Comprehensive Approaches to Managing Gout Effectively: Combining Medical and Natural Remedies
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for managing gout through a combination of medical treatments and natural remedies. It covers medication options, lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and home care tips to help prevent future attacks, reduce inflammation, and protect joint health. Designed for individuals seeking long-term relief, this article emphasizes the importance of professional guidance and holistic approaches for successful gout management, ensuring improved quality of life and minimized complications.
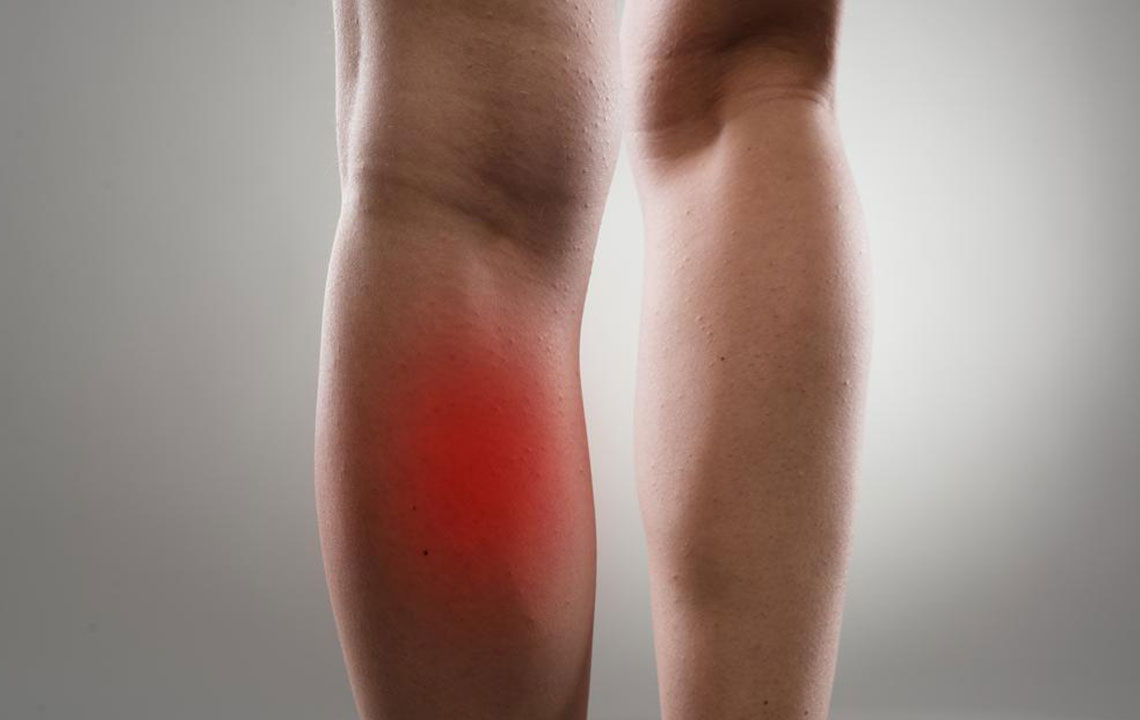
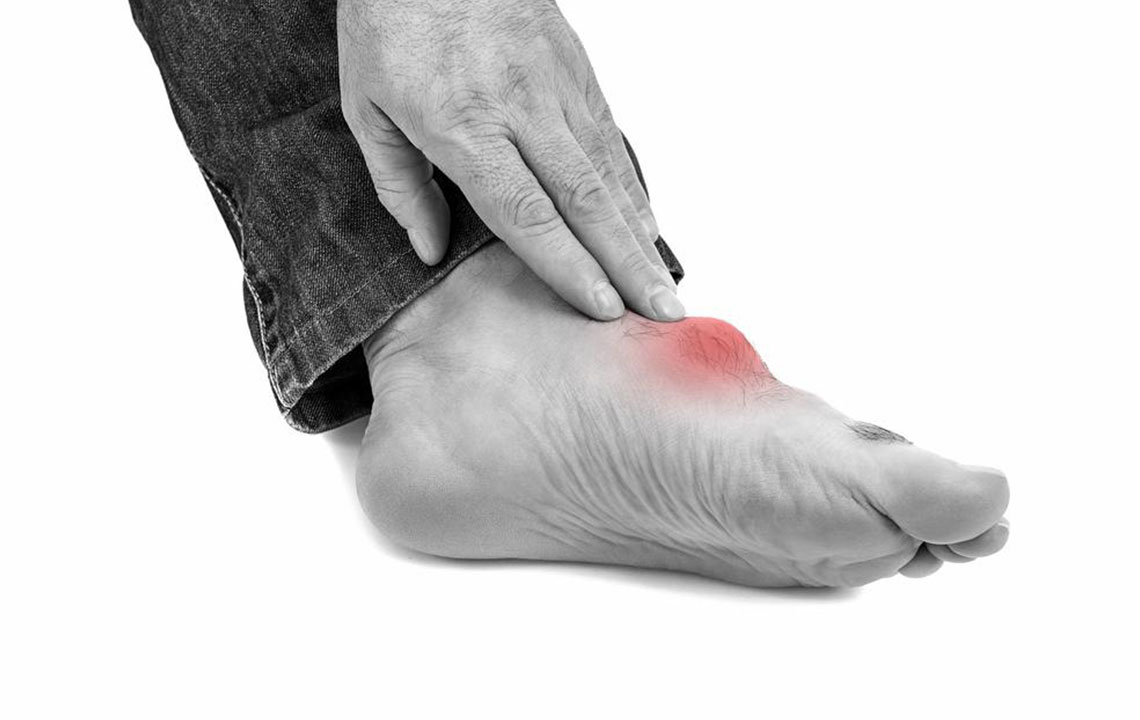
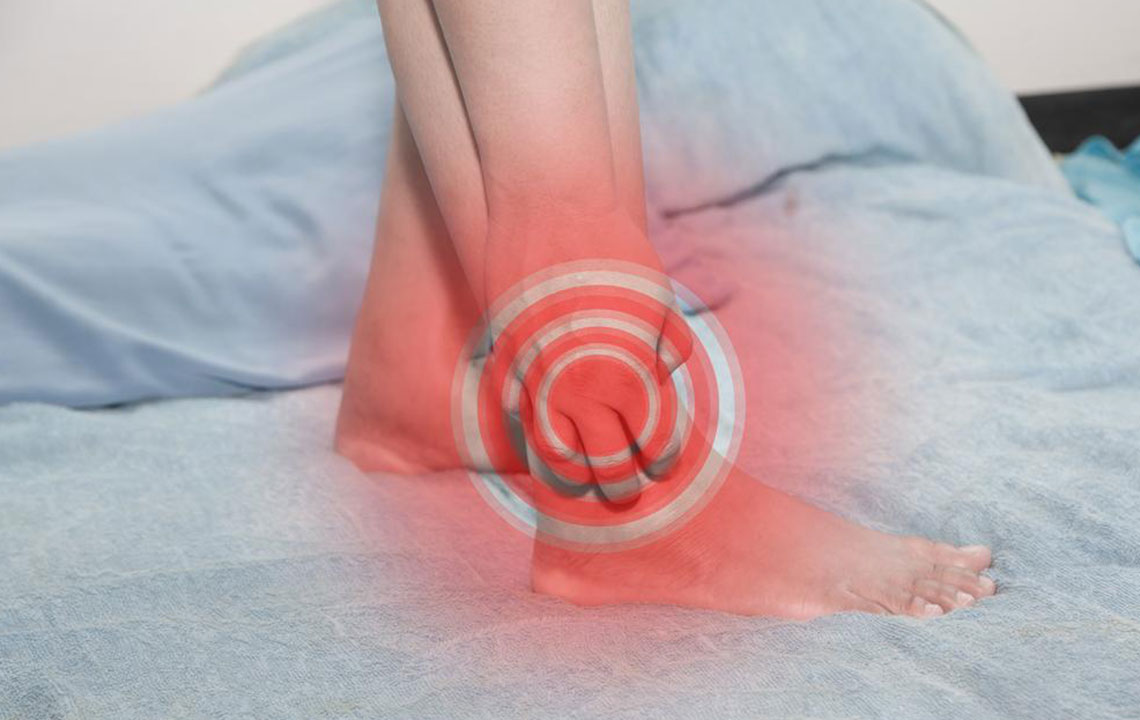
Gout stands out as one of the most common types of arthritis globally, primarily caused by high levels of uric acid in the bloodstream. This condition leads to the formation of sharp uric acid crystals that settle into joints, often targeting areas like the big toe, knees, fingers, and wrists. These crystal deposits trigger intense pain, inflammation, redness, and swelling, significantly impairing daily activities and overall quality of life.
Understanding gout's underlying causes is crucial for effective management. Uric acid is a waste product resulting from the natural breakdown of purines found in many foods. When the body produces too much uric acid or fails to excrete enough through the kidneys, it results in hyperuricemia—an excess of uric acid in the blood, which can lead to gout attacks.
Left untreated, gout can lead to devastating joint damage, chronic arthritis, and complications such as kidney stones or renal dysfunction. Therefore, prompt medical intervention combined with lifestyle and dietary adjustments becomes essential in managing this condition effectively.
Medical Treatments for Gout
The primary goal of medical treatment for gout is to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation during acute attacks while also controlling uric acid levels for long-term prevention. Healthcare providers typically prescribe a combination of medications tailored to individual patient needs.
Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen, naproxen, or indomethacin are often the first line of defense during gout flares. These medications help reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation rapidly. It is vital to take NSAIDs under medical supervision, as they can have side effects, especially with prolonged use.
Corticosteroids
For severe cases or when NSAIDs are contraindicated, corticosteroids such as prednisone may be administered orally or via injections directly into the affected joints. Corticosteroids are highly effective at controlling intense inflammation and alleviating pain in acute episodes.
Colchicine
Colchicine is another medication specifically used for gout attacks. It works by reducing the inflammatory response triggered by uric acid crystals. While effective, colchicine can have adverse effects like gastrointestinal upset, hence it requires careful dosing and monitoring.
Long-term Management and Preventive Strategies
Beyond symptom relief during attacks, controlling uric acid levels is essential to prevent future gout episodes and joint damage. Long-term strategies often involve urate-lowering therapies that reduce serum uric acid concentrations.
Urate-Lowering Medications
Drugs such as allopurinol, febuxostat, and probenecid are prescribed to patients with frequent or severe gout attacks. These medications work by inhibiting uric acid production or enhancing renal uric acid excretion, effectively maintaining uric acid within safe limits.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medication, lifestyle and dietary modifications play a pivotal role in managing gout. Patients are encouraged to adopt low-purine diets, avoid alcohol—especially beer and spirits—and stay well-hydrated to facilitate uric acid excretion.
Natural Remedies and Home Care Tips for Gout Relief
Complementing medical treatment with natural remedies can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall comfort. While these remedies do not replace prescribed medication, they can be effective adjuncts in managing gout episodes.
Dietary Adjustments and Herbal Remedies
**Garlic:** Rich in sulfur compounds, garlic has anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce joint pain. Incorporating raw garlic into meals or taking garlic supplements can be beneficial.
**Ginger:** Known for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, ginger can be consumed as fresh root, tea, or supplements to help ease gout symptoms.
**Turmeric:** Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, possesses anti-inflammatory qualities. Adding turmeric to food or taking supplements can support joint health.
**Apple Cider Vinegar:** Believed to alkalize the body, apple cider vinegar may assist in lowering uric acid levels. Diluting one to two tablespoons in a glass of water and drinking daily is a common practice.
Home Remedies for Symptom Relief
**Ice Therapy:** Applying ice packs to inflamed joints for 15-20 minutes can help reduce swelling and numb pain.
**Soaking in Apple Cider Vinegar Water:** Immersing affected joints in warm water mixed with apple cider vinegar may provide relief from discomfort.
**Herbal Teas:** Drinking ginger or turmeric tea not only hydrates but also offers anti-inflammatory benefits.
Consultation and Personalized Medical Advice
Effective management of gout requires a collaborative approach involving healthcare professionals. Regular check-ups, blood tests to monitor uric acid levels, and personalized treatment plans are vital for managing this complex condition. Patients should seek advice before starting any herbal supplements or home remedies to ensure safety and suitability.
In summary, managing gout effectively involves a combination of prescribed medications, dietary and lifestyle changes, and natural remedies. Early intervention and consistent management can significantly reduce pain, prevent joint damage, and improve overall quality of life for those affected by gout.