Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Gout Flare-ups: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
This comprehensive guide explains the causes, symptoms, and progression of gout flare-ups. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis, lifestyle modifications, and proper treatment to prevent joint damage and recurrence. Understanding gout helps patients manage their condition effectively and improve their quality of life.
The Detailed Process Behind a Gout Flare-up
Gout, medically known as hyperuricemia, is a complex form of inflammatory arthritis that primarily affects the joints. It arises when excess uric acid in the bloodstream crystallizes and deposits in the joints and surrounding tissues. These uric acid crystals are sharp, needle-like formations that provoke a sudden and intense inflammatory response, resulting in a gout attack. Although the precise mechanisms triggering these attacks are not fully understood, research indicates that a combination of genetic predisposition, environmental factors, diet, and lifestyle contribute significantly to uric acid levels and the likelihood of experiencing gout episodes.
Understanding the pathophysiology of gout is essential for effective management and prevention. The process begins with hyperuricemia, a condition characterized by elevated uric acid levels (>6.8 mg/dL), resulting from either increased production or decreased excretion of uric acid. When these levels exceed the solubility threshold, crystals start forming and deposit in joints, tendons, and soft tissues. The immune system recognizes these crystals as foreign bodies, triggering an inflammatory cascade. This response leads to the classic symptoms of a gout attack, including severe pain, redness, swelling, warmth, and stiffness of the affected joint.
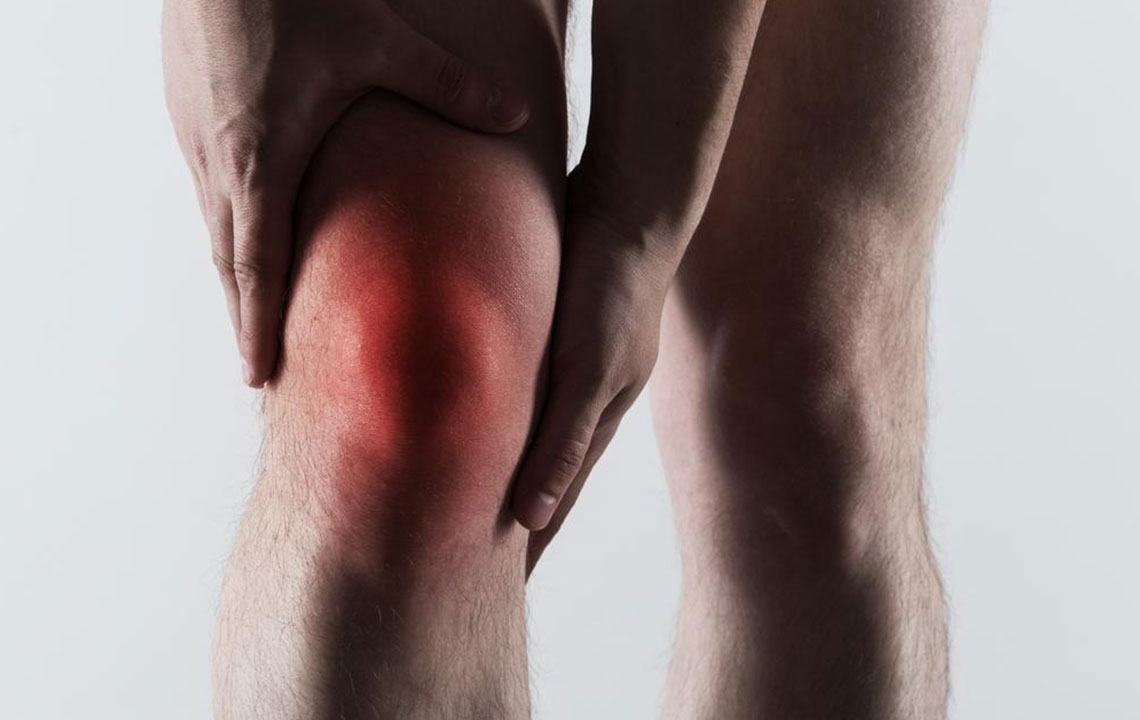
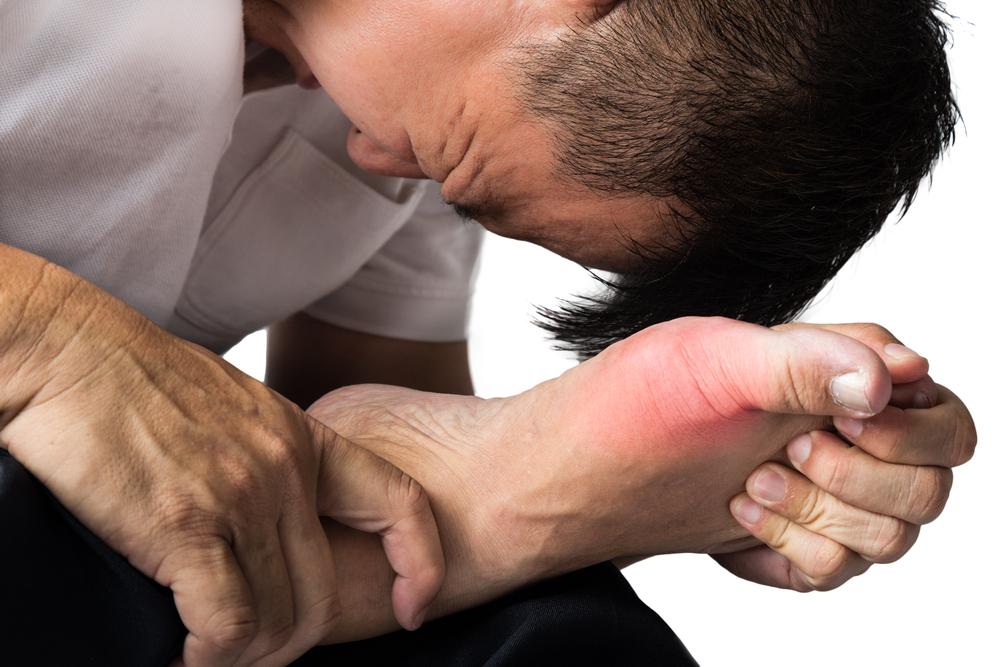
The big toe, particularly the joint at the base of the toe (the metatarsophalangeal joint), is the most common site for gout attacks — a condition sometimes referred to as podagra. However, gout can also affect other joints, such as the ankles, knees, fingers, wrists, and elbows. The symptoms are often sudden, peaking within 12 to 24 hours, and are characterized by intense pain that can radiate and worsen with movement or contact. The affected joint becomes visibly red, swollen, and warm to the touch, with a burning or throbbing sensation that can be debilitating.
Gout episodes tend to be recurrent over time. While the initial attacks may resolve spontaneously within a few hours or days, they often recur, sometimes becoming more frequent and severe if left untreated. The episodes may diminish in intensity over time but can lead to permanent joint damage, deformities, and the formation of tophi—hard crystalline deposits under the skin. It is common for many individuals to mistake early symptoms of gout for minor injuries such as sprains or tendinitis, which often delays diagnosis and treatment.
Most gout attacks typically occur at night, possibly due to changes in body temperature, decreased activity, or dietary factors. Mild initial pain can escalate rapidly, causing significant discomfort that hampers daily activities and sleep quality. While minor episodes might resolve within hours, more severe attacks can last several days and even extend into weeks if not properly managed. Persistent inflammation and repeated attacks contribute to joint deterioration and chronic joint deformities.
Statistics show that most individuals who experience a gout attack will have subsequent episodes within 6 months to 2 years. Therefore, early diagnosis and prompt treatment are critical to prevent worsening of the disease. Lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, and dietary adjustments are vital in managing uric acid levels and reducing the frequency and severity of attacks. Ignoring the symptoms or delaying treatment can lead to increased joint damage, reduced mobility, and long-term health complications.
In conclusion, understanding how gout manifests, progresses, and affects the body is essential for effective prevention and management. Recognizing the early signs of a gout flare-up and seeking medical guidance promptly can significantly improve quality of life and prevent irreversible joint damage. For those predisposed or experiencing recurrent gout episodes, ongoing medical care, combined with lifestyle changes, forms the cornerstone of successful management strategies.