Comprehensive Guide to Effective COPD Management and Lifestyle Improvements
This comprehensive guide provides detailed insights into managing COPD effectively, including early symptom recognition, lifestyle adjustments, medications, and supportive therapies. It aims to help patients improve their quality of life while minimizing disease progression and complications through proactive care and management strategies.

In-Depth Strategies for Managing Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a persistent, long-term lung condition that significantly impacts breathing and overall health. Characterized by narrowing of the airways and ongoing lung inflammation, COPD presents a range of symptoms—including wheezing, a persistent cough, and excessive mucus production—that can interfere with daily life. As a progressive disease, COPD mainly develops due to prolonged exposure to irritants such as cigarette smoke, environmental pollutants, and harmful chemicals. Despite its severity, COPD is manageable through comprehensive treatment plans, lifestyle modifications, and regular medical attention, which collectively help patients improve their quality of life while minimizing complications.
Understanding COPD in Detail
Emphysema and chronic bronchitis are the two primary types of COPD, each affecting the lungs differently. Emphysema involves the destruction of alveoli—the tiny air sacs in the lungs responsible for gas exchange—leading to a reduction in the surface area available for oxygen intake and carbon dioxide release. This damage hampers efficient breathing, especially during physical exertion. Chronic bronchitis, on the other hand, causes inflammation of the bronchial tubes, resulting in excessive mucus production and persistent coughing. Both conditions often coexist, contributing to the overall decline in lung function.
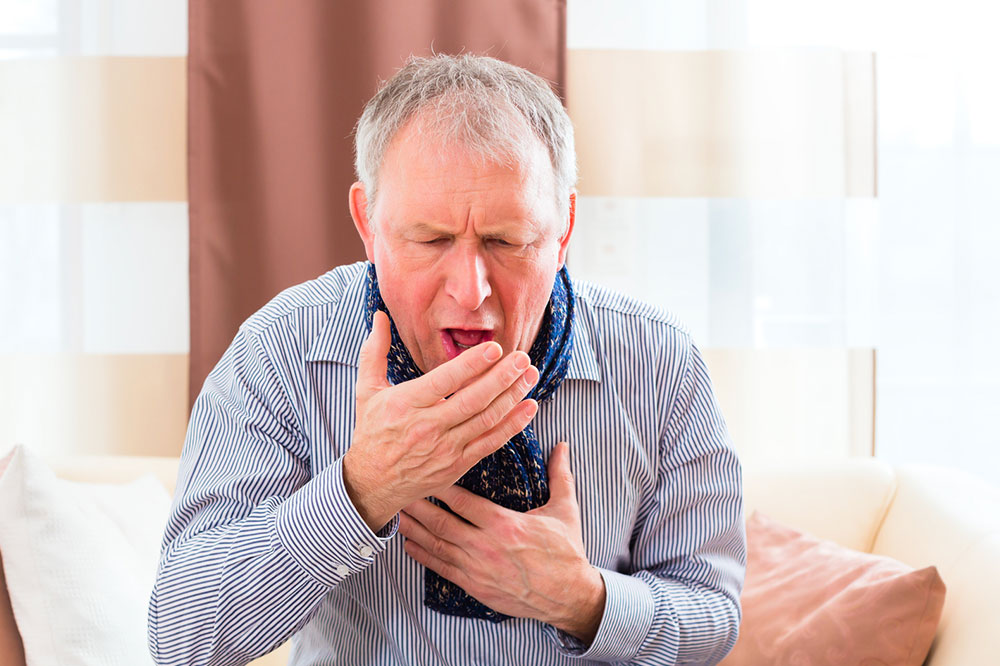
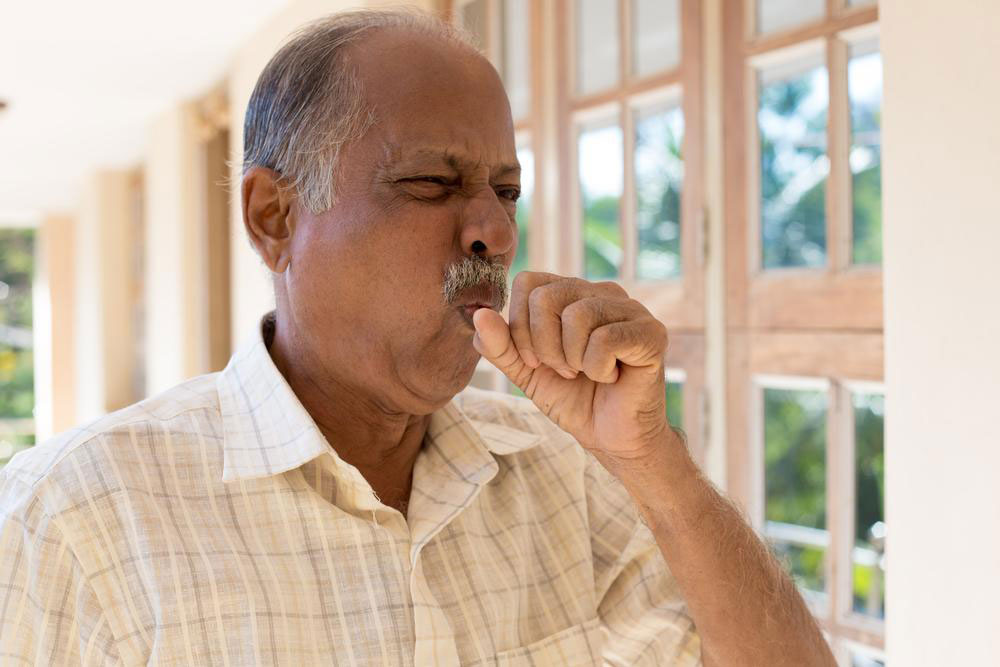
Recognizing the early symptoms of COPD can significantly impact disease management. Initially, symptoms like shortness of breath during exertion, occasional cough, and mucus production might be mistaken for common colds or allergies. However, as the disease progresses, these symptoms intensify, leading to difficulty breathing even during rest, wheezing, chest tightness, fatigue, and weight fluctuations. Advanced COPD may also cause swelling in the ankles or legs, frequent respiratory infections, and a noticeable decline in physical energy. Early detection and intervention are crucial for controlling the disease, preventing complications, and maintaining a better quality of life.
Detecting Symptoms of COPD Early
By understanding the signs of COPD, patients and caregivers can facilitate early diagnosis and prompt treatment. Initial indicators include occasional shortness of breath after physical activity, chronic cough, and mucus production. As the condition advances, symptoms become more persistent and severe—patients may experience breathlessness during moderate activities, wheezing, chest discomfort, and daily coughing with mucus. Over time, additional signs such as fatigue, swelling of the limbs, unintended weight loss, and recurrent respiratory infections may emerge. Recognizing these symptoms early allows healthcare providers to intervene sooner, which can significantly slow disease progression and improve patient outcomes.
Home and Lifestyle Strategies for Managing COPD Effectively
Living with COPD requires adherence to certain lifestyle adjustments to reduce symptom severity and prevent exacerbations. Key strategies include avoiding exposure to cigarette smoke, dust, fumes, and other environmental pollutants that can irritate the lungs. Patients should follow prescribed medication regimens meticulously and attend routine checkups. Incorporating deep breathing exercises can strengthen lung capacity, while engaging in light physical activity—such as walking or stretching—can improve overall endurance without overexertion. Nutritional support is vital; a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can bolster immune function. Staying adequately hydrated thins mucus, making it easier to clear from the airways. Additionally, joining support groups or participating in COPD therapy sessions can provide emotional comfort, practical advice, and motivation to stick with management plans, fostering resilience in daily living.
Comprehensive Treatment Options for COPD Patients
The primary goals of COPD treatment are symptom relief, reducing the frequency and severity of exacerbations, and preventing disease progression. A multifaceted approach combines medication, lifestyle adjustments, and supportive therapies tailored to individual patient needs.
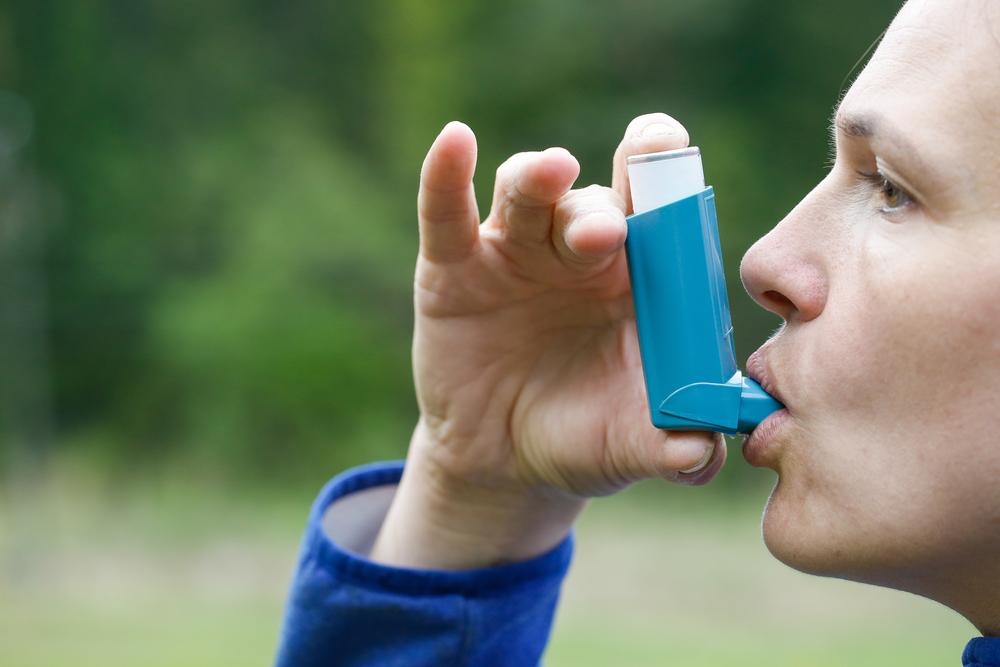
Bronchodilators
These are the cornerstone medications for COPD management. Inhaled bronchodilators, such as beta-agonists and anticholinergics, relax the smooth muscles of the airways, making breathing easier. They provide rapid relief from acute symptoms and are often used as maintenance therapy to keep airflow open.
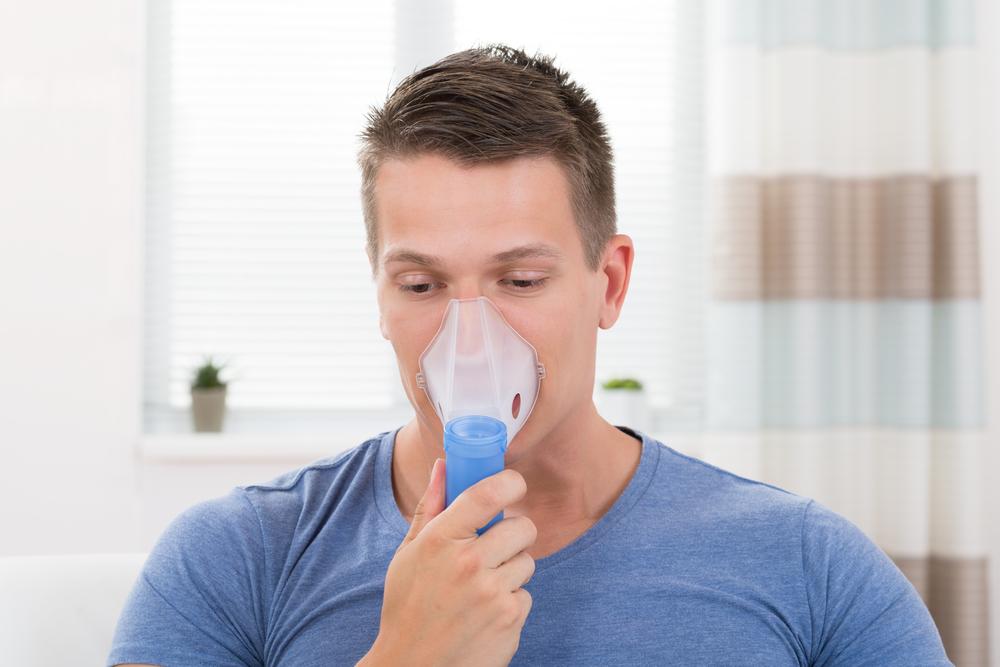
Oxygen Therapy
For patients experiencing low blood oxygen levels, supplemental oxygen via portable tanks or concentrators can enhance oxygen intake, improve energy levels, and prevent complications like pulmonary hypertension and heart strain. Proper oxygen management can significantly boost daily activity levels and overall well-being.
Vaccinations and Preventive Care
Immunizations against influenza, pneumonia, and COVID-19 are crucial in reducing respiratory infections, which can worsen COPD symptoms. Regular vaccination schedules help protect vulnerable lungs from infections, thereby decreasing hospitalization risks.
Other Pharmacological Treatments
Anticholinergic drugs not only relax airway muscles but also facilitate mucus clearance, easing breathing and preventing blockages. Antihistamines, generally used for allergy management, should be used cautiously in COPD patients as they can dry out mucus membranes. Antivirals may be prescribed during flu seasons to prevent or treat viral infections, which tend to be more severe in COPD patients.
Managing Treatment Costs
Effective COPD management can sometimes be costly due to ongoing medication, devices, and hospital visits. Securing proper insurance coverage or exploring assistance programs can help reduce financial burdens. Regular consultations and medication adherence are vital to prevent costly hospitalizations caused by unmanaged exacerbations. Developing a sustainable financial plan ensures consistent access to necessary treatments and improves long-term health outcomes.