Comprehensive Guide to Gout Management: Effective Treatments and Prevention Strategies
This comprehensive guide provides detailed insights into managing gout, including symptoms, causes, effective treatments, and lifestyle changes. Discover how medications and dietary modifications can help prevent future gout attacks, protect your joints, and improve your quality of life. Learn practical strategies for long-term management and prevention, enabling you to take proactive steps and maintain better health. This detailed overview is essential for anyone seeking to understand and control gout effectively.
Comprehensive Guide to Gout Management: Effective Treatments and Prevention Strategies
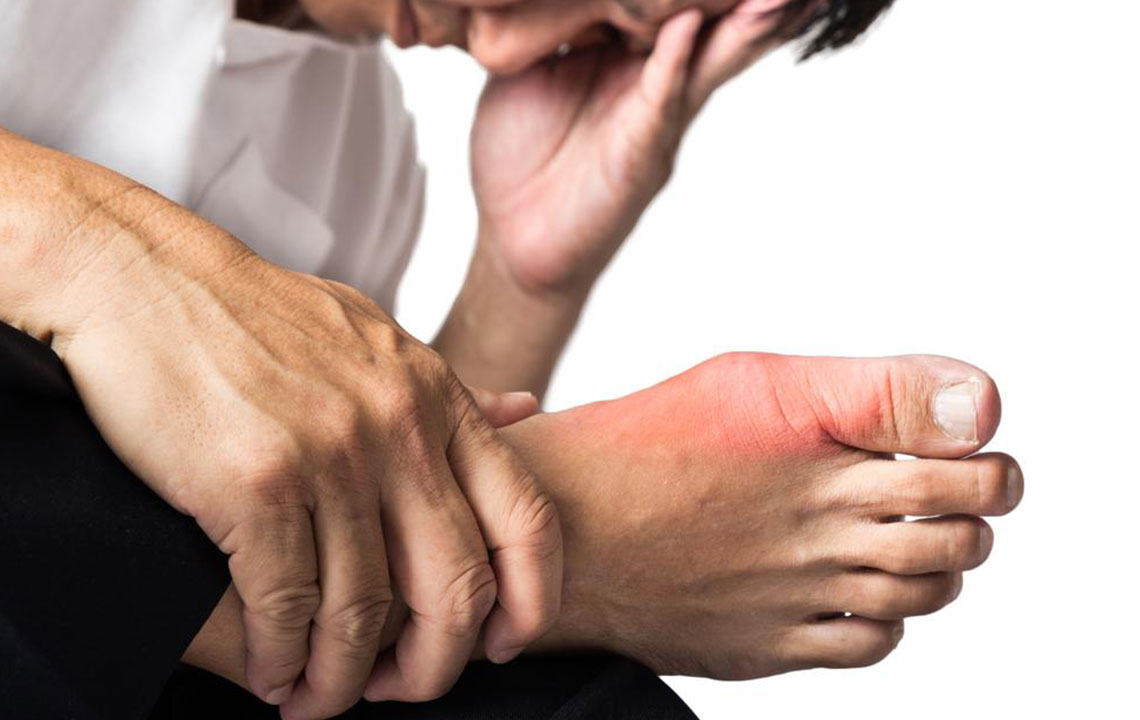
Gout is a painful and often debilitating form of arthritis that can significantly impact quality of life. Characterized by sudden and intense flare-ups, gout leads to joint redness, swelling, warmth, and excruciating pain. Understanding its causes and exploring effective treatment options are vital for those affected, not only to alleviate pain but also to prevent future episodes. This comprehensive guide delves into the details of gout, covering its symptoms, causes, treatment options, and lifestyle changes that can help manage and prevent this condition.
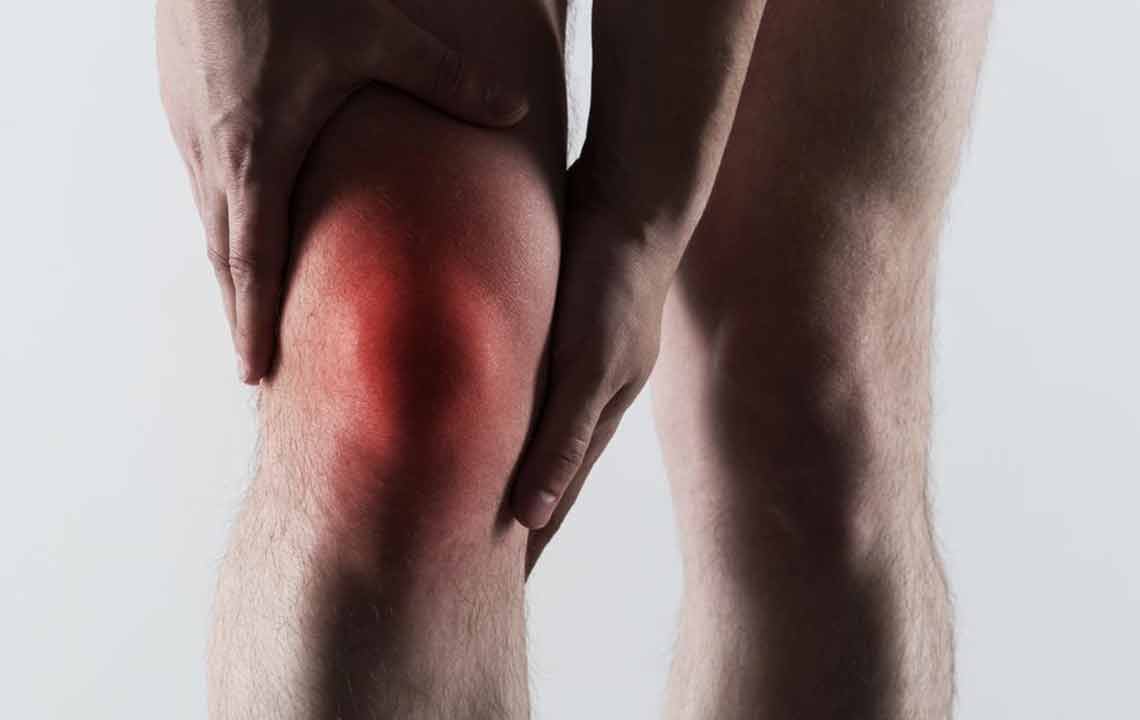
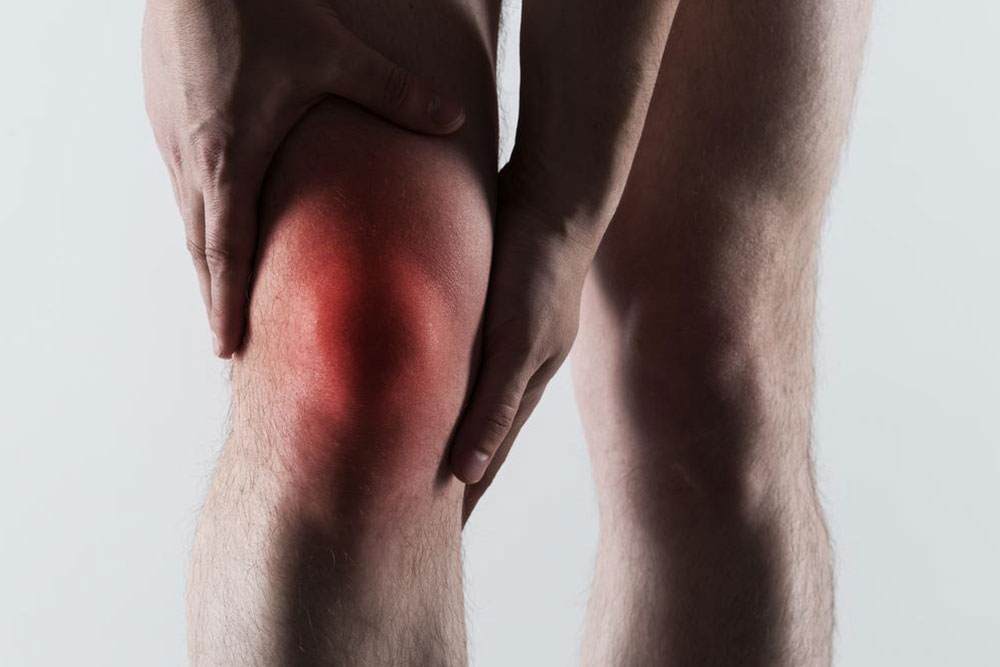
Gout episodes typically occur suddenly, often overnight, and can affect any joint but commonly target the big toe, ankles, knees, wrists, and fingers. The affected joint becomes extremely tender, sometimes so sensitive that even the weight of a bedsheet causes discomfort. The severity of pain can vary from mild to severe and may last for days or weeks if not properly managed. Repeated attacks can lead to joint damage and the formation of tophi—visible deposits of urate crystals under the skin. Therefore, understanding and managing gout effectively is essential to prevent long-term joint issues.
Understanding the Causes of Gout
Gout is primarily caused by an excess of uric acid in the blood, a condition known as hyperuricemia. Uric acid is a waste product formed when the body breaks down purines—substances found naturally in the body and in various foods. Normally, uric acid dissolves in the blood and passes through the kidneys into the urine. However, when the body produces too much uric acid or the kidneys excrete too little, uric acid levels rise, leading to the formation of needle-like crystals in the joints and surrounding tissues.
Several factors contribute to high uric acid levels, including:
Diet rich in purines: Red meats, organ meats, certain seafood like shellfish and sardines, and processed foods.
Obesity: Excess weight increases uric acid production and reduces kidney efficiency.
Alcohol consumption: Beer and spirits are particularly known to elevate uric acid levels.
Certain medications: Diuretics, low-dose aspirin, and others may interfere with uric acid excretion.
Genetics: Family history can predispose individuals to gout.
Other health issues: Hypertension, chronic kidney disease, and metabolic syndrome also increase risks.
Understanding these causes helps in formulating effective prevention and management strategies.
Symptoms and Diagnosing Gout
Gout symptoms can be quite distinctive, but sometimes they may resemble other forms of arthritis, making diagnosis crucial. Typical signs include:
Sudden and intense joint pain, often at night.
Swelling and tenderness around the affected joint.
Redness and warmth of the skin over the joint.
Limited range of motion in affected joints.
If you experience these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis, which may involve blood tests to measure uric acid levels, joint fluid analysis to detect urate crystals, and imaging tests to assess joint damage.
Medical Treatments for Gout
Managing gout effectively requires a combination of medications, lifestyle adjustments, and dietary modifications. The primary goals are to relieve acute pain and inflammation and to prevent future attacks by controlling uric acid levels.
Acute Gout Attack Treatments
During a gout flare-up, swift relief is essential. Medications used include:
NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen, naproxen, indomethacin, and celecoxib are commonly prescribed. They help reduce pain and inflammation effectively.
Colchicine: An effective anti-inflammatory drug that can be used during attacks to relieve pain and prevent crystal formation if taken early.
Corticosteroids: Prednisone or other corticosteroids may be prescribed orally or via joint injections if NSAIDs or colchicine are contraindicated.
Long-Term Management and Prevention
To prevent recurrent attacks and avoid joint damage, doctors often recommend medications that lower uric acid levels:
Allopurinol: Reduces uric acid production and is often the first-line choice for long-term management.
Febuxostat: An alternative to allopurinol, especially in people who cannot tolerate allopurinol.
Probenecid: Increases uric acid excretion through the kidneys, helping to maintain normal levels.
Lesinurad: A newer medication that enhances uric acid clearance when used with XOI therapy.
Regular blood tests monitor uric acid levels, ensuring they stay within target ranges, typically below 6 mg/dL. Achieving and maintaining this goal helps reduce attack frequency and joint damage.
Lifestyle Modifications to Prevent Gout
Through lifestyle changes, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of gout attacks. Important measures include:
Dietary Control: Limit intake of purine-rich foods such as red meats, organ meats, and certain seafood. Incorporate more low-purine foods like dairy, fruits, vegetables, and grains.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a major risk factor, so weight loss through diet and exercise can help lower uric acid levels.
Limit Alcohol Consumption: Especially beer and spirits, which increase uric acid production.
Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps dilute uric acid and promotes its excretion.
Increase Vitamin C Intake: Foods like oranges, strawberries, broccoli, and bell peppers can help lower uric acid levels.
Avoid Sugary Drinks and Processed Foods: These can contribute to weight gain and increased uric acid production.
In addition to diet, regular exercise, adequate hydration, and abstinence from excessive alcohol can create a comprehensive approach to preventing gout.
Additional Tips and Considerations
Managing gout effectively also involves being vigilant about early symptoms and adhering to prescribed treatments. Stress management and avoiding rapid weight changes are also important, as they can trigger attacks. Regular follow-ups with healthcare professionals ensure optimal management and adjustments to treatment plans as needed.
While gout can be a challenging condition, understanding its causes and treatment options allows individuals to lead healthier lives with fewer episodes of pain. Adopting a proactive approach combining medication, lifestyle adjustments, and dietary control offers the best chance of managing this condition effectively.
Conclusion
Gout is a complex but manageable form of arthritis that, with proper treatment and lifestyle changes, can be controlled effectively. From medications to diet modifications, understanding the triggers and adhering to a comprehensive management plan can improve quality of life and prevent joint damage. If you suspect you might have gout or are experiencing symptoms, seek prompt medical advice to begin an appropriate treatment plan and reduce the risk of future attacks.