Complete Overview of Deep Vein Thrombosis: Causes, Symptoms, Preventive Measures, and Treatments
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a common yet dangerous condition involving blood clots in deep veins, primarily in the legs. This detailed guide covers causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and prevention strategies. Awareness of DVT can lead to early detection and effective management, reducing the risk of severe complications such as pulmonary embolism. Regular movement, healthy habits, and medical consultations are essential steps in preventing DVT. Learn how to identify symptoms early and follow proper treatment protocols to safeguard your vascular health and prevent long-term health issues.

Complete Overview of Deep Vein Thrombosis: Causes, Symptoms, Preventive Measures, and Treatments
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition characterized by the formation of blood clots within the deep veins, most commonly occurring in the thigh or calf area. Although it often presents with mild or subtle symptoms, if left untreated, it can lead to severe complications such as pulmonary embolism, which can be life-threatening. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the causes, recognition symptoms, diagnostic procedures, treatment options, and effective prevention strategies for DVT. Understanding this condition is crucial, especially since early detection and management can save lives and prevent long-term health consequences.
Deep vein thrombosis usually develops when blood flow in the deep veins slows down or becomes stagnant. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including prolonged immobility, certain medical conditions, pregnancy, obesity, and genetic predispositions. Prolonged immobility during long flights, bed rest after surgery, or sedentary lifestyles greatly increase the risk of DVT. Hormonal changes during pregnancy or the use of hormone therapy can also elevate risk, as do inherited clotting disorders and certain cancers. Recognizing these common causes helps individuals and healthcare providers take appropriate preventive actions.
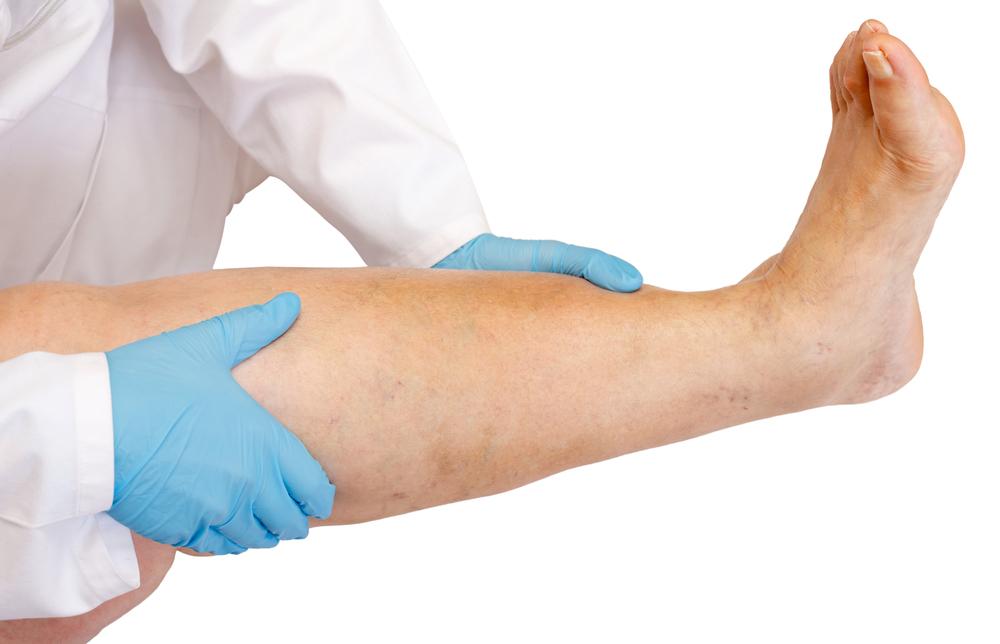
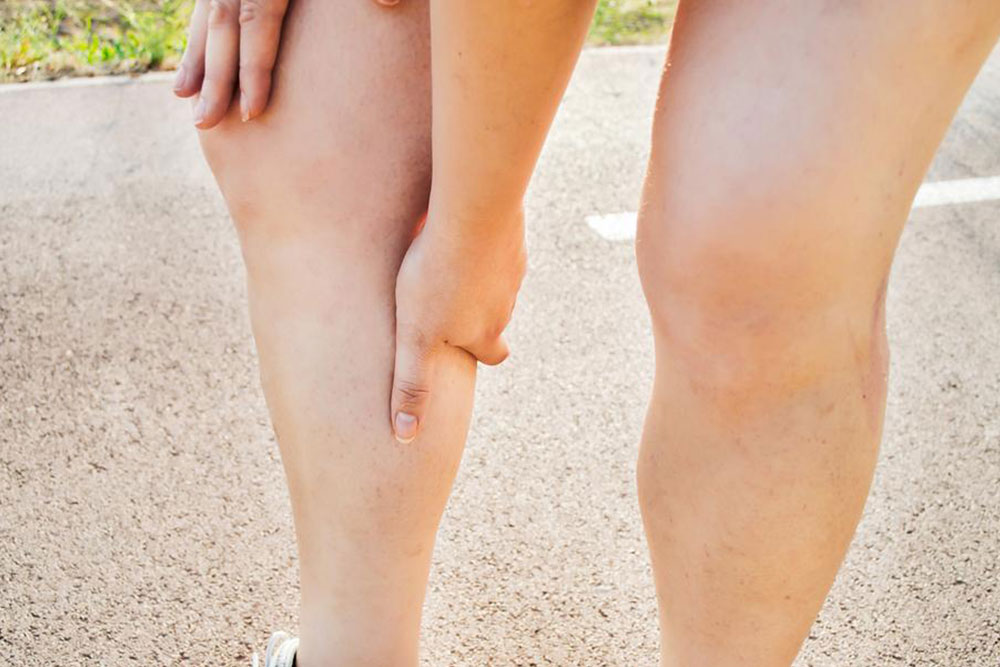
The symptoms of DVT can be quite diverse. Many patients experience swelling, warmth, tenderness, or discoloration of the affected limb, especially in the calf or thigh. However, these symptoms can sometimes be mild or mistaken for other conditions. Leg pain, aching, or cramping are common signs that warrant prompt medical evaluation. Importantly, some individuals may not experience obvious symptoms at all, underlining the importance of awareness for at-risk groups.
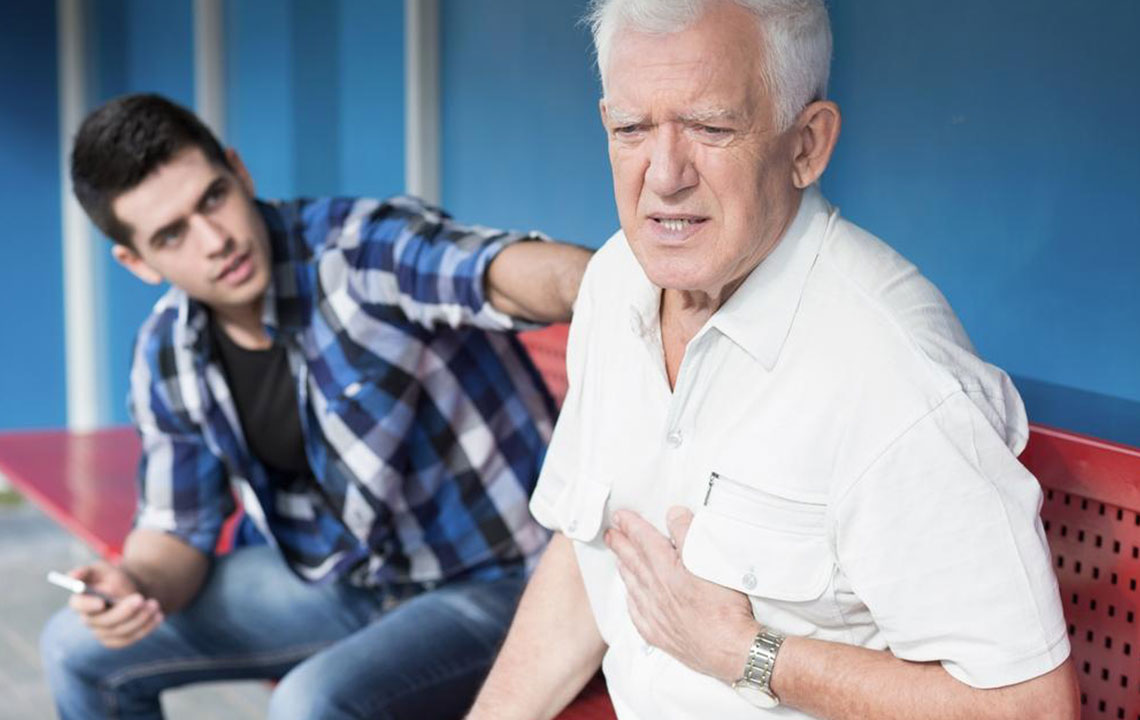
Diagnosis of DVT involves multiple medical assessments, including blood tests, ultrasound imaging, CT scans, and venography, which uses contrast dye to visualize blood flow. Ultrasound Doppler is the most common initial test due to its non-invasive nature and high accuracy. Early diagnosis is essential to prevent potential complications, especially pulmonary embolism, where a clot dislodges and blocks blood flow in the lungs—this incidence accounts for significant morbidity and mortality weekly.
When it comes to treatment, the primary goals are to prevent clot growth, reduce symptoms, and minimize the risk of pulmonary embolism. Therapeutic options include anticoagulant medications like heparin or warfarin, which thin the blood and prevent further clot formation. Thrombolytic drugs may be used in severe cases to dissolve existing clots. Compression stockings are also recommended to improve blood flow and reduce swelling. In certain situations, surgical interventions or catheter-directed thrombolysis may be necessary for large or persistent clots.
Prevention is key in managing DVT risk. Regular physical activity and mobility, especially after surgery or extended periods of sitting, significantly lower the risk. Maintaining a healthy weight, staying hydrated, and avoiding smoking are also effective preventive measures. For individuals with a history of DVT or genetic risk factors, healthcare providers may recommend blood-thinning medications prophylactically during high-risk periods, such as hospitalization or pregnancy.
Public awareness about DVT has increased in recent years, emphasizing the importance of early detection and lifestyle modifications. Healthcare professionals encourage at-risk populations—such as travelers, postoperative patients, pregnant women, and those with clotting disorders—to adopt preventive behaviors and seek medical advice when symptoms appear.
In conclusion, deep vein thrombosis is a potentially life-threatening condition that requires prompt attention. By understanding its causes, recognizing the symptoms, and adhering to recommended diagnostic and treatment strategies, individuals can effectively reduce their risk of serious complications. Maintaining a healthy, active lifestyle and consulting healthcare professionals regularly can play a vital role in DVT prevention and management. Early intervention not only saves lives but also improves quality of life for those affected by this condition.