Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing the Symptoms and Signs of Stomach Cancer
This comprehensive guide explores the key signs and symptoms of stomach cancer, emphasizing the importance of early detection. It provides insights into early warning signs, advanced symptoms, diagnosis methods, and treatment options. Understanding these critical aspects can help individuals seek timely medical care, improving outcomes and survival rates for those affected by gastric carcinoma. Stay informed about risk factors and ensure regular health screenings, especially if you belong to a higher-risk group for stomach cancer.

Stomach cancer, medically known as gastric carcinoma, is a serious health concern that arises when normal cells lining the stomach lining undergo abnormal changes. These transformed cells multiply uncontrollably, forming tumors that can be either benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Malignant tumors have the capacity to invade surrounding tissues and metastasize to distant parts of the body, making early detection and intervention crucial. Globally, stomach cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality, highlighting the importance of awareness and prompt diagnosis.
Understanding the early warning signs of stomach cancer is essential for timely medical intervention. Often, the initial symptoms are subtle and easily mistaken for less severe gastrointestinal issues, which can delay diagnosis. Individuals over the age of 40 are more commonly affected, with men experiencing it approximately twice as often as women. Recognizing these signs and understanding their significance can significantly improve prognosis and treatment outcomes.
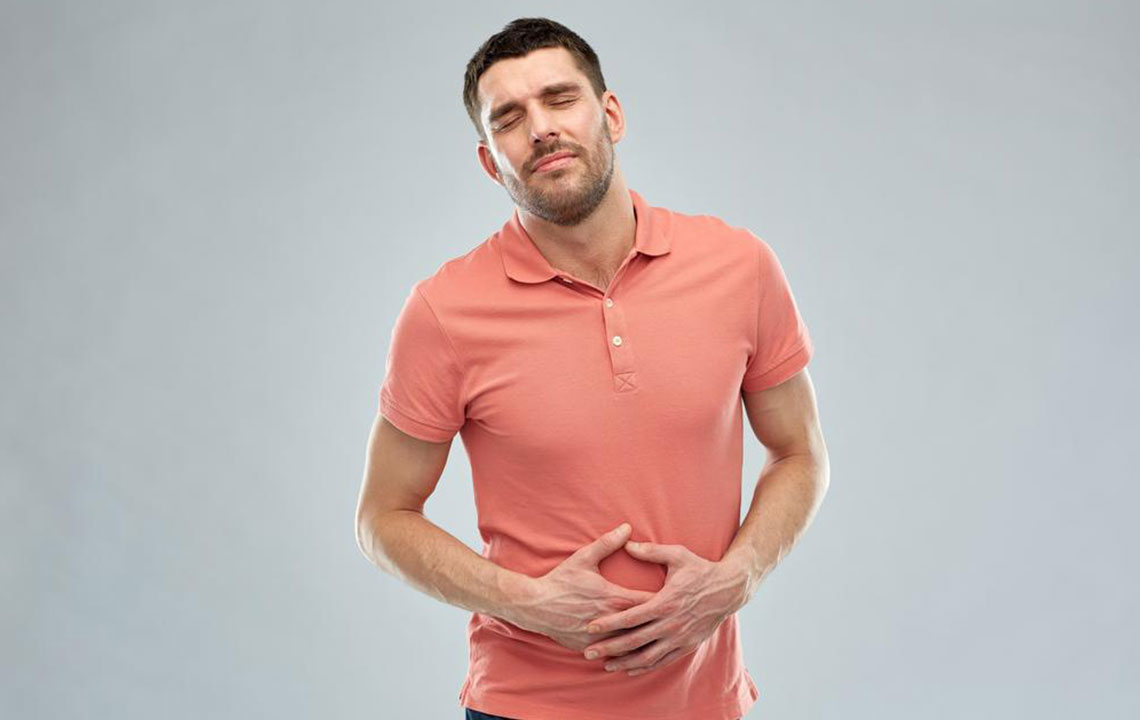
Early symptoms of stomach cancer typically include persistent stomach discomfort or pain, unexplained fatigue, frequent indigestion, loss of appetite, bloating after meals, feeling full rapidly, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), mild nausea, and recurrent burping. Because these symptoms are non-specific and common in benign conditions like gastritis or ulcers, patients may ignore them or self-medicate. However, persistent or worsening symptoms necessitate medical evaluation for potential gastric malignancies.
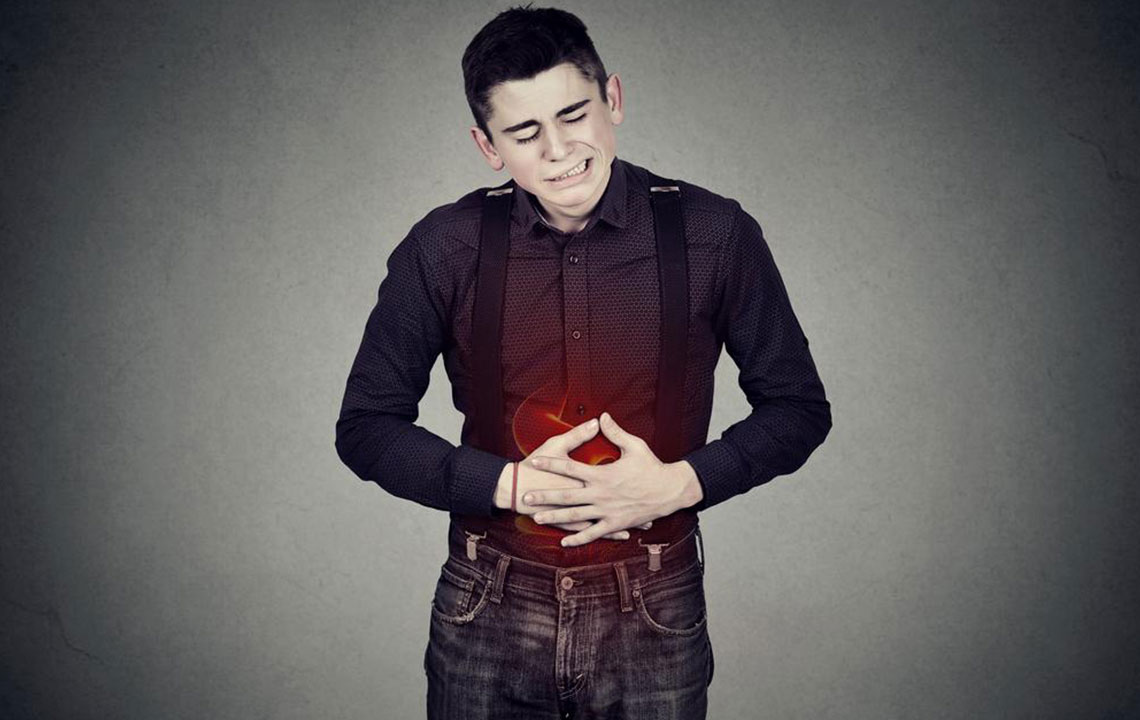
As the disease progresses, additional and more severe symptoms may develop. These include vomiting (which may be tinged with blood), dark or tarry stools indicating gastrointestinal bleeding, persistent stomach pain, unintended weight loss, anemia, and a sense of abdominal fullness that does not improve. Patients experiencing these symptoms, especially those over 55 who have ongoing issues like heartburn or indigestion, should seek urgent medical assessment. Diagnostic tools such as endoscopy with biopsy are essential for confirming the presence of stomach cancer. These procedures allow doctors to visualize the stomach lining directly and obtain tissue samples for pathological examination. The accurate staging of the cancer helps in planning effective treatment strategies, which may include surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy, depending on the disease stage and overall health of the patient.
In conclusion, awareness of the early signs and symptoms of stomach cancer plays a vital role in enhancing survival rates. Regular check-ups, especially for individuals with risk factors such as a family history of gastric cancer, Helicobacter pylori infection, certain dietary habits, smoking, and excessive alcohol intake, are recommended. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment can significantly improve the prospects for affected individuals. If you experience any persistent gastrointestinal symptoms or are part of a higher-risk group, consult your healthcare provider promptly for comprehensive evaluation and early intervention.