Comprehensive Guide to Thrombosis: Types, Causes, and Symptoms
This comprehensive article explores the various types of thrombosis, including deep vein thrombosis, Budd-Chiari syndrome, renal vein thrombosis, and more. It details their causes, symptoms, and treatment options, emphasizing early diagnosis and prevention to reduce health risks associated with blood clots. Perfect for understanding thrombosis's impact on health and the importance of timely intervention.
Understanding the Different Types of Thrombosis and Their Impact on Health
Thrombosis refers to the formation of blood clots within blood vessels, which can significantly impair circulation and pose serious health risks if left untreated. While blood clot formation is a natural response to vessel injury aimed at preventing excessive bleeding, abnormal clot formation can occur without injury, leading to potentially life-threatening conditions. Recognizing the various types of thrombosis, their causes, and symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. The classification of thrombosis depends on the affected blood vessels, primarily distinguishing between arterial and venous thromboses. This comprehensive guide explores the major forms of thrombosis, elucidates their underlying causes, common symptoms, and available treatment options.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
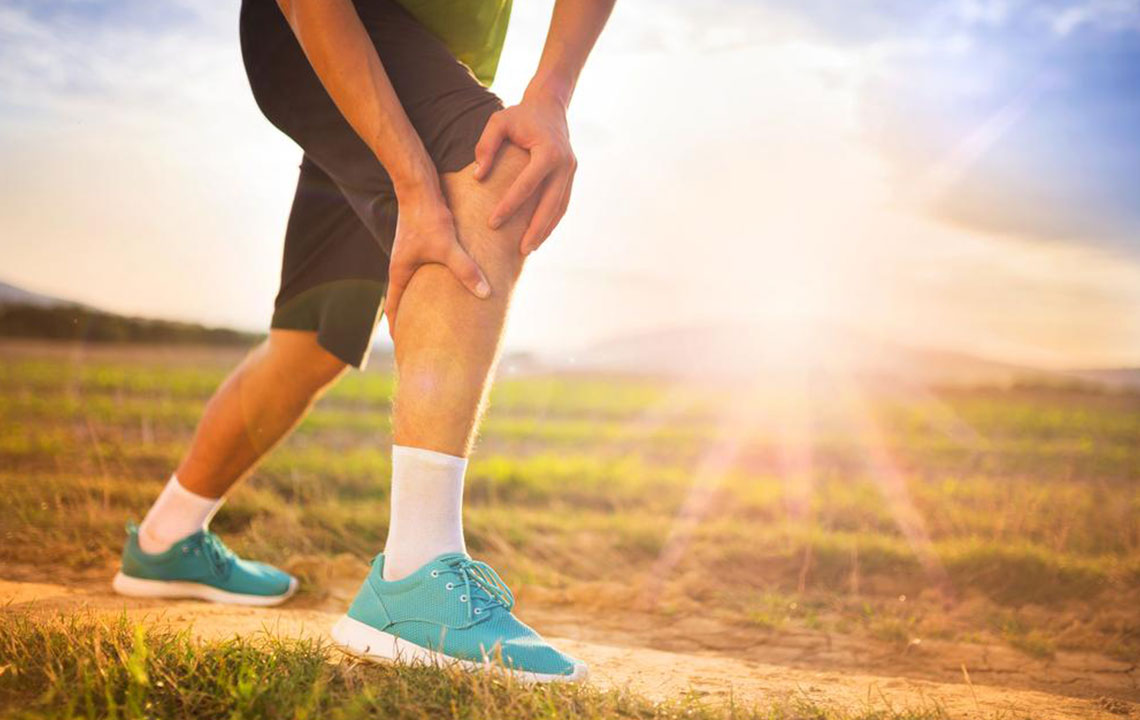
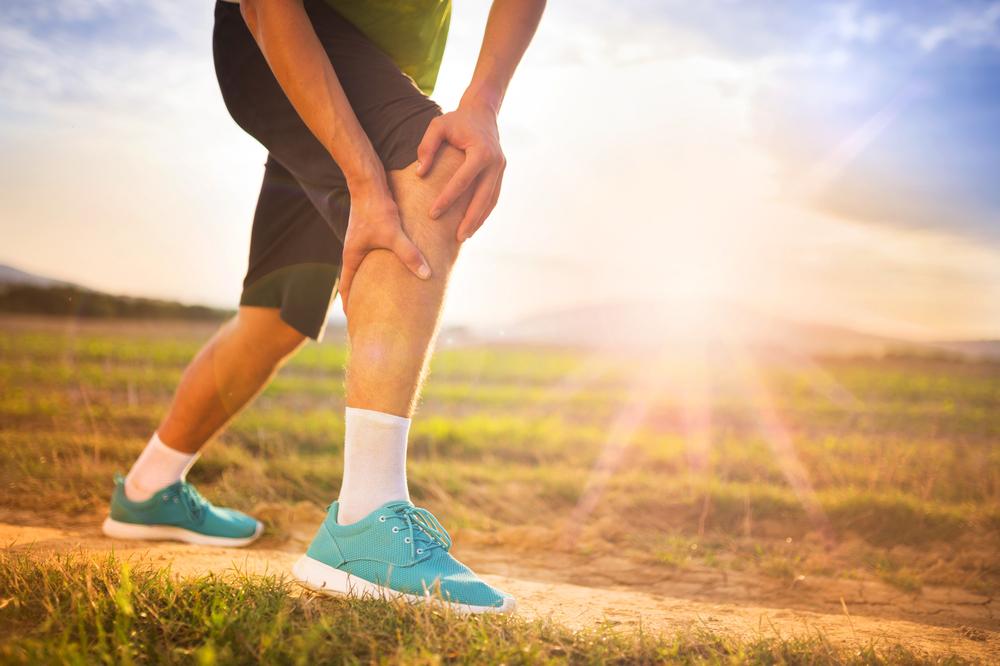
Deep Vein Thrombosis occurs when blood clots form in deep veins, most commonly in the legs, particularly in large veins such as the femoral veins. This condition can lead to serious complications like pulmonary embolism if the clot dislodges and travels to the lungs. Factors that contribute to DVT include sluggish blood flow due to prolonged immobility, increased blood viscosity, and damage to the vessel walls from injury or inflammation. Recognizing early symptoms like swelling, pain, and skin discoloration is essential for prompt treatment.
Budd-Chiari Syndrome
This rare condition involves blockage of the hepatic veins or the inferior vena cava, which impedes blood flow from the liver back to the heart. It causes symptoms such as abdominal pain, hepatomegaly (enlarged liver), ascites, and jaundice. The underlying causes include blood disorders like clotting abnormalities, infections, or certain cancers. Treatment strategies involve anticoagulants, thrombolytic therapy, or surgical interventions like shunt procedures to restore proper blood flow and prevent liver failure.
Renal Vein Thrombosis
When clots obstruct the renal veins, they impair kidney drainage and can lead to kidney damage or infarction. This condition generally presents with flank pain, hematuria (blood in urine), and swelling. It is often associated with nephrotic syndrome or certain coagulation disorders, necessitating anticoagulation therapy and investigation of underlying causes.
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis (CVST)
CVST is a rare but serious form of stroke caused by clot formation in the dural venous sinuses of the brain. It can result in increased intracranial pressure, leading to symptoms like persistent headaches, visual disturbances, weakness, and seizures. Diagnosis is primarily via magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans. Treatment typically involves anticoagulation to dissolve the clot and manage symptoms, with close neurological monitoring.
Portal Vein Thrombosis
This type involves clot formation in the portal vein, which carries blood from the gastrointestinal organs to the liver. It can cause portal hypertension, leading to complications such as variceal bleeding, splenomegaly, and ascites. Underlying causes include cirrhosis, infections, or malignancies. Managing portal vein thrombosis involves anticoagulation, addressing the primary liver disease, and sometimes surgical interventions.
Jugular Vein Thrombosis
Jugular vein thrombosis is often caused by infections, catheter placements, or intravenous drug use. It presents as painful, swollen neck veins, which can sometimes extend to the face and chest. Due to the variable location and nonspecific symptoms, diagnosis can be challenging. Treatment involves anticoagulation, antibiotics if infection is involved, and removal of any precipitating factors.
Paget-Schroetter Disease
Also known as effort thrombosis, this condition involves thrombosis of the veins in the upper extremities, specifically the axillary or subclavian veins. It is often triggered by vigorous activity or repetitive arm movements, commonly seen in young athletes or healthy individuals engaged in strenuous physical activities. Symptoms include sudden arm swelling, pain, and cyanosis. Treatment typically involves anticoagulation, thrombolysis, and sometimes surgical decompression to prevent further complications.
Understanding the different types of thrombosis is vital for early detection and treatment. While some forms like DVT and CVST pose immediate health threats, others may develop insidiously. Prevention strategies include maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing underlying health conditions, and timely medical intervention at the first signs of symptoms. Advances in diagnostic imaging and anticoagulant therapies have significantly improved patient outcomes, but awareness remains key to reducing the risks associated with thrombotic diseases.