Complete Guide to Managing Pulmonary Fibrosis: Treatments, Strategies, and Insights
Pulmonary fibrosis is a serious lung disease marked by scarring that hampers breathing. This comprehensive guide explores effective management options including medications like antifibrotics, oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation, and advanced interventions like lung transplants. Early diagnosis and personalized treatment plans are key to improving quality of life and slowing disease progression. Learn how healthcare providers tailor strategies to manage symptoms and support patients through ongoing care and emerging research. Stay informed to better navigate this complex condition and enhance your well-being.
Complete Guide to Managing Pulmonary Fibrosis: Treatments, Strategies, and Insights
Pulmonary fibrosis is a complex and progressive lung disease characterized by the thickening and scarring of lung tissue. This scarring leads to a decline in lung function, resulting in increasingly severe breathing difficulties. As the disease advances, patients often experience symptoms like persistent cough, fatigue, and significant shortness of breath which can severely impact daily activities and overall quality of life. Despite extensive research, the exact cause of pulmonary fibrosis remains unknown in many cases, leading to the classification of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis when no specific reason can be identified. Understanding and managing this condition requires an integrated approach aimed at alleviating symptoms, slowing disease progression, and enhancing patients' quality of life.
Since lung tissue damage from fibrosis is irreversible, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing further damage. Healthcare professionals tailor treatment plans based on the severity of each patient’s condition, taking into account overall health, disease stage, and comorbidities. The available options encompass a range of therapies designed to improve breathing, reduce symptoms, and slow disease advancement. Here are some of the most common and effective treatments:
Medications: The development of novel drugs has significantly impacted pulmonary fibrosis management. Antifibrotic agents such as pirfenidone and nintedanib have been approved to slow down the progression of the disease. These drugs help prevent the worsening of lung scarring but do not reverse existing damage. Proper administration under medical supervision is essential to minimize side effects and optimize benefits.
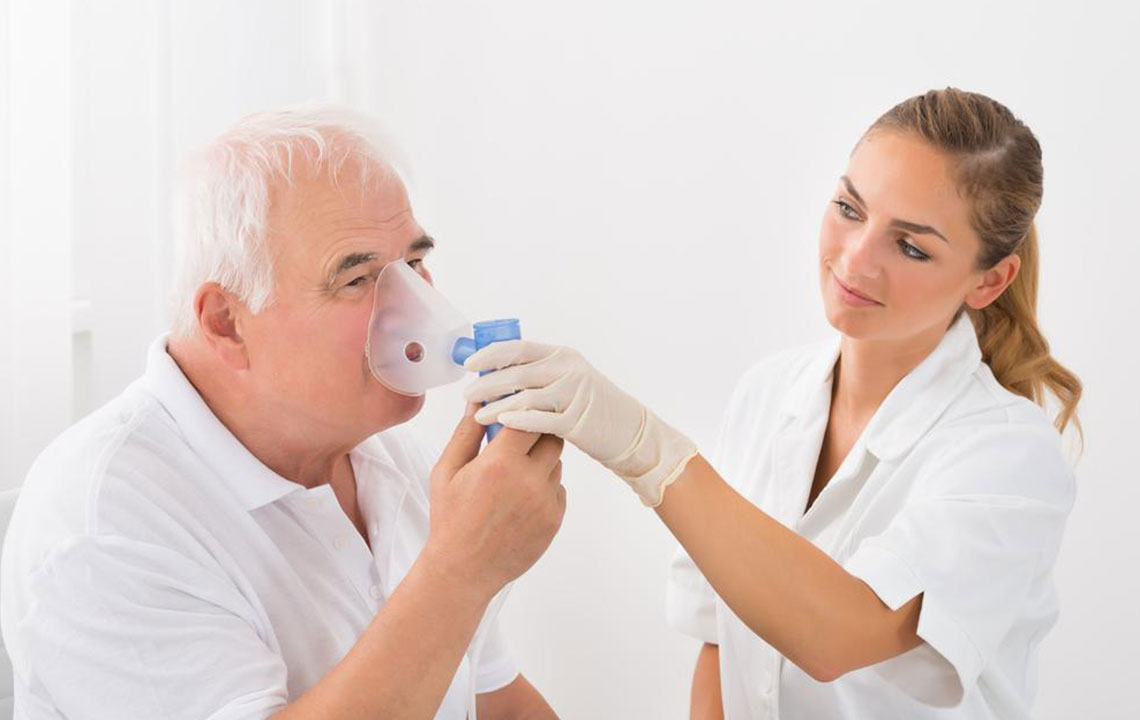
Oxygen Therapy: Supplemental oxygen is a cornerstone in managing advanced pulmonary fibrosis. It helps alleviate shortness of breath, improves oxygen saturation in the bloodstream, and prevents complications like pulmonary hypertension and right heart failure. Continuous oxygen use during daily activities ensures tissues receive adequate oxygen, thereby improving overall energy levels and comfort.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation: This multidisciplinary program includes exercise training, education, and support designed to enhance physical and emotional well-being. Patients learn breathing techniques, improve stamina, and receive guidance on managing symptoms, which can significantly enhance their ability to perform daily routines.
Management of Comorbidities: Addressing associated conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), sleep apnea, and cardiovascular issues is vital. Managing these comorbidities can improve respiratory outcomes and overall health.
Advanced Interventions and Research: For selected patients, lung transplantation may be an option when other treatments fail, especially in severe cases. Ongoing research continues to explore new therapeutic avenues, including stem cell therapy and gene editing techniques, aiming to restore lung function or halt fibrosis altogether.
It's important to note that early diagnosis and intervention are crucial in managing pulmonary fibrosis effectively. Regular monitoring through pulmonary function tests, imaging studies, and clinical evaluations help physicians adjust treatments timely. Patients are encouraged to adopt a healthy lifestyle—avoid smoking, stay active within their limits, and maintain good nutrition—to support overall health and potentially slow disease progression.
Above all, clear communication with healthcare providers is essential for optimizing treatment outcomes. Developing a personalized care plan that considers the patient's specific needs and circumstances ensures the best possible management of this challenging condition. Remember, although pulmonary fibrosis is a chronic, progressive disease, advances in treatment options and supportive care significantly improve the quality of life for many patients.