Comprehensive Guide to Preventing and Treating Gum Disease for Optimal Oral Health
This comprehensive guide offers detailed insights into preventing and treating gum disease. It covers causes, early signs, prevention strategies, and advanced treatment options to help you maintain healthy gums. Emphasizing oral hygiene, lifestyle changes, and timely dental care, it aims to empower individuals to protect their oral health and overall well-being, reducing the risk of severe dental and systemic health problems through proactive measures.
Comprehensive Guide to Preventing and Treating Gum Disease for Optimal Oral Health
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is one of the most common dental problems affecting millions worldwide. If not properly managed or prevented, it can lead to severe complications such as tooth loss, bone deterioration, and even impact overall health. This extensive guide aims to provide in-depth insights into the causes, early signs, preventive strategies, and effective treatment options for gum disease. Understanding these aspects is crucial for maintaining healthy gums and safeguarding your overall oral and systemic health.
According to statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), roughly 50% of adult populations in the United States are affected by some form of gum disease. The prevalence increases with age, especially among seniors aged 65 and above. The good news is that many cases are preventable through simple yet consistent oral hygiene routines and lifestyle choices. Being proactive about oral health not only preserves your smile but also reduces the risk of serious health issues associated with periodontal problems.
Understanding the Causes of Gum Disease
At the core of gum disease is bacterial accumulation in dental plaque, a sticky film that forms on teeth and along the gum line. This bacterial community thrives on sugars and carbohydrates present in our daily diet. When bacteria metabolize these sugars, they release harmful toxins that irritate and inflame the gum tissue, causing redness, swelling, bleeding, and pain. Persistent plaque buildup can mineralize into tartar or calculus, a hardened deposit that irritates gums even further and makes removal difficult without professional cleaning.
Several factors can increase susceptibility to gum disease, including poor oral hygiene practices, high sugar consumption, tobacco use, genetic predisposition, and compromised immune system function. Additionally, hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause, or menstrual cycles can influence gum health, making inflammation more likely. Lifestyle factors such as stress and inadequate nutrition further weaken gum tissues, making them more vulnerable to bacterial attack.
Recognizing Early Signs and Symptoms
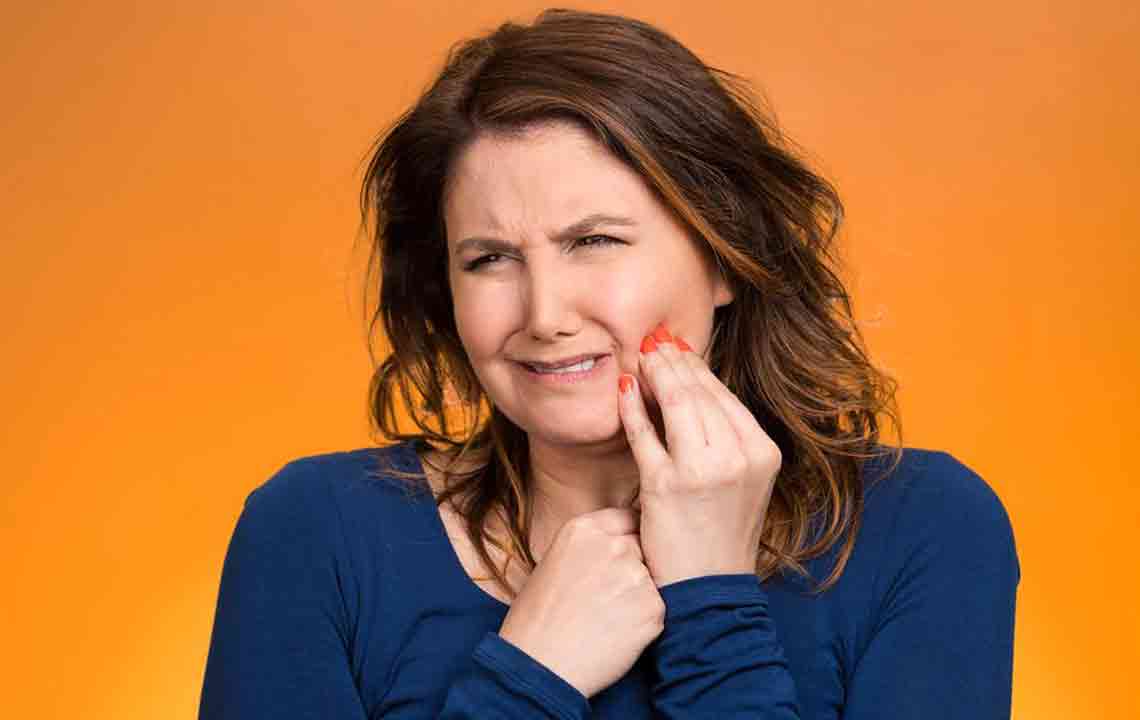
Early detection of gum disease is critical for preventing progression and more invasive treatments. Commonly observed warning signs include bleeding gums during brushing or flossing, persistent bad breath, red or swollen gums, and gums that recede away from the teeth. Sensitivity to hot or cold foods and liquids, looseness of teeth, and changes in bite alignment may also indicate underlying periodontal issues. Noticing these symptoms early encourages timely professional intervention.
Gum disease primarily manifests as two conditions: gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is the initial stage, characterized by inflammation without significant bone loss. If untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form where the supporting structures of teeth, including bone and connective tissue, become damaged, leading to tooth mobility and eventual loss. Therefore, awareness of these signs empowers individuals to seek early dental care.
Effective Prevention Strategies for Healthy Gums
Preventing gum disease starts with establishing and maintaining meticulous oral hygiene routines. Brushing your teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste ensures the removal of plaque from tooth surfaces and along the gum line. Using an electric toothbrush can enhance cleaning efficiency, reaching areas that manual brushes may miss. Flossing daily removes plaque and food debris from between teeth and beneath the gum line, preventing tartar formation.
Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are vital. Dental professionals can remove tartar that home care cannot eliminate, evaluate gum health, and identify early signs of periodontal issues. Scheduling bi-annual visits allows for early detection and management of any emerging problems. Additionally, adopting a balanced diet low in processed sugars and rich in essential vitamins and minerals supports immune health and gum tissue integrity.
Avoiding tobacco products and limiting alcohol consumption are crucial components of gum health. Smoking impairs blood flow to the gums, slowing healing and increasing infection risk. Furthermore, managing stress through relaxation techniques can reduce hormonal influences that exacerbate inflammation. Staying well-hydrated and maintaining overall good health also play supportive roles in oral tissue resilience.
Advanced Treatment Options for Gum Disease
If periodontal disease is diagnosed, several treatment modalities are available depending on severity. Non-surgical treatments include scaling and root planing, a deep cleaning procedure that removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line and smooths the tooth roots to discourage bacterial colonization. Antibiotic therapy may be prescribed to control infection.
For more advanced cases, surgical interventions might be necessary. Procedures such as flap surgery or pocket reduction surgery lift the gums, remove tartar, and secure the tissues back in position. Bone grafts, tissue regeneration, and guided tissue regeneration are options to restore lost bone and gum tissue, helping to preserve natural teeth and prevent further deterioration.
Emerging technologies like laser therapy offer minimally invasive alternatives with faster recovery times. Regular maintenance visits and proper home care post-treatment are essential for long-term periodontal stability. Addressing gum disease early not only saves teeth but also prevents the potential cascade of systemic health issues linked to chronic periodontal infections, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory problems.
By understanding the causes, recognizing warning signs, adopting preventative habits, and seeking prompt professional care when needed, individuals can effectively manage and prevent gum disease. Committing to good oral health practices today is a crucial investment in your overall health and well-being for years to come.