Effective Strategies for Managing COPD and Improving Long-Term Health Outcomes
Manage COPD effectively by adopting lifestyle modifications, adhering to medication routines, engaging in pulmonary rehab, and avoiding environmental triggers. These strategies can significantly improve quality of life and extend longevity despite the chronic nature of the disease. Collaboration with healthcare providers is key to personalized care and optimal health outcomes.
Effective Strategies for Managing COPD and Improving Long-Term Health Outcomes
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disorder that significantly impacts respiratory function and overall health. It is characterized by persistent airflow limitation, commonly caused by long-term exposure to irritating gases or particulate matter, most notably cigarette smoke. COPD is considered a major global health challenge due to its high prevalence, chronic nature, and the fact that there is currently no known cure. Despite this, contemporary management strategies allow patients to live longer, more comfortable lives and maintain a better quality of life. Recognizing and implementing comprehensive COPD management approaches is essential for patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers alike.
Understanding COPD's progression and effective interventions can help in reducing symptom severity, preventing exacerbations, and prolonging survival. This detailed guide explores the most effective strategies to manage COPD comprehensively, emphasizing lifestyle modifications, medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and supportive therapies. By adopting these measures, patients can significantly enhance their health outcomes and enjoy a more active, fulfilling life despite their respiratory condition.
Let's delve into key strategies that are proven to optimize COPD management:
Establish Realistic and Personal Health Goals. Managing COPD requires a tailored approach. Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop achievable health objectives. These goals might include improving exercise tolerance, reducing symptom frequency, increasing energy levels, or maintaining independence. Setting concrete, realistic targets helps patients stay motivated and engaged in their treatment plans.
Minimize Exposure to Air Pollutants and Cease Smoking. Environmental factors play a crucial role in COPD progression. Patients should avoid areas with high pollution levels, smog, or occupational irritants. Smoking cessation is the single most important step in slowing disease progression. Quitting smoking not only improves lung function but also enhances the effectiveness of other treatments. Support programs, counseling, and pharmacotherapy can significantly increase the chances of successfully quitting smoking.
Strict Adherence to Medication Protocols. Proper medication use is vital for managing COPD symptoms and preventing exacerbations. Inhalers, bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and other prescribed medications should be used exactly as directed. Incorrect use or missed doses can lead to worsening symptoms and higher risk of complications. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure optimal medication management and adjustments when necessary.
Engage in Light Physical Activity and Breathing Exercises. While intense workouts may not be suitable for all COPD patients, moderate exercise can boost physical fitness, improve respiratory capacity, and reduce symptoms like breathlessness. Breathing techniques such as pursed-lip breathing and diaphragmatic breathing strengthen lung function and enhance oxygen exchange. Consulting with a respiratory therapist can help tailor exercise regimens that suit individual needs.
Participate in Pulmonary Rehabilitation Programs. Pulmonary rehab is a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach that combines physical training, education, nutritional counseling, and psychosocial support. These programs aim to improve respiratory muscle strength, increase endurance, and foster mental well-being. Evidence shows that pulmonary rehabilitation reduces hospitalizations, alleviates symptoms, and enhances quality of life in COPD patients.
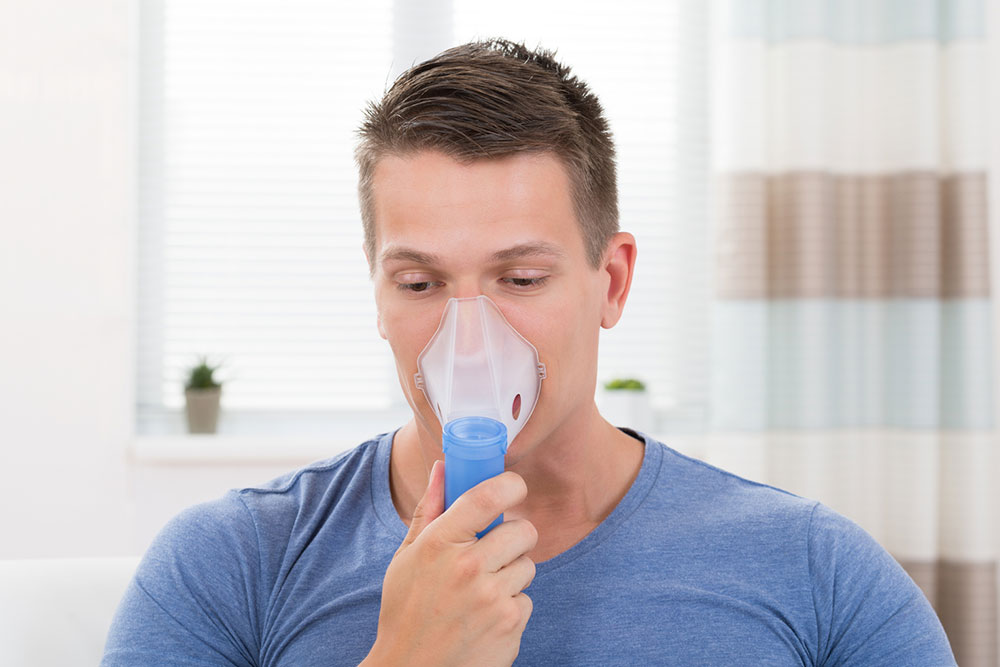
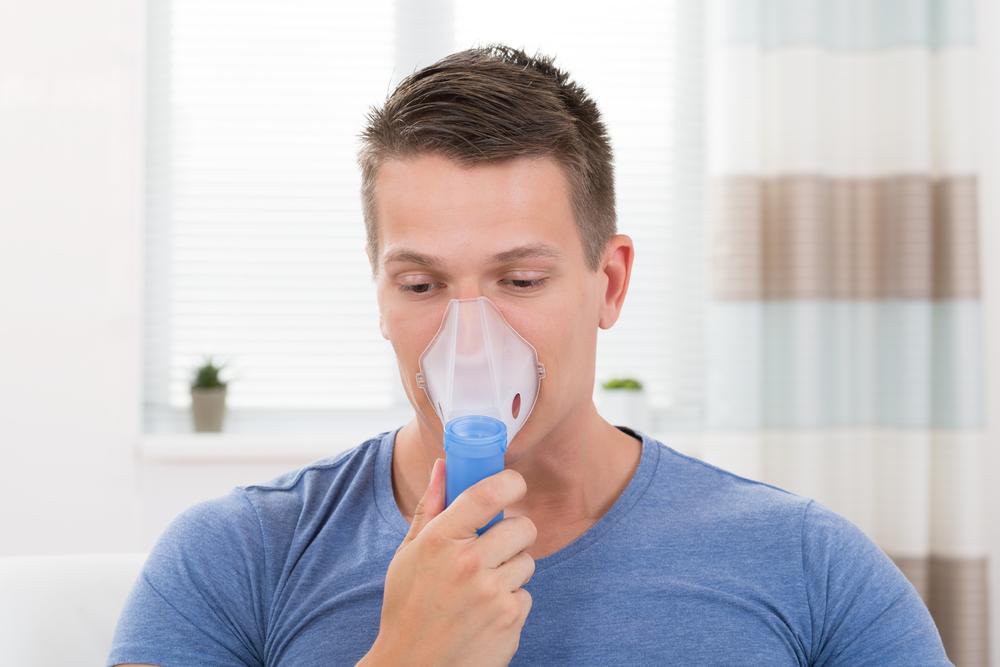
Utilize Oxygen Therapy When Indicated. In advanced COPD stages where blood oxygen levels are critically low, supplemental oxygen therapy becomes essential. Administering oxygen through nasal cannulas or masks helps alleviate breathlessness, prevents tissue damage, and can extend lifespan. Regular monitoring and proper equipment maintenance are critical for effective oxygen therapy.
Prompt Treatment of Infections with Antibiotics. COPD patients are prone to respiratory infections, which can trigger exacerbations and accelerate disease progression. Timely and appropriate antibiotic therapy during infections helps control bacterial pathogens, reduce hospital admissions, and prevent severe complications. Vaccinations, such as influenza and pneumococcal vaccines, provide additional protection against respiratory infections.
In conclusion, while COPD remains a chronic and incurable condition, a proactive management plan involving lifestyle adjustments, medication adherence, and supportive therapies can greatly improve life expectancy and quality. Patients are encouraged to work collaboratively with healthcare teams to implement these strategies effectively. Staying informed about the latest treatments and participating in routine health evaluations will help maintain respiratory health and reduce disease burden over time.





