Comprehensive Guide to Unveiling the Causes Behind Joint Discomfort and Pain
Discover the detailed causes behind joint discomfort, including gout, sarcoidosis, Lyme disease, and fibromyalgia. Learn how to recognize symptoms, understand underlying health issues, and find effective treatment options with this comprehensive guide on joint pain and stiffness.

Joint discomfort and pain are common issues affecting many individuals worldwide, often resulting in restricted movement, swelling, and persistent soreness. While experiencing joint pain can sometimes be a simple response to overuse or injury, it frequently signals underlying health conditions that require proper diagnosis and treatment. Recognizing the different causes of joint pain not only helps in managing symptoms effectively but also in preventing potential complications. This detailed guide explores the various factors, diseases, and health conditions that can manifest as joint discomfort, providing valuable insights for those seeking clarity on their symptoms.
Understanding Joint Stiffness and Its Causes
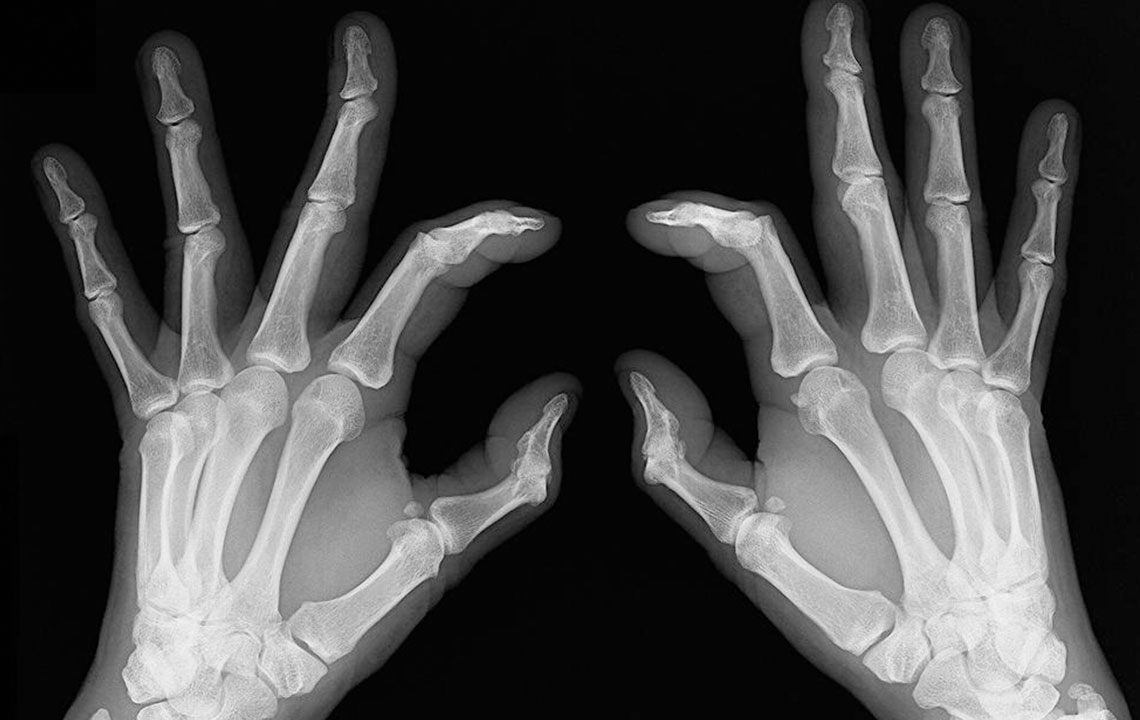
One of the most noticeable symptoms accompanying joint pain is stiffness. Joint stiffness can significantly impair mobility and comfort, particularly after periods of inactivity or upon waking. The causes of stiffness are diverse, often linked to inflammatory processes, structural changes, or degenerative conditions. Symptoms can vary, but common indicators include redness, warmth, tenderness, numbness, or tingling sensations around the affected joints. This array of symptoms is typically referred to as arthralgia and requires careful evaluation to identify the root cause.
What Your Joint Symptoms Might Be Trying to Tell You
The human body often communicates underlying issues through joint discomfort. Recognizing these signals can aid in early diagnosis and targeted treatment. Here are some key conditions associated with joint pain:
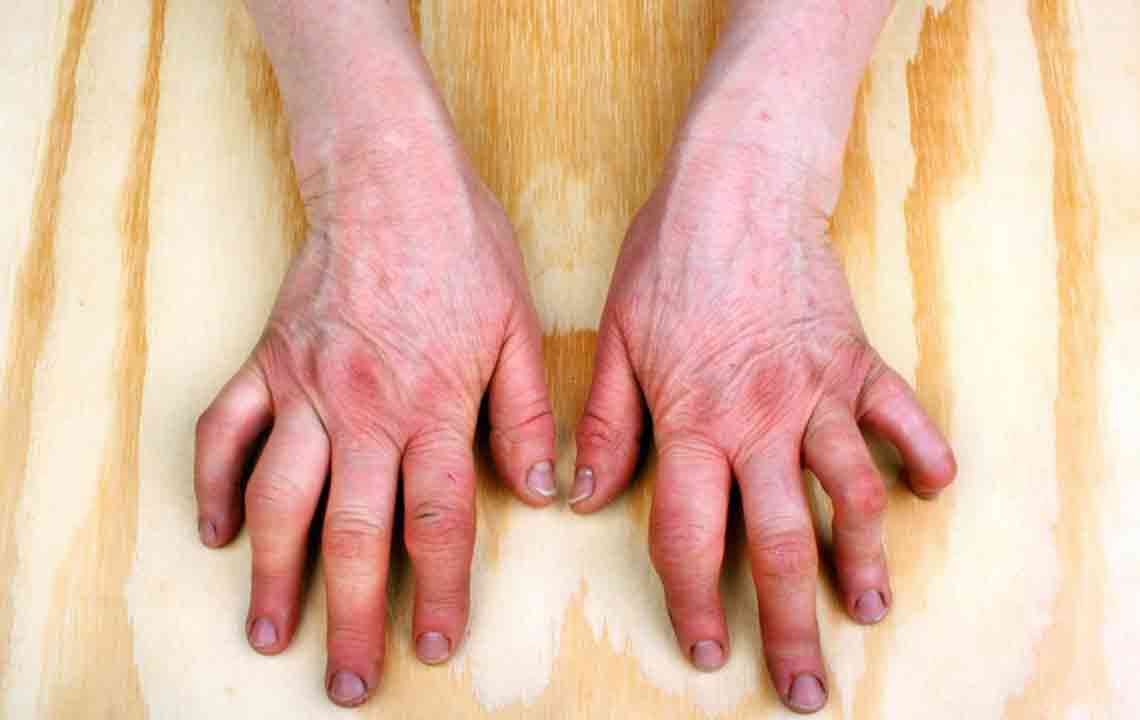
Gout: Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals within the joints. Uric acid is a waste product normally excreted by the kidneys, but when levels become excessively high, crystals form and trigger painful inflammation. Gout usually begins affecting the big toe, causing intense pain, redness, and swelling. Over time, it can involve other joints like knees, ankles, or wrists. Risk factors include a diet rich in purine-heavy foods such as red meats and shellfish, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, and certain medical conditions like hypertension. Postmenopausal women are also more susceptible. Treatment strategies typically involve anti-inflammatory medications, lifestyle modifications including dietary changes, weight management, and avoiding alcohol to prevent flare-ups.
Sarcoidosis: This is an immune-mediated disorder characterized by abnormal inflammation that produces granulomas—small clusters of immune cells—in various organs, including the joints. While sarcoidosis more commonly affects the lungs, skin, and lymph nodes, joint involvement can lead to pain, swelling, and stiffness. Symptoms often include fatigue, fever, and general malaise. The exact cause remains unknown, though it is believed to involve genetic and environmental factors. Diagnosis involves imaging and biopsy, and treatment usually includes corticosteroids and immunosuppressive therapies to control inflammation.
Lyme Disease: Transmitted through tick bites, Lyme disease is a bacterial infection caused by the Borrelia burgdorferi bacterium. One of its main symptoms is joint pain, particularly affecting large joints like the knees. Early symptoms also include fever, headache, fatigue, and a characteristic skin rash known as erythema migrans. If not promptly treated with antibiotics, Lyme disease can spread to other parts of the body, leading to chronic joint inflammation and neurological issues. Prevention focuses on avoiding tick bites through protective clothing and using repellents, with antibiotics being the primary treatment if infected.
Fibromyalgia: Predominantly affecting women, fibromyalgia is a chronic condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and mood disorders. Although it does not cause inflammation in joints, the central nervous system becomes hypersensitive to pain signals, resulting in persistent discomfort. Triggers can include stress, trauma, or infections. Symptoms often include headaches, depression, anxiety, and cognitive disturbances. Managing fibromyalgia involves a multidisciplinary approach, including medication, physical therapy, stress management techniques, and lifestyle changes to improve quality of life.
It’s important to appreciate that joint pain can be a warning sign of more serious health issues. Accurate diagnosis requires medical assessment—often involving blood tests, imaging, and physical examination—to identify the specific cause. Early intervention is key to preventing progression and ensuring effective management of underlying conditions.
In conclusion, while joint discomfort can sometimes be mild and temporary, persistent or severe pain warrants professional medical attention. Addressing the root cause not only alleviates symptoms but also promotes overall health and well-being. If you experience ongoing joint symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for an appropriate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. Staying informed about the potential causes of joint pain empowers individuals to take proactive measures for their health and comfort.