Comprehensive Guide to Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Symptoms, Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment
This comprehensive guide delves into Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT), highlighting its symptoms, diagnostic methods, prevention strategies, and treatment options. Understanding DVT is vital for early detection and effective management to prevent severe complications like pulmonary embolism. Learn about the risk factors, common signs, modern diagnostic tools, and lifestyle modifications that can help reduce the risk of DVT. Early intervention and proactive health habits are key to mitigating the dangers of this potentially life-threatening condition.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): An In-Depth Overview of Symptoms, Accurate Diagnosis, Prevention Strategies, and Effective Treatment Options
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a medical condition characterized by the formation of a blood clot, known as a thrombus, within the deep veins of the body. Most commonly, these clots develop in the veins of the thighs or pelvis, but they can also occur in other deep veins of the arms or legs. DVT is a serious health concern because it can lead to life-threatening complications like pulmonary embolism if the clot dislodges and blocks blood flow to the lungs. Awareness of DVT symptoms, understanding of diagnostic methods, and knowledge of prevention and treatment options are vital for health professionals and the general public alike.
Understanding the Causes and Risk Factors of DVT
The formation of blood clots in deep veins is often the result of a combination of factors influenced by Virchow’s triad: hypercoagulability (increased tendency of blood to clot), venous stasis (slow blood flow), and vessel wall injury. Various risk factors can predispose individuals to develop DVT, including prolonged immobility (such as long flights or bed rest), obesity, pregnancy, smoking, advanced age, certain inherited blood clotting disorders, and some cancers. Family history also plays a significant role, making genetic predispositions an important consideration in risk assessments.
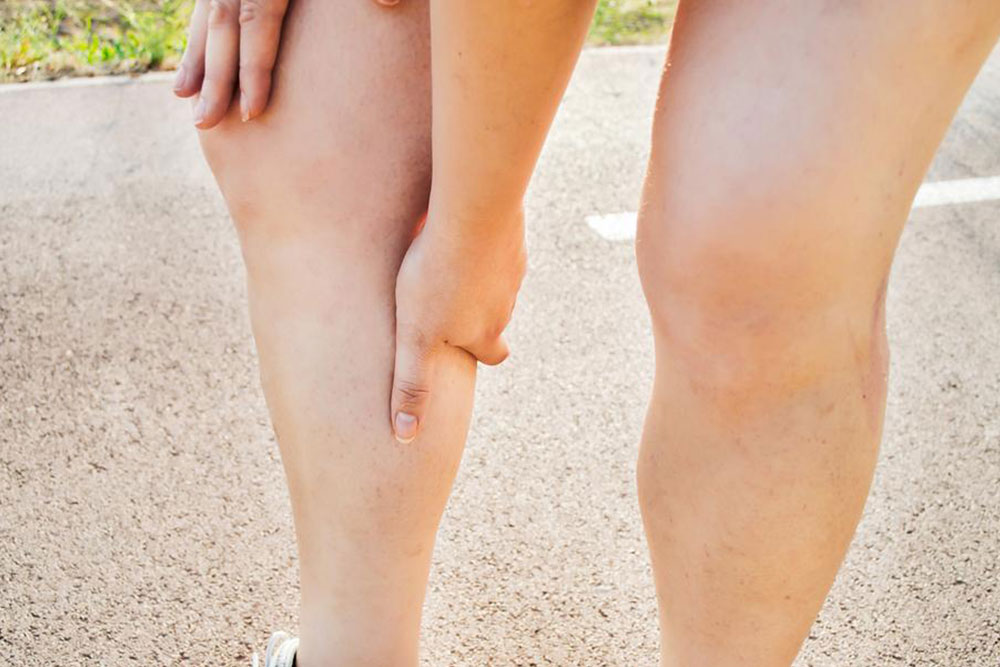
Recognizing Symptoms of DVT
Early recognition of DVT symptoms is crucial for prompt medical intervention. Symptoms can vary widely among individuals, and some may be asymptomatic. Common signs include swelling of the affected limb, usually one leg, which appears suddenly or gradually worsens. The swelling is often accompanied by pain or tenderness, especially when standing or walking. Discoloration of the skin—ranging from redness and warmth to bluish or purple hues—is another characteristic sign. Enlarged superficial veins can also become visible near the affected area. In some cases, patients may experience skin warmth and a feeling of heaviness or aching in the limb.
It’s important to note that not all DVT cases present obvious symptoms. Therefore, individuals at high risk or experiencing subtle signs should seek medical advice promptly to prevent complications like pulmonary embolism.
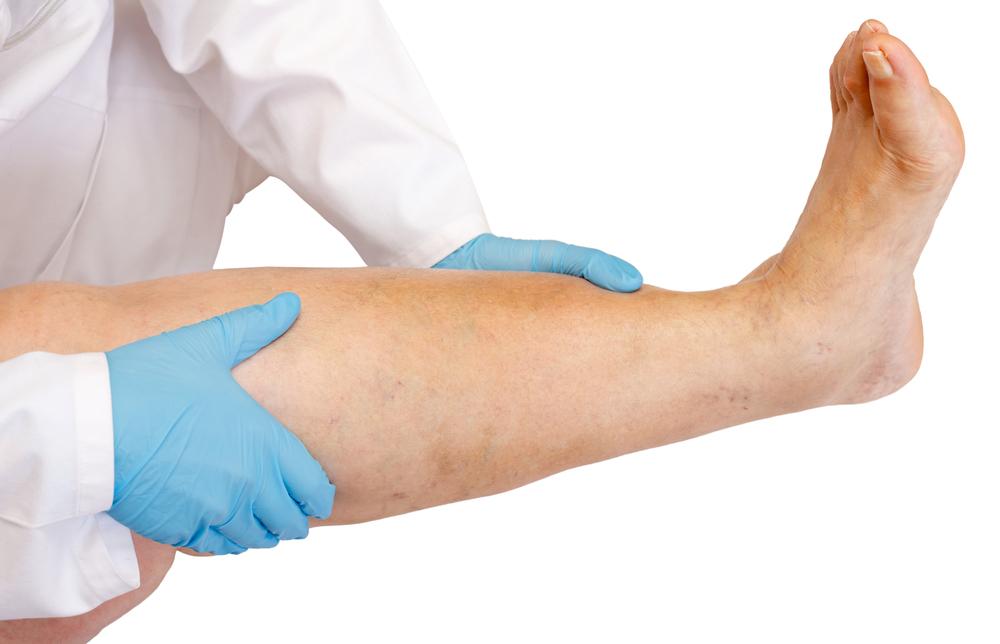
Diagnostic Techniques for DVT
Accurate diagnosis of DVT relies on a combination of clinical assessment and diagnostic tests. Healthcare providers often start with a thorough medical history and physical examination. To confirm the presence of a clot, imaging techniques such as Doppler ultrasound are the first-line diagnostic tools because of their non-invasive nature and high accuracy. This method evaluates blood flow within the veins and can detect obstructions effectively.
In certain cases, if ultrasound results are inconclusive, additional imaging procedures like venography or contrast-enhanced CT scans may be used. Blood tests, including D-dimer levels, are helpful in ruling out DVT; elevated D-dimer suggests the presence of a clot but is not definitive on its own. Thus, combining clinical evaluation with imaging and laboratory tests provides the most reliable diagnosis.
Effective Treatment Approaches for DVT
Once diagnosed, prompt treatment is essential to prevent clot growth, reduce symptoms, and avoid severe complications. The cornerstone of DVT treatment involves anticoagulant medications, which thin the blood to prevent the clot from enlarging and new ones from forming. Common anticoagulants include heparin, warfarin, and newer direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) such as rivaroxaban and dabigatran.
For cases with extensive clot burden or risk of embolism, thrombolytic therapy using clot-dissolving drugs might be employed. In addition to medication, compression stockings can help reduce swelling and improve blood flow in affected limbs. Lifestyle modifications, such as elevating the limb, regular movement, and avoiding prolonged immobility, play critical roles in management.
Severe cases may require surgical interventions or placement of an inferior vena cava (IVC) filter to prevent clots from reaching the lungs. Close monitoring of anticoagulation therapy and periodic imaging assessments are part of long-term management to ensure proper treatment response and minimize risks.
Preventing Deep Vein Thrombosis: Practical Tips
The best approach to DVT is prevention, especially for individuals with multiple risk factors. Regular physical activity, such as walking or stretching exercises, improves circulation and reduces venous stasis. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced diet and consistent exercise decreases overall risk. Avoiding smoking and quitting if currently smoking significantly lowers the likelihood of clot formation.
For travelers embarking on long journeys, wearing compression stockings and taking frequent breaks to move around can prevent blood pooling. Post-surgical patients and those on prolonged bed rest should follow medical advice regarding anticoagulants and mobilization strategies. Regular check-ups and informing healthcare providers of personal risk factors help catch issues early.
Conclusion: The Importance of Awareness and Timely Action
Deep Vein Thrombosis remains a major health concern worldwide due to its potential for severe complications. Recognizing symptoms early, obtaining accurate diagnosis through modern imaging techniques, and adhering to appropriate treatment protocols are essential steps toward effective management. With proactive prevention strategies, lifestyle adjustments, and medical oversight, many cases of DVT can be effectively controlled, reducing the risk of life-threatening outcomes like pulmonary embolism. It is crucial for individuals to stay informed about their risk factors and to seek immediate medical attention if symptoms arise, ensuring better health outcomes and quality of life.