Comprehensive Dietary Strategies for Effective Gout Management
This comprehensive guide offers effective dietary strategies to manage gout, focusing on reducing uric acid levels and preventing flare-ups. It outlines foods to avoid, hydration tips, beneficial fruits, vegetables, dairy, and moderate coffee intake. Emphasizing the importance of long-term lifestyle changes, this article provides practical advice for those dealing with gout to control symptoms naturally. Consulting healthcare professionals for personalized plans is recommended, making it a valuable resource for understanding and managing gout through diet.

Comprehensive Dietary Strategies for Effective Gout Management
Understanding Gout and Its Impact on Health
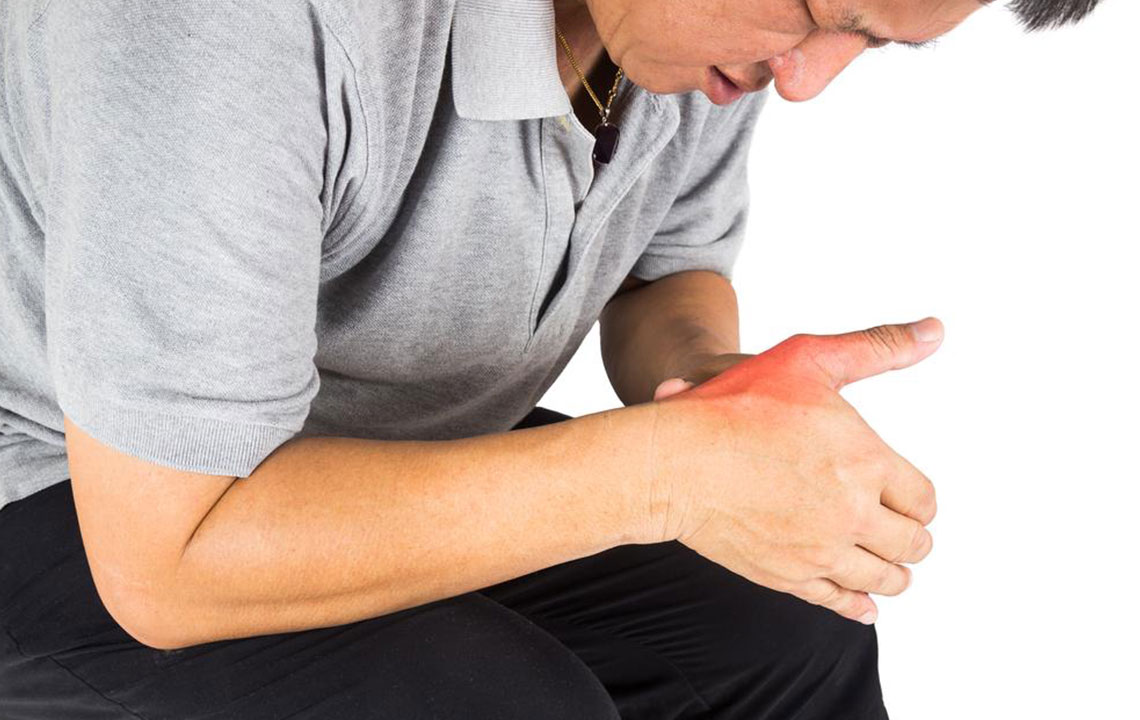
Gout is a complex form of inflammatory arthritis that arises due to elevated levels of uric acid in the bloodstream, a condition known as hyperuricemia. When uric acid accumulates excessively, it can crystallize and deposit around joints, triggering severe bouts of pain, swelling, and redness. These episodes can be sudden and debilitating, often forcing individuals to seek urgent medical attention. Managing gout effectively requires a detailed understanding of its underlying causes, risk factors, and the role of diet and lifestyle modifications in controlling uric acid levels. A combination of medical treatment and dietary adjustments can significantly improve quality of life for those affected.
Implementing an anti-gout diet is crucial in reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups. While medication can help manage symptoms and underlying causes, dietary changes are essential in controlling uric acid levels naturally. It’s recommended to work closely with a healthcare provider to craft a personalized plan. Once approved, integrating specific dietary habits into daily routines can make a substantial difference in managing uric acid buildup and preventing future attacks.
Foods That Should Be Limited or Avoided
The foundation of a gout-friendly diet involves reducing intake of foods rich in purines, which break down into uric acid. High-purine foods include red meats such as beef and lamb, organ meats like liver and kidneys, and sea creatures like shellfish and sardines. Certain vegetables, although generally healthy, such as spinach, mushrooms, peas, asparagus, and cauliflower, also contain higher purine levels that may contribute to increased uric acid, especially in sensitive individuals. Sugary foods and beverages, including sodas, processed fruit juices, candies, and baked goods with refined sugar, can induce insulin resistance and promote uric acid synthesis. Alcohol, particularly beer and spirits, dramatically raises uric acid levels and should be minimized or avoided altogether. Fast food and processed meals often contain unhealthy fats, salt, and additives that can exacerbate inflammation and should be replaced with home-cooked, nutrient-rich options.
Prioritize Hydration
Proper hydration is one of the simplest yet most effective strategies for managing gout. Drinking sufficient water aids in diluting uric acid in the bloodstream and promotes kidney excretion, thereby reducing the risk of crystal formation. Health experts recommend consuming at least eight glasses (approximately 2 liters) of water each day, with more intake during hot weather or physical activity. Adequate hydration supports overall kidney health and helps prevent the dehydration that can trigger gout attacks.
Cherries and Their Role in Gout Prevention
Cherries have gained popularity as a natural remedy for gout inflammation. Rich in antioxidants like anthocyanins, cherries and cherry juice can inhibit uric acid production and reduce inflammatory responses. Incorporating fresh or organic cherry products into your diet may help lessen the frequency and severity of gout attacks. While cherries should not replace medical treatment, they can be a beneficial complement when combined with other dietary measures.
Incorporate Low-fat Dairy Products
Low-fat dairy items, including skimmed milk, yogurt, and cheese, provide essential proteins without contributing to uric acid increase. Research indicates that consuming low-fat dairy can help lower serum uric acid levels and decrease the risk of gout. These foods are also rich in calcium and vitamin D, supporting bone health and overall wellness. Including these options regularly in your diet can be a prudent step toward managing gout more effectively.
Choose Appropriate Carbohydrates and Vegetables
Carbohydrate sources such as oats, brown rice, quinoa, sweet potatoes, and whole wheat bread supply energy without the excessive purine content found in some grains. Vegetables like broccoli, Brussels sprouts, kale, and lima beans are low in purines and beneficial for overall health. Incorporating these into your meals provides essential nutrients and fiber, promoting a healthy digestive system and reducing inflammation.
Adding Fruits to Your Diet
Fruits such as strawberries, oranges, bananas, pineapples, mangoes, and watermelons are packed with vitamins, antioxidants, and fiber. They aid in detoxification, support immune health, and help regulate uric acid levels. A colorful fruit-rich diet can boost overall well-being and may lessen gout symptoms when combined with other lifestyle changes.
Moderate Coffee Consumption
Coffee contains chlorogenic acid, an antioxidant linked to reduced risk of gout flare-ups. Moderate intake of unsweetened coffee can be beneficial for individuals managing gout, as it may lower uric acid levels and improve metabolic health. As with all dietary modifications, consult your healthcare provider to determine the appropriateness of coffee in your diet, especially if you have other health conditions or are sensitive to caffeine.
Developing a long-term, sustainable dietary habit focusing on anti-gout principles is essential for effective management. Lifestyle modifications should be viewed as part of an integrated approach including medication, physical activity, and stress management. Early intervention, coupled with consistent dietary and medical strategies, can significantly reduce joint and kidney complications caused by gout, dramatically improving the patient's quality of life.