Comprehensive Guide to TMJ Disorder: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Strategies
This comprehensive article explores TMJ disorder, detailing its causes, symptoms, and various treatment options. It emphasizes conservative management like self-care, physical therapy, and dental devices while also discussing advanced surgical options for severe cases. Readers learn how to identify TMJ issues early and explore effective strategies to restore normal jaw function, reduce pain, and improve quality of life through multidisciplinary care. Perfect for patients seeking an in-depth understanding of TMJ health and management.

The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) plays a crucial role in human anatomy by connecting the lower jaw (mandible) to the temporal bones of the skull, which are situated just in front of each ear. This joint functions as a hinge that facilitates the wide range of jaw movements necessary for speaking, chewing, yawning, and other essential activities. When the TMJ or its associated muscles and structures experience dysfunction, it leads to a condition known as temporomandibular disorder (TMD) or TMJ disorder. Understanding this condition involves exploring its causes, symptoms, and various treatment options available today.
TMJ disorders can significantly impact daily life by causing persistent discomfort and limiting jaw mobility. The root causes of TMJ issues are diverse, often resulting from various factors such as trauma, stress, or degenerative changes. Commonly, individuals may experience jaw injuries or trauma from accidents, sports injuries, or dental procedures that affect the joint’s stability and function. Additionally, impact to the face or localized trauma can lead to inflammation or dislocation within the joint components.
Muscle strain also significantly contributes to TMJ problems. Excessive tension in the muscles surrounding the jaw, neck, and face—often caused by stress, anxiety, or habitual clenching—can lead to pain and dysfunction. One prevalent cause is teeth grinding (bruxism), which often occurs unconsciously during sleep, exerting abnormal forces on the TMJ. Clenching the jaw tightly during stressful situations or even habitual tightening can also strain the joint and surrounding muscles, resulting in inflammation and pain.
Other notable causes involve disc dislocation within the joint. The articular disc acts as a cushion between the mandibular condyle (the rounded end of the lower jaw) and the temporal bone. If this disc slips out of position due to injury, degeneration, or muscle imbalance, it can cause clicking sounds, pain, and restricted movement. Arthritis—either osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis—can also affect the TMJ, leading to degeneration of joint surfaces, inflammation, and chronic pain. These degenerative changes contribute to reduced mobility and increased discomfort over time.
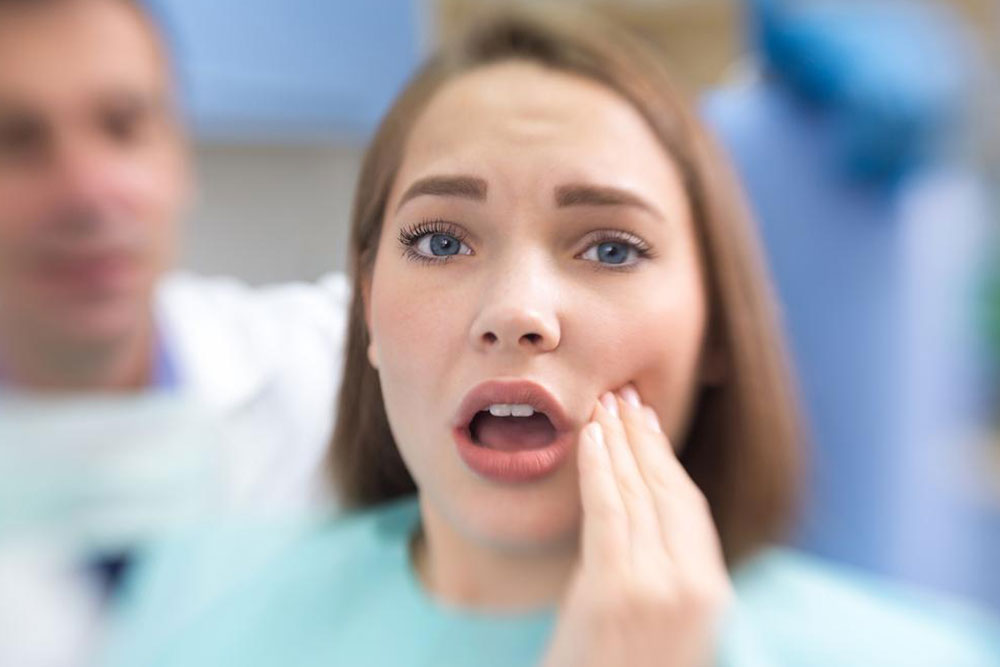
Symptoms associated with TMJ disorder are varied and can range from mild to severe. The most common symptoms include facial or jaw pain, which may radiate to the ear, neck, or shoulders. Patients often experience difficulty opening the mouth fully or feel a sensation of the jaw locking in a certain position. Clicking, popping, or grating sounds during jaw movement are typical indicators of TMJ dysfunction, signaling disc displacement or joint surface irregularities. Some individuals also report headaches, earaches, or a sensation of fullness in the ears, which are often mistaken for ear infections but are actually related to TMJ dysfunction.
Diagnosing TMJ disorder involves a comprehensive clinical examination, patient history, and sometimes imaging studies such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans. The goal of diagnosis is to identify the specific source of the dysfunction—be it disc displacement, arthritis, muscle imbalance, or other causes—to guide appropriate treatment.
The primary aim of TMJ treatment is to restore normal jaw function, eliminate pain, and prevent further joint damage. Early intervention is essential to manage symptoms effectively and avoid complications. Most initial treatments are conservative and focus on self-care and symptom management. This approach includes lifestyle modifications, behavioral changes, and over-the-counter medications.
Self-care strategies are fundamental in managing TMJ symptoms. Applying hot or cold packs to the affected area can reduce inflammation and relieve muscle tension. Soft diets that minimize jaw exertion help prevent aggravating the joint. Patients are advised to avoid hard or chewy foods that require excessive jaw movement, as well as to practice gentle jaw exercises to improve mobility.
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can significantly reduce discomfort associated with TMJ disorder. These medications are often recommended during flare-ups or periods of increased pain. However, they should be used judiciously under healthcare provider guidance to avoid potential side effects.
In addition to medication and lifestyle adjustments, physical therapy plays a crucial role in TMJ management. Techniques such as massage, stretching exercises, and guided jaw relaxation can alleviate muscle tension and improve joint mobility. Biofeedback therapy, which helps patients control muscle tension through monitoring, can also be beneficial. Such therapies not only reduce symptoms but also empower patients to manage stress-related triggers that exacerbate TMJ issues.
For persistent or more severe cases, dental interventions may be necessary. Dental splints, night guards, or bite plates are custom-made devices designed to stabilize the jaw, reduce teeth grinding, and prevent disc displacement. Wearing these devices, especially during sleep, can significantly lessen symptoms and protect the joint from further damage. Dentists often recommend these appliances as part of a comprehensive treatment plan to manage TMJ dysfunction effectively.
In some instances, when conservative therapies do not provide relief, more advanced procedures such as corticosteroid injections or minimally invasive surgeries may be considered. Surgical options include arthroscopy or open joint surgery aimed at repairing or replacing damaged joint components. These procedures are generally reserved for cases where other treatments have failed or where structural abnormalities significantly impair joint function.
Living with TMJ disorder requires a multidisciplinary approach. Patients benefit from collaboration between dentists, oral surgeons, physical therapists, and sometimes psychologists to address the physical and emotional impacts of the condition. Stress management techniques like meditation and counseling can reduce the frequency of muscle clenching and grinding, further alleviating TMJ symptoms.
In conclusion, TMJ disorder is a common condition that affects many individuals, impacting their ability to eat, speak, and perform daily activities comfortably. Understanding its causes, recognizing the symptoms early, and pursuing appropriate treatment options can significantly improve quality of life. Whether through conservative self-care measures or advanced medical interventions, controlling TMJ symptoms is achievable with proper management and a proactive approach. If you experience persistent jaw pain, clicking sounds, or restricted movement, consulting with a healthcare professional specializing in TMJ can help determine the best course of action to restore normal jaw function and reduce discomfort.