Comprehensive Guide to the Top 5 Gum Diseases and Prevention Strategies
This comprehensive article explores the top 5 types of gum diseases, detailing their symptoms, causes, and effective prevention strategies. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis, professional dental care, and maintaining good oral hygiene to safeguard your oral and overall health. Learn how to identify early signs and protect your smile from periodontal issues.
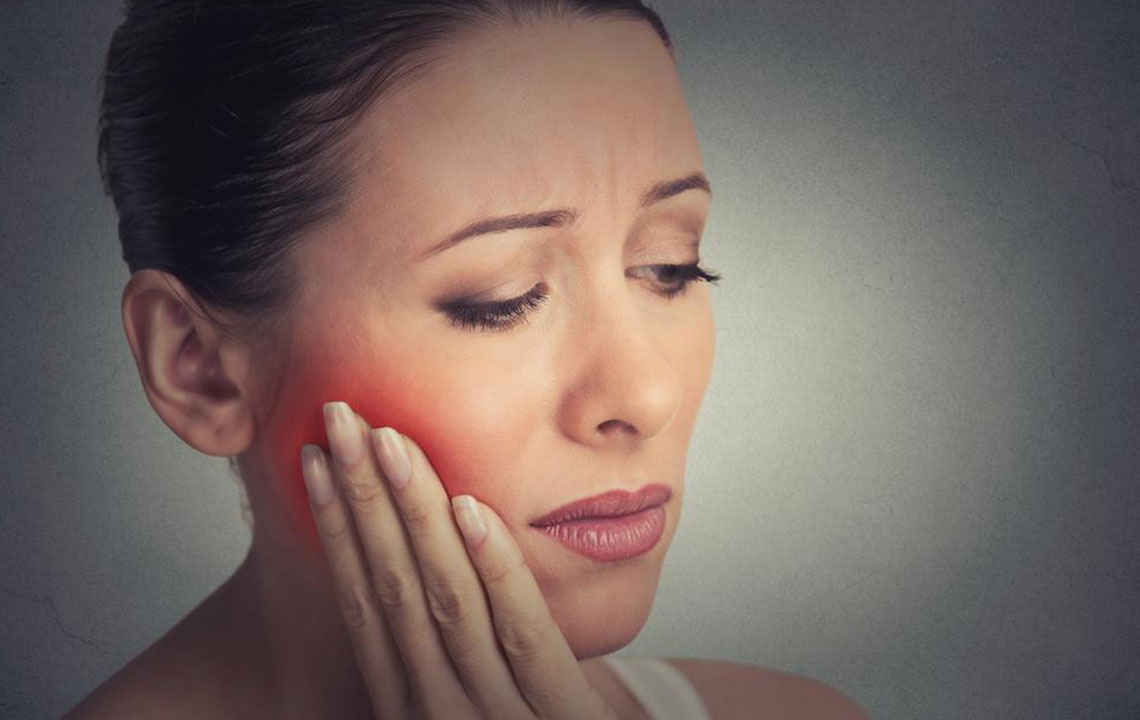
A Complete Overview of the Top 5 Types of Gum Diseases and How to Prevent Them
Gum disease, scientifically referred to as periodontal disease, is a widespread oral health concern that affects millions worldwide. It is a progressive bacterial infection that damages the tissues supporting the teeth, including the gums, periodontal ligament, and jawbone. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to unpleasant symptoms such as bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, gum recession, tooth sensitivity, and even tooth loss. Recognizing early signs and understanding the different types of gum diseases are crucial steps toward maintaining oral health and preventing more severe complications.
This detailed guide explores the five most common types of periodontal conditions, highlighting their characteristics, causes, symptoms, and recommended treatment options. By educating yourself about these issues, you can take proactive measures to protect your smile and overall health.
Understanding Gum Disease: Causes and Risk Factors
Gum disease primarily results from the accumulation of plaque—a sticky film full of bacteria—that forms on teeth and along the gum line. If not effectively removed through daily brushing and flossing, plaque hardens into tartar, which can only be removed by professional dental cleaning. Persistent plaque and tartar irritate the gums, causing inflammation and infection.
Several risk factors can increase susceptibility to gum disease, including poor oral hygiene practices, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, diabetes, hormonal changes, certain medications, genetic predisposition, and stress. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, including twice-daily brushing, daily flossing, and routine dental visits, plays a vital role in prevention.
The 5 Most Common Types of Gum Diseases
Gingivitis: The Mildest Form
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease, characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing. It's caused by plaque buildup at the gum line. Fortunately, gingivitis is reversible with proper oral hygiene, professional cleanings, and regular dental checkups. Ignoring gingivitis can lead to more serious conditions like periodontitis.
Chronic Periodontal Disease
This form of gum disease primarily affects adults over 45 but can occur at any age. It involves a slow progression of inflammation beneath the gums, leading to the destruction of supporting tissues and bone. Gums often recede, making teeth look longer and appear spaced out. Treatment usually involves deep cleaning procedures such as scaling and root planing, alongside antimicrobial treatments as recommended by dental professionals. Early intervention can halt further tissue damage and prevent tooth loss.
Aggressive Periodontal Disease
Unlike chronic periodontitis, aggressive periodontal disease develops rapidly and affects younger individuals, including adolescents and young adults. It is characterized by rapid tissue destruction, significant bone loss, and deep periodontal pockets. Factors such as smoking, family history, and poor immune response can exacerbate its severity. Management typically involves extensive dental interventions, including antibiotics and surgical procedures, alongside rigorous oral hygiene routines.
Periodontal Disease Associated with Systemic Illnesses
This category encompasses gum disease that is linked to systemic health conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and lung infections. These health problems can alter the body's immune response, making gums more vulnerable to infections. Conversely, periodontal disease can exacerbate systemic conditions, creating a bidirectional relationship. Collaborative care involving dentists and healthcare providers is essential for managing both oral and systemic health effectively.
Necrotizing Periodontal Disease
Considered the most severe form of gum disease, necrotizing periodontal disease often occurs in individuals with compromised immunity, such as those suffering from malnutrition, stress, or heavy smoking. It causes rapid destruction of gum tissues, ulceration, and spread to the jawbone, leading to severe pain and swelling. Immediate, aggressive treatment involving antibiotics, thorough debridement, and supportive care is critical for halting the progression of this destructive disease.
Preventive Measures and Oral Hygiene Tips
Preventing gum diseases requires consistent and meticulous oral care. Brushing at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily to remove debris from between teeth, and using antibacterial mouthwash can significantly reduce plaque accumulation. Regular dental checkups—at least twice a year—allow for professional cleaning and early detection of potential issues.
Diet also plays a role; limiting sugary foods and drinks helps decrease plaque formation. Quitting smoking and managing underlying health conditions like diabetes contribute to healthier gums. Educating oneself about the early signs of gum issues empowers individuals to seek prompt professional intervention, reducing the risk of invasive treatments and preserving natural teeth.
The Importance of Professional Dental Care
Professional dental care is essential for diagnosing, treating, and preventing gum diseases. Routine cleanings remove calculus that cannot be eliminated through brushing alone. Dentists can identify early signs of inflammation or tissue loss and recommend personalized treatment plans. Advanced cases may require surgical procedures, such as flap surgery, grafts, or laser therapy, to restore periodontal health.
Integrating good oral hygiene habits with regular dental visits ensures long-term periodontal health and overall wellness. Promoting awareness about gum disease helps reduce its prevalence and associated healthcare costs.