Comprehensive Dietary Strategies to Prevent and Manage Gout Attacks
This comprehensive article explores effective dietary strategies for preventing and managing gout attacks. Learn about beneficial foods like fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy, as well as foods to avoid such as organ meats, sugary drinks, and seafood. Discover how dietary choices impact uric acid levels and how to adopt a gout-friendly diet to reduce flare-ups and support joint health. Coupled with lifestyle tips, this guide provides a holistic approach to controlling gout through nutrition.

Comprehensive Dietary Strategies to Prevent and Manage Gout Attacks
Gout, a complex form of inflammatory arthritis, is caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the bloodstream, leading to the formation of sharp urate crystals within the joints. These crystals trigger severe inflammation, resulting in intense pain, swelling, redness, and stiffness, predominantly affecting the big toe but also other joints. Gout can significantly interfere with everyday activities, diminish quality of life, and increase the risk of persistent joint damage if not properly managed. While medication plays a crucial role, adopting specific dietary habits is fundamental to controlling uric acid levels, preventing flare-ups, and maintaining overall joint health.
Understanding how diet influences gout is essential. Making informed food choices by incorporating anti-inflammatory, uric acid-lowering foods, and avoiding certain triggers can greatly improve management strategies. The impact of diet on uric acid levels underscores the importance of a balanced nutritional approach tailored for individuals prone to gout.
Adopting a gout-friendly diet involves emphasizing beneficial foods while minimizing those that raise uric acid. This detailed guide provides insights into what to eat and what to avoid to reduce the incidence of gout attacks and promote joint health.
Key Foods to Incorporate for Gout Management
Building a diet that supports healthy uric acid levels involves adding nutrient-dense, anti-inflammatory foods. These selections help mitigate joint pain and prevent sudden flare-ups:
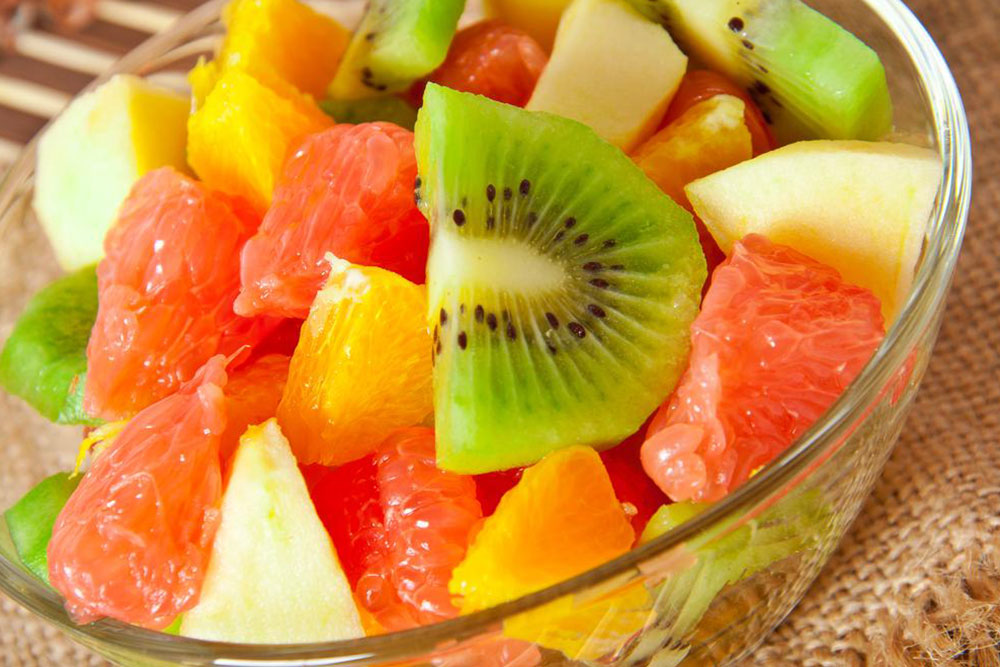
Fruits and Vegetables: Rich sources of vitamin C, fruits like oranges, strawberries, and cherries have been shown to reduce uric acid concentrations. Berries, especially cherries, contain antioxidants with anti-inflammatory properties. Vegetables such as red bell peppers, spinach, kale, and cabbage are high in nutrients and low in purines, making them excellent choices for gout sufferers.
Moreover, incorporating a variety of colorful produce not only ensures a broad spectrum of antioxidants but also supports overall immune and joint health.
Protein Sources: When selecting proteins, prioritize lean meats like chicken and turkey, along with plant-based options like legumes. Low-fat dairy products such as skim milk and yogurt are beneficial because they contain proteins that help lower uric acid levels. These choices contribute to muscle health without elevating purine levels that can trigger gout attacks.
Coffee and Tea: Interestingly, moderate coffee intake has been linked with a decreased risk of gout, possibly due to its ability to lower uric acid levels. Coffee contains antioxidants and compounds that may improve kidney function, thus promoting uric acid excretion. Similarly, green tea is a good alternative for its anti-inflammatory properties.
Foods to Limit or Avoid for Gout Prevention
While including beneficial foods is vital, avoiding foods that elevate uric acid is equally important to prevent gout episodes. Here are key items to minimize:
Organ Meats: Liver, kidneys, heart, and other organ meats are exceptionally rich in purines, which the body breaks down into uric acid, thereby increasing the risk of gout attacks. Limiting their intake is highly recommended.
Sugary and Sweetened Beverages: Drinks such as soft drinks, energy drinks, and processed fruit juices with high fructose content are directly associated with higher uric acid levels. Fructose increases purine metabolism, exacerbating the risk of gout flares.
Processed and Packaged Foods: Foods such as white bread, canned soups, fast foods, and processed meats often contain excessive salts, preservatives, and refined sugars that promote systemic inflammation and hinder uric acid regulation.
Seafood: Shellfish like shrimp, crab, and high-purine fish such as sardines, anchovies, and tuna are known to contribute significantly to uric acid buildup. Moderation or avoidance is advisable for those susceptible to gout.
In addition to dietary adjustments, staying well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water, limiting alcohol intake—particularly beer and spirits—and maintaining a healthy weight are crucial aspects of comprehensive gout management. Combining these lifestyle modifications with medical advice can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of gout attacks, ultimately improving quality of life.