Comprehensive Treatment Strategies for Advanced Prostate Cancer: Enhancing Quality of Life
This comprehensive article explores the latest treatment options for advanced prostate cancer, focusing on hormone therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and supportive measures for bone metastases. It emphasizes personalized care strategies designed to control disease progression, reduce symptoms, and improve the quality of life for patients. Updated insights into innovative therapies and supportive care highlight the importance of multidisciplinary approaches in managing this complex disease effectively.
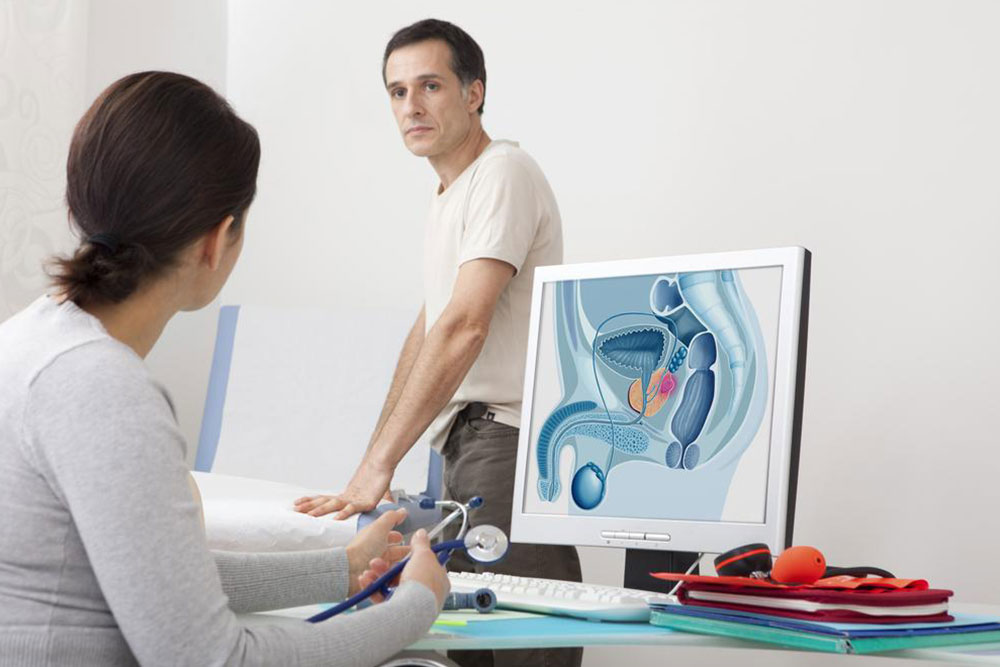
Effective and Innovative Approaches for Managing Advanced Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer, when it progresses to stage IV or metastasizes, presents significant challenges but can be managed effectively with a multidisciplinary approach. Although it remains incurable at this stage, advancements in treatment have enabled healthcare providers to control disease progression, alleviate symptoms, and significantly improve patients’ quality of life. Understanding the available treatment options—including hormone therapy, immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and supportive treatments for bone metastasis—is essential for patients and caregivers navigating this complex condition.
Hormone Therapy: The Cornerstone of Advanced Prostate Cancer Treatment
Hormone therapy plays a central role in managing advanced prostate cancer. This approach aims to reduce the levels of male hormones—primarily testosterone—that fuel the growth of prostate cancer cells. There are different methods of hormone suppression, including surgical and medical options. Orchiectomy, which involves the surgical removal of the testes, results in immediate reduction of testosterone production. Alternatively, medical castration uses medications such as luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) analogs, which inhibit the body's ability to produce testosterone. Often, hormone therapy is combined with anti-androgens—drugs that block the action of androgens on prostate cancer cells—to improve therapeutic outcomes. Hormone therapy can effectively slow tumor growth and control symptoms for many patients, often extending survival times significantly.
Chemotherapy: Targeting Cancer Cells Systemically
Chemotherapy involves the use of potent drugs that circulate throughout the body via the bloodstream to target and kill rapidly dividing cancer cells. In advanced prostate cancer, chemotherapy is typically administered when hormone therapy alone is insufficient or when the disease progresses despite hormone suppression. Traditional chemotherapy agents, such as docetaxel and cabazitaxel, have been used effectively to prolong survival and improve symptoms. However, chemotherapy can be associated with side effects including immune suppression, hair loss, fatigue, and gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea. Recent developments have focused on targeted therapies and novel drug combinations aiming to minimize these adverse effects while maintaining efficacy.
Immunotherapy: Boosting the Body’s Defense Against Cancer
Immunotherapy represents a revolutionary approach that harnesses the body's immune system to recognize and attack prostate cancer cells. This includes treatments such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies, cytokine therapies, and cancer vaccines. While immunotherapy has shown promise for certain cancers, its role in prostate cancer is an area of active research. Some patients with advanced disease have experienced benefits, especially when combined with other treatment modalities. Immunotherapy aims to stimulate the immune system to provide long-lasting protection against tumor recurrence, improving overall survival and quality of life.
Addressing Bone Metastasis: Managing Pain and Preventing Fractures
One of the most common complications of advanced prostate cancer is metastasis to the bones. Bone metastases can cause severe pain, increase fracture risk, and lead to hypercalcemia—a dangerous condition characterized by high calcium levels in the blood. To combat these issues, a combination of medications, radiation therapy, and supportive treatments are employed. Bisphosphonates and denosumab are drugs that inhibit bone resorption, helping to strengthen bones and reduce pain. Radiation therapy can target specific painful bone lesions to provide relief, improve mobility, and prevent fractures. Managing bone health is crucial for maintaining the patient's independence and quality of life in advanced disease.
Radiation Therapy: Localized Control of Tumors
Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-ray beams to target specific areas affected by tumor growth. In cases of bone metastases or locally advanced prostate cancer, radiation provides effective pain relief and helps control disease progression. It can be delivered externally or internally (brachytherapy) depending on the location and extent of the disease. Advances in precision radiation techniques, such as stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT), minimize damage to surrounding healthy tissue and increase treatment effectiveness. Combining radiation with systemic therapies often results in better symptom management and improved patient outcomes.
Overall, managing advanced prostate cancer requires a personalized approach that considers the patient’s overall health, disease extent, and response to previous treatments. Ongoing research continues to explore new therapies, including targeted agents and immunotherapies, to improve survival rates and quality of life. Supportive care—including pain management, nutritional support, and psychological counseling—is equally vital in comprehensive treatment plans. Collaborating with a multidisciplinary healthcare team ensures patients receive tailored interventions that address both the physical and emotional challenges posed by advanced prostate cancer.