Comprehensive Guide to Xarelto Side Effects and Safety Precautions
This comprehensive guide delves into Xarelto’s potential side effects, including common and rare adverse reactions. It emphasizes the importance of vigilance, early symptom recognition, and collaboration with healthcare providers to ensure safe anticoagulant therapy. The article also explores DVT and the role of Xarelto in prevention and treatment, providing valuable insights for patients and clinicians alike.

In-Depth Insights into Xarelto Adverse Reactions and Safety Considerations
Xarelto is widely prescribed for the prevention and treatment of blood clots, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism. Like all anticoagulant medications, it carries potential side effects that patients should be aware of. This comprehensive guide provides detailed information on the possible adverse effects associated with Xarelto, helping users understand the risks, recognize early warning signs, and manage their health effectively.
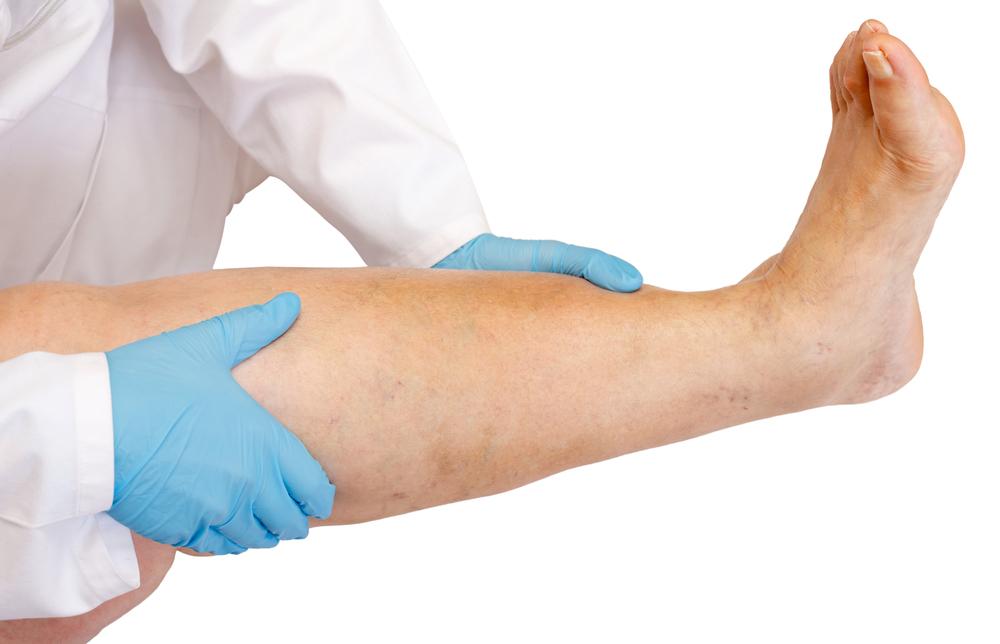
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition characterized by the formation of blood clots in the deep veins, most commonly in the legs. If left untreated, these clots can migrate to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism, which can be life-threatening. Recognizing the symptoms of DVT and understanding the treatment options, including medications like Xarelto, are crucial for effective management and prevention of complications.
Clinically, DVT often presents with symptoms such as swelling, tenderness, redness, warmth, and pain in the affected leg. Some patients might experience no symptoms at all, making it essential to undergo regular medical examinations if risk factors are present. If untreated, DVT can lead to parts of the clot breaking off and traveling to the lungs, resulting in pulmonary embolism, which manifests with chest pain, shortness of breath, fainting, and sometimes rapid heartbeat. Typically, DVT affects one leg, with pain often increasing when flexing the foot toward the knee.
The exact causes of DVT are not always clear. However, several risk factors are associated with increased likelihood of developing blood clots:
Prolonged periods of immobility—such as after surgery, lengthy travel, or bed rest—can slow blood flow and promote clot formation. Underlying medical conditions also contribute, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, blood disorders like clotting abnormalities, infections, and pulmonary or lung diseases. Lifestyle factors, such as smoking and obesity, further amplify risk, making preventative measures and vigilant monitoring important.
Standard medical treatments for DVT primarily include anticoagulant therapies like heparin and warfarin. Complementary approaches involve elevating the affected limb, using compression stockings, engaging in appropriate exercises, and in some cases, inserting filters into the vena cava to trap emerging clots. According to guidelines from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), rivaroxaban (marketed as Xarelto) offers an effective alternative for managing DVT and preventing recurrent clots.
Xarelto functions by selectively inhibiting Factor Xa, a key component in the clotting cascade, thereby reducing the formation of new blood clots and preventing existing clots from enlarging. Treatment regimens typically involve a daily dosage over three months, but duration may vary based on individual patient factors. Although Xarelto is highly effective, like all blood thinning medications, it can cause side effects. It is crucial for patients to be informed about these potential reactions to manage their treatment safely.
Common Side Effects Associated with Xarelto
Bleeding complications are among the most prominent adverse effects associated with Xarelto, given its blood-thinning properties. Patients might experience bleeding in different parts of their body, which ranges from minor to severe. Other frequent side effects include:
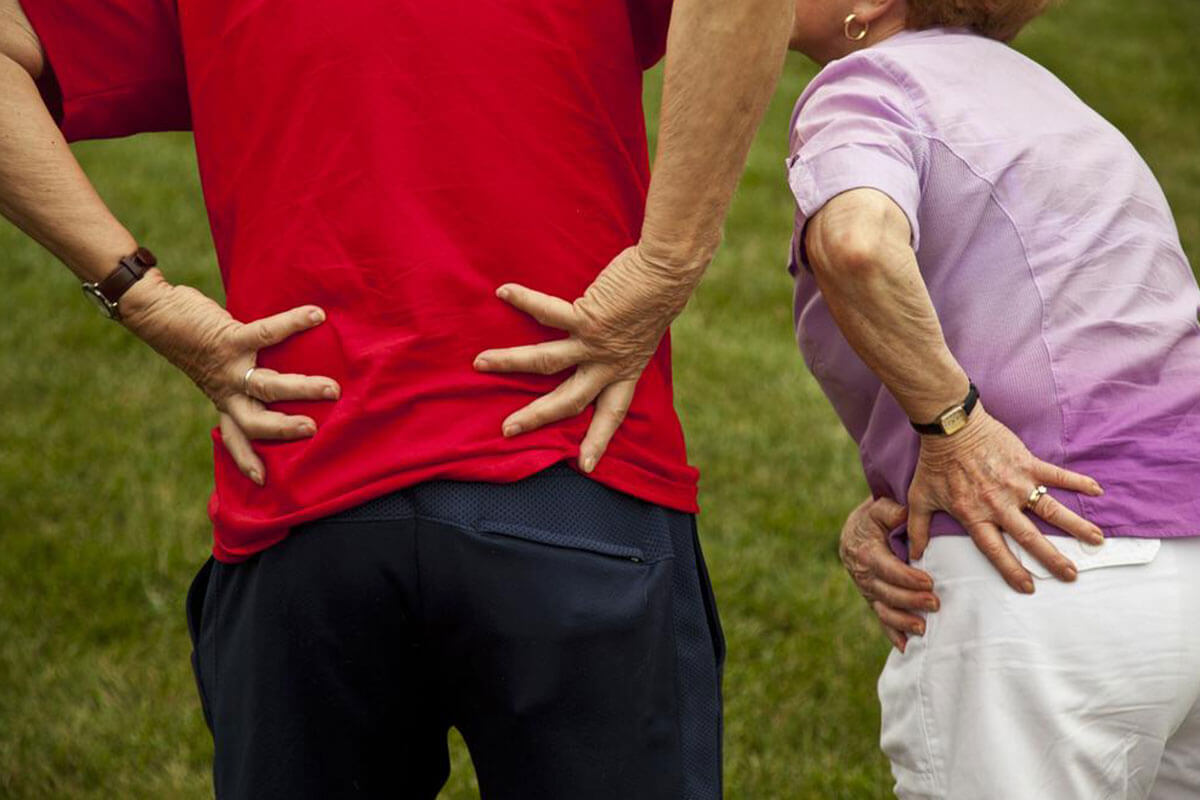
Back pain
Dizziness or feelings of faintness
Elevated liver enzymes indicating potential liver stress
Indigestion or gastrointestinal discomfort
Itching or skin irritation
General stomach upset
Toothache
Urinary tract infections
Joint inflammation or discomfort
Muscle cramps and weakness
Nasal congestion or runny nose
Fatigue or general tiredness
Less Common but Serious Side Effects
While most side effects are mild, some individuals may experience infrequent yet potentially severe reactions. These serious adverse effects require immediate medical attention and include:
Thrombocytopenia (low blood platelet count), increasing bleeding risk
Abdominal bleeding, which may manifest as severe pain or bruising
Intracranial hemorrhage, leading to neurological symptoms
Allergic reactions such as hives, swelling, and difficulty breathing
Hepatitis and liver inflammation
Spinal hematomas, which can cause nerve compression and pain
Strokes or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) in some cases
Severe allergic reactions, including Steven-Johnson Syndrome
Heavy, prolonged menstrual bleeding
Leukopenia or decreased granulocyte levels, weakening immune response
Blood pooling under the skull, leading to dangerous intracranial pressure
If you experience any of these severe side effects while on Xarelto, it is imperative to seek emergency medical care promptly. Some side effects may diminish over time, but persistent or worsening symptoms should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional. It is critical not to stop taking the medication abruptly without consulting your doctor, as this can increase the risk of clot formation and other complications.
Understanding the scope of possible side effects allows patients and healthcare providers to work together to ensure safe and effective treatment. Regular monitoring and communication with your healthcare team are key to minimizing risks associated with Xarelto therapy. If adverse reactions occur, alternative anticoagulants or treatments can often be considered to maintain effective blood clot management tailored to individual health needs.