Understanding Diverticulitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Options
Diverticulitis is an inflammatory condition affecting small pouches in the colon, caused by dietary and lifestyle factors like low fiber intake and obesity. Recognizing symptoms such as severe lower abdominal pain, fever, and rectal bleeding is vital for diagnosis. Treatment options range from dietary modifications and antibiotics to surgery for severe cases. Prevention emphasizes high-fiber diets, hydration, and regular exercise. Stay informed about risk factors and symptoms for early intervention and effective management of this common gastrointestinal disorder.
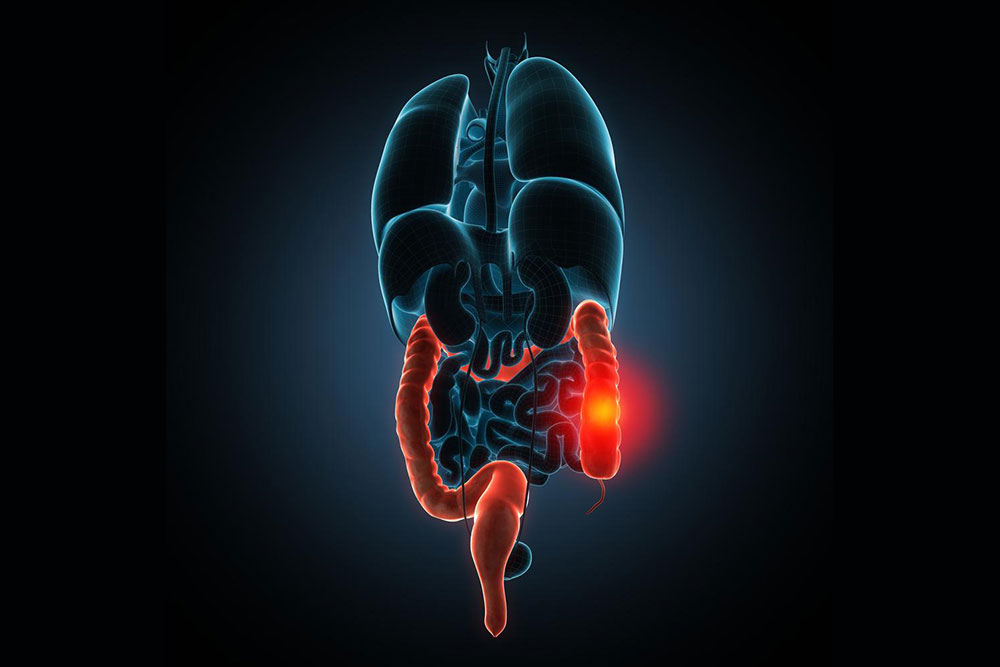
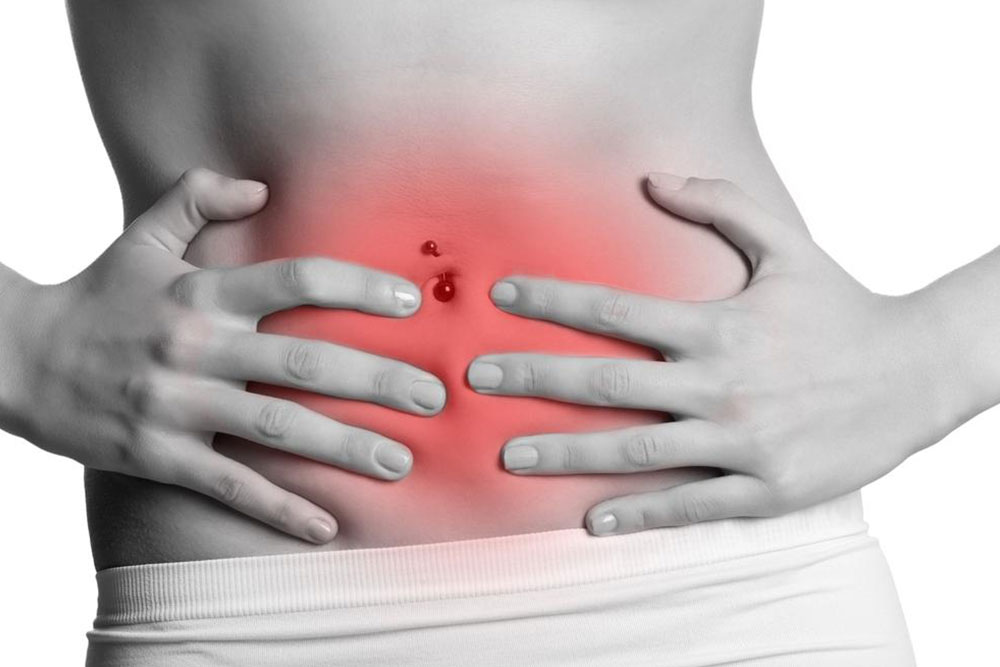
Diverticulitis is a condition characterized by the inflammation or infection of small pouches called diverticula that develop along the walls of the large intestine. These pouches are typically tiny, sac-like protrusions that form as a result of weakened areas in the colon lining. While diverticulitis most commonly occurs in the sigmoid colon, it can also develop in other parts of the digestive tract, including the small intestine and potentially other regions of the gastrointestinal system. Understanding the nature of diverticulitis requires a deep dive into its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Although the precise etiology of diverticulitis remains partly unclear, medical research indicates that several lifestyle and age-related factors play a significant role. Poor dietary habits, especially low intake of dietary fiber, chronic constipation, and a sedentary lifestyle are critical contributors. Furthermore, aging is associated with weakening of the intestinal walls, increasing vulnerability to diverticula formation and subsequent inflammation. In addition to dietary and lifestyle factors, obesity has been linked to an increased risk of developing diverticulitis. Excess weight can exert additional pressure on the colon walls, heightening the likelihood of diverticula formation and subsequent inflammation. Other risk factors include smoking and a genetic predisposition, which may predispose certain individuals to develop this condition. ### Recognizable Symptoms of Diverticulitis Recognizing the symptoms of diverticulitis is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. The hallmark symptom is a sudden, persistent pain that is usually localized in the lower left quadrant of the abdomen. This pain can be severe and may become more intense over time. Patients often report tenderness in this area, often accompanied by a palpable mass in some cases. Additional symptoms can include: - Nausea and vomiting - Sudden diarrhea or constipation - Abdominal bloating and cramping - Rectal bleeding, which may be minimal or significant - Fever and chills, indicating infection or inflammation In some cases, the symptoms may mimic other gastrointestinal conditions such as appendicitis, irritable bowel syndrome, or inflammatory bowel disease, making accurate diagnosis essential. ### Diagnosis of Diverticulitis To confirm diverticulitis, physicians rely on a combination of physical examinations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. During the physical exam, tenderness in the lower abdomen, especially the left side, may be detected. Blood tests are often performed to identify signs of infection or inflammation, such as elevated white blood cell counts. Imaging techniques play a crucial role in diagnosis. The most common imaging modality is a computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis, which can identify inflamed diverticula, localized abscesses, perforations, and other complications. In some cases, ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be utilized. ### Treatment Options for Diverticulitis The treatment for diverticulitis depends on the severity of the condition. Mild cases often respond well to conservative management, including dietary modifications and antibiotics. Hospitalization may be necessary for more severe cases involving complications. #### Conservative Treatment For uncomplicated diverticulitis, the primary treatment involves resting the bowel, reducing inflammation, and preventing complications. Patients are typically advised to follow a clear liquid diet initially, progressing gradually to a high-fiber diet once symptoms subside. This dietary approach helps reduce stress on the colon and promotes healing. Antibiotics are prescribed to eliminate the infection, especially if bacteria are involved. Pain management with over-the-counter medications or prescribed pain relievers can also help relieve discomfort. #### Surgical Intervention In cases where complications arise—such as perforation, abscess formation, fistulas, or bowel obstruction—surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgery can range from removal of the affected segment of the colon (colectomy) to more extensive procedures depending on the extent of damage. Minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopic surgery, are increasingly preferred due to their reduced recovery time and lower risk of complications. ### Prevention and Lifestyle Adjustments Prevention of diverticulitis relies heavily on lifestyle and dietary modifications. Incorporating a high-fiber diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes helps maintain regular bowel movements and decrease pressure inside the colon. Staying well-hydrated and engaging in regular physical activity further supports gastrointestinal health. Avoiding smoking, managing weight through proper diet and exercise, and minimizing the risk of constipation are critical steps. For individuals with a history of diverticulitis, regular medical check-ups and early intervention at the first signs of symptoms can prevent severe episodes. ### Advancements in Research and Future Directions Ongoing research aims to better understand the pathophysiology of diverticulitis and improve treatment strategies. Emerging therapeutic approaches include probiotics to promote healthy gut flora and novel minimally invasive surgical techniques to reduce recovery times. In conclusion, diverticulitis is a manageable condition with proper diagnosis, treatment, and lifestyle adjustments. Awareness of symptoms and risk factors enables early intervention, significantly reducing the risk of complications and improving quality of life for affected individuals.