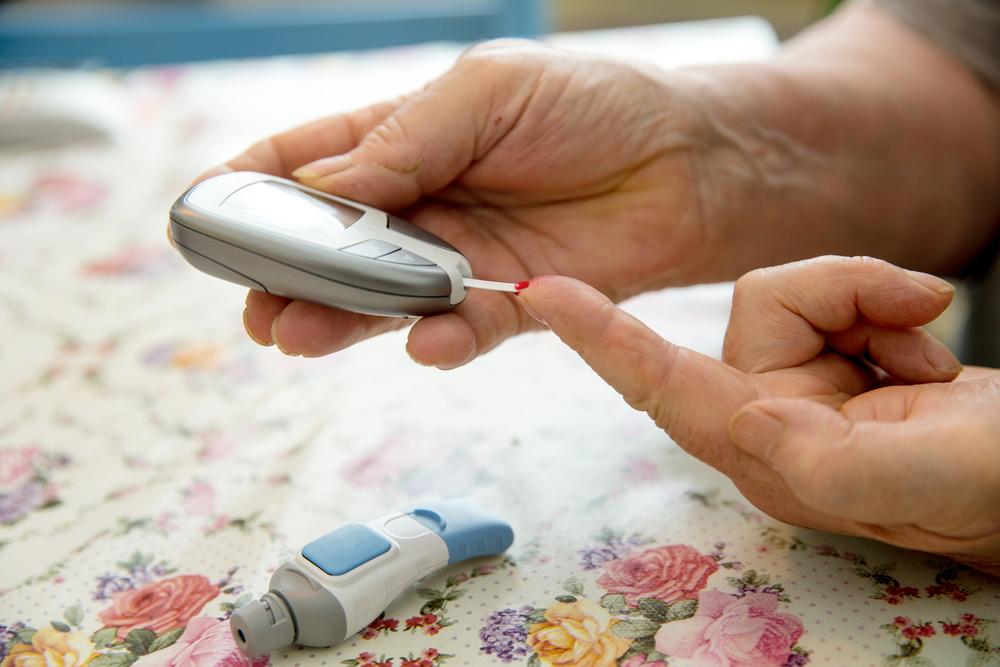
Monitoring blood glucose levels diligently is critical for successful diabetes management. This can be achieved through fingerstick testing and advanced CGMs, guiding insulin administration and dietary choices. Regular healthcare visits allow for the assessment of potential complications, such as kidney disease, nerve damage (neuropathy), eye problems (retinopathy), and cardiovascular issues. Preventative care and routine screenings are vital components of ongoing management.
Preventing long-term complications is achievable with diligent care. Managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels reduces cardiovascular risks, while regular eye exams and kidney function tests help detect early signs of damage. Maintaining a comprehensive diabetes management plan tailored to individual needs empowers patients to lead active, healthy lives despite their condition.
In summary, living with type 1 diabetes requires a proactive approach rooted in early diagnosis, precise insulin therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and lifelong health monitoring. When managed effectively, individuals can achieve excellent glycemic control, minimize the risk of complications, and enjoy a vibrant, fulfilling life. Education and support from healthcare professionals, combined with personal responsibility, form the foundation of successful diabetes management.