Comprehensive Guide to Secondary Hyperhidrosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
Secondary hyperhidrosis involves widespread excessive sweating caused by underlying health conditions. This comprehensive guide explores its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, including medications, Botox, microwave therapy, and surgical procedures. Proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plans are crucial for effective management. If you experience persistent, generalized sweating, seeking medical advice can help address the root causes and significantly improve quality of life.
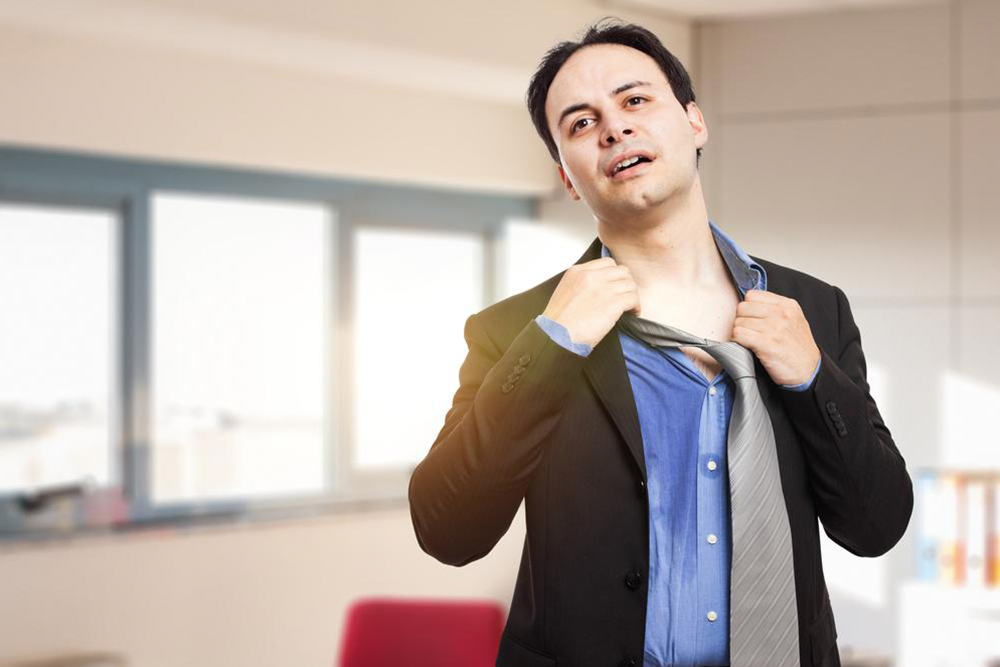

Secondary hyperhidrosis is a form of excessive sweating that differs significantly from primary hyperhidrosis, primarily because of its underlying causes. While primary hyperhidrosis usually manifests as localized sweating in specific areas such as the hands, feet, or armpits without any discernible medical condition, secondary hyperhidrosis is characterized by pervasive, excessive sweating across larger parts of the body or even the entire body. This condition typically occurs during alertness and activity, disrupting daily life and signaling potential other health issues.
Understanding the Root Causes of Secondary Hyperhidrosis
One of the most important aspects of managing secondary hyperhidrosis is understanding its causes. It can be a symptom arising from a variety of medical conditions or external factors. Various health issues and circumstances can lead to generalized excessive sweating, including but not limited to medication side effects, hormonal fluctuations, metabolic disorders, and neurological conditions.
Specifically, conditions such as hormonal changes brought on by pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid dysfunctions are common triggers. Obesity can place additional strain on the body’s temperature regulation, leading to increased sweating. Metabolic and endocrine disorders like diabetes and hyperthyroidism significantly affect the body’s energy and heat regulation systems, resulting in excessive sweating. Cardiovascular issues, Parkinson's disease, certain cancers like lymphoma, and gout also contribute to the development of secondary hyperhidrosis.
The diagnosis process involves a thorough medical history, physical examinations, and specific tests to identify the underlying cause. Blood tests measuring hormone levels, thyroid function, and blood sugar levels are often part of the evaluation. Sometimes, imaging studies and nerve tests are required to pinpoint neurological causes. Accurate diagnosis is critical to ensure that treatment addresses the root problem rather than just alleviating symptoms.
Recognizing Symptoms and When to Seek Medical Help
Patients experiencing persistent, widespread sweating that does not respond to typical antiperspirants should seek medical advice. Symptoms may include constant sweating during wakefulness, especially in situations where sweating is not prompted by heat or physical activity. Accompanying symptoms such as weight loss, fatigue, or other systemic signs should also prompt a healthcare consultation. Early diagnosis can prevent complications and improve the quality of life.
Effective Treatment Strategies for Secondary Hyperhidrosis
Treatment of secondary hyperhidrosis focuses on managing symptoms while addressing the underlying health conditions. It is essential to work closely with healthcare providers to develop an individualized treatment plan that might include a combination of therapies.
For mild cases, topical treatments like antiperspirants containing aluminum chloride are the first line of defense. These are often available over-the-counter but can be prescribed in stronger formulations for more persistent cases. These formulations work by blocking sweat ducts, reducing perspiration in localized areas.
In cases where topical treatments are insufficient, more advanced options are available. One of the most effective treatments involves the use of botulinum toxin (commonly known as Botox) injections. Botox works by temporarily blocking the nerve signals responsible for stimulating sweat glands. While initially used for localized hyperhidrosis, Botox has proven highly effective in treating secondary hyperhidrosis, especially in underarm regions. The effects typically last for over a year, providing significant relief for patients suffering from severe sweating episodes.
Beyond injections, other modern therapies such as microwave and laser treatments are gaining popularity. These procedures aim to destroy sweat glands in affected areas, reducing excessive sweating long-term. These minimally invasive techniques offer longer-lasting results and fewer risks compared to surgical options.
In more severe or refractory cases, surgical approaches such as thoracic sympathectomy may be considered. This procedure involves severing or disrupting the nerves that stimulate sweating in specific regions. While often effective, surgery carries potential risks such as compensatory sweating elsewhere on the body, nerve damage, or other complications, emphasizing the importance of careful patient selection and thorough consultation with a specialist.
Managing secondary hyperhidrosis also involves addressing the underlying condition. For example, controlling thyroid function, managing blood sugar levels, or treating neurological conditions can significantly reduce sweating episodes. Lifestyle modifications, including wearing breathable clothing, avoiding triggers like spicy foods or caffeine, and maintaining a healthy weight, are also beneficial components of a comprehensive management plan.
In conclusion, secondary hyperhidrosis is a complex condition often rooted in other health issues. Its management requires an integrated approach that combines symptomatic relief with underlying disease control. If you experience persistent or severe excessive sweating, consult a healthcare professional to determine the cause and explore the most suitable treatment options. Early intervention can vastly improve daily comfort and overall health.