Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Advanced Lung Cancer: A Complete Guide
This comprehensive guide explores effective management strategies for advanced lung cancer, emphasizing modern treatments like chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and radiation. It highlights the importance of personalized treatment plans, early detection, and supportive care to improve quality of life and increase survival rates for patients dealing with metastatic lung cancer. The article discusses risk factors, disease progression, and advances in medical science that continue to innovate patient care, offering hope in this challenging field.

Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Advanced Lung Cancer: A Complete Guide
Lung cancer remains one of the most formidable and challenging health issues worldwide, accounting for a significant percentage of cancer-related mortality. Its complexity is compounded when the disease progresses to advanced stages, where treatment options become more limited and survival rates decrease substantially. Understanding the nuances of managing advanced lung cancer is essential for patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers to improve quality of life and extend survival. This article explores in-depth the causes, risk factors, progression, and cutting-edge treatment strategies that form the backbone of managing advanced lung cancer effectively.
Despite advancements in medical sciences, lung cancer remains a leading cause of cancer deaths globally. The primary cause is smoking—both active and passive exposure—though other environmental and genetic factors also play crucial roles. Exposure to pollutants like air particulates, asbestos, and radon gas significantly increases risk. The disease typically originates in the lung tissue itself, often starting in a localized area before rapidly spreading to other parts of the body such as bones, brain, liver, and adrenal glands. As lung cancer progresses, treatment becomes more complex, shifting focus from curative intent to disease control, symptom management, and maintaining patient quality of life.
Effective management strategies involve a multifaceted approach tailored to individual patient conditions, tumor characteristics, and progression stage. Modern oncological treatments focus on controlling the tumor, preventing further metastasis, relieving symptoms, and improving overall survival rates. This comprehensive approach requires combining various treatment modalities and supportive care practices to optimize outcomes for patients battling advanced lung cancer.
Below, we delve deeper into main therapeutic options and emerging treatments that have revolutionized the approach to managing metastatic lung cancer:
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy remains a cornerstone of treatment for advanced lung cancer. It involves the use of potent drugs that target rapidly dividing cancer cells, aiming to reduce tumor size, slow progression, and eradicate microscopic disease that may not be visible through imaging. Standard chemotherapy regimens often include platinum-based agents such as cisplatin or carboplatin, combined with other drugs like pemetrexed, gemcitabine, or paclitaxel to enhance efficacy. Patients undergoing chemotherapy often experience side effects, including fatigue, hair loss (alopecia), nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and gastrointestinal disturbances. Despite these challenges, chemotherapy can significantly prolong survival and improve symptoms.
Immunotherapy
A breakthrough in cancer treatment, immunotherapy harnesses the patient's immune system to target and destroy cancer cells. Immune checkpoint inhibitors like pembrolizumab, nivolumab, and atezolizumab block proteins such as PD-1 and PD-L1 that cancer cells exploit to evade immune detection. This strategy has demonstrated promising results, leading to improved response rates and survival benefits, especially in tumors expressing high levels of PD-L1. However, individual responses vary, and some patients may experience immune-related adverse events, including inflammation of organs, skin rashes, and endocrine dysfunctions. Ongoing research aims to optimize patient selection and combination therapies.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy focuses on specific genetic mutations or molecular pathways involved in tumor growth. For example, drugs like osimertinib target EGFR mutations, while crizotinib addresses ALK rearrangements. These therapies are highly effective in carefully selected patient populations, often leading to significant tumor regression. They tend to have fewer side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy but require detailed genetic profiling for effective implementation. Combining targeted therapy with other treatment modalities can further improve outcomes and delay resistance development.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy employs high-energy radiation beams like X-rays or proton beams to target and kill cancer cells precisely. External beam radiation is commonly used for symptom relief, tumor control, or as a palliative measure to alleviate pain, bleeding, or neurological symptoms caused by metastases. Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) delivers high doses directly to tumor sites with minimal damage to surrounding tissues. Brachytherapy involves placing radioactive sources directly within or near the tumor, offering localized control. Advances in radiation technology enable better targeting, reduced side effects, and improved tumor stabilization.
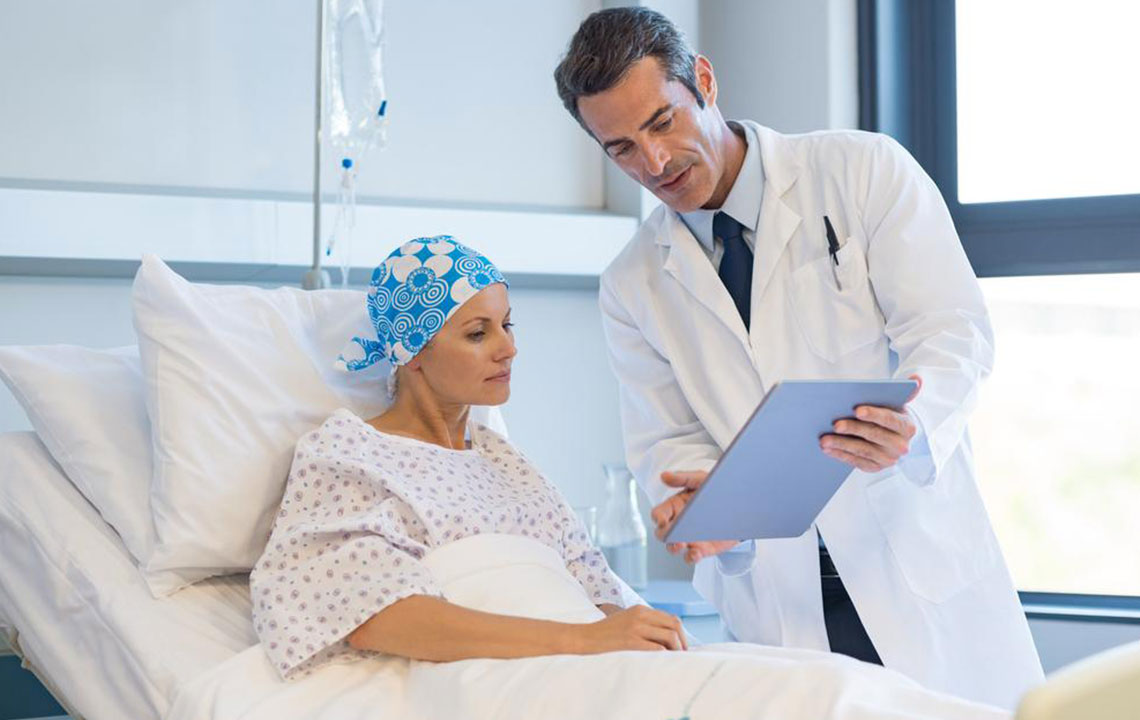
Palliative and Supportive Care
While curative options are limited in advanced stages, palliative care plays a crucial role in maintaining patient comfort, relieving pain, managing symptoms, and enhancing quality of life. Interventions may include pain management, respiratory support, nutritional assistance, and psychological counseling. Palliative care should be integrated early in the disease course to ensure holistic support and address the emotional, physical, and social challenges faced by patients and their families.
Recent advances in molecular biology, genomics, and immunology continue to drive innovation in lung cancer management. Clinical trials exploring novel drug combinations, personalized immunotherapies, and targeted anti-metastatic agents promise to expand the arsenal against this disease. Multidisciplinary teams involving oncologists, radiologists, nutritionists, and palliative care specialists are key to devising comprehensive, patient-centered treatment plans. The goal remains clear: to improve survival, prolong quality of life, and provide dignity and comfort to those facing advanced lung cancer.
This extensive exploration underscores the vital importance of early detection, personalized medicine, and the integration of emerging therapies to combat the relentless progression of advanced lung cancer and improve patient outcomes.