Comprehensive Guide to Blood Cancer: Types, Symptoms, and Modern Treatment Strategies
Blood cancer is a complex disease that disrupts normal blood cell functions, impacting immune health and organ systems. This comprehensive guide covers its types, symptoms, and modern treatment options, emphasizing the importance of early detection and advanced therapies like stem cell transplants, chemotherapy, and radiation. Understanding blood cancer helps patients and caregivers better navigate diagnosis, treatment, and management strategies, providing hope for improved outcomes and quality of life.

Understanding Blood Cancer: Types, Symptoms, and Cutting-Edge Treatment Options
An In-Depth Overview of Blood Cancer and Its Impact on Human Health
Blood is an essential component of the human body, responsible for transporting oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and removing metabolic waste. It also plays a crucial role in immune defense. When abnormal cells proliferate uncontrollably within blood and related tissues, blood cancer develops, disrupting these vital functions. This disease primarily affects the blood itself, the bone marrow—where blood cells are produced—and the lymphatic system, which is integral to immune response. The abnormal growth of cancerous cells within blood fluids or tissues results in tumors and impairs the production of healthy blood components, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These disruptions lead to a range of severe health issues, including immune deficiency, anemia, bleeding problems, and increased susceptibility to infections.
Defining Blood Cancer: What It Is and How It Affects the Body
Blood cancer fundamentally alters the normal activity and lifecycle of blood cells, impairing their ability to perform key functions.
This disease hampers the body's capacity to fight infections, carry oxygen, and prevent bleeding, due to the abnormal growth and accumulation of malignant cells.
Malignant tumors develop within the circulatory system, often originating in the bone marrow or lymphatic tissues.
Blood cancer also impacts the lymph nodes, spleen, and other organs involved in blood cell production and immune function, leading to widespread health complications.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Blood Cancer
Frequent episodes of fever accompanied by chills that persist over time
Ongoing weakness and chronic fatigue that do not improve with rest
Swollen or enlarged lymph nodes, particularly in areas such as the neck, armpits, and groin
Persistent bone and joint pain affecting mobility and comfort
Severe and recurring headaches
Nausea, vomiting, and a notable decrease in appetite
Unintentional weight loss over a short period
Night sweats that drench clothing and bedsheets
Abdominal discomfort and swelling
Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
Skin rashes, persistent itching, and recurrent infections, indicating immune suppression
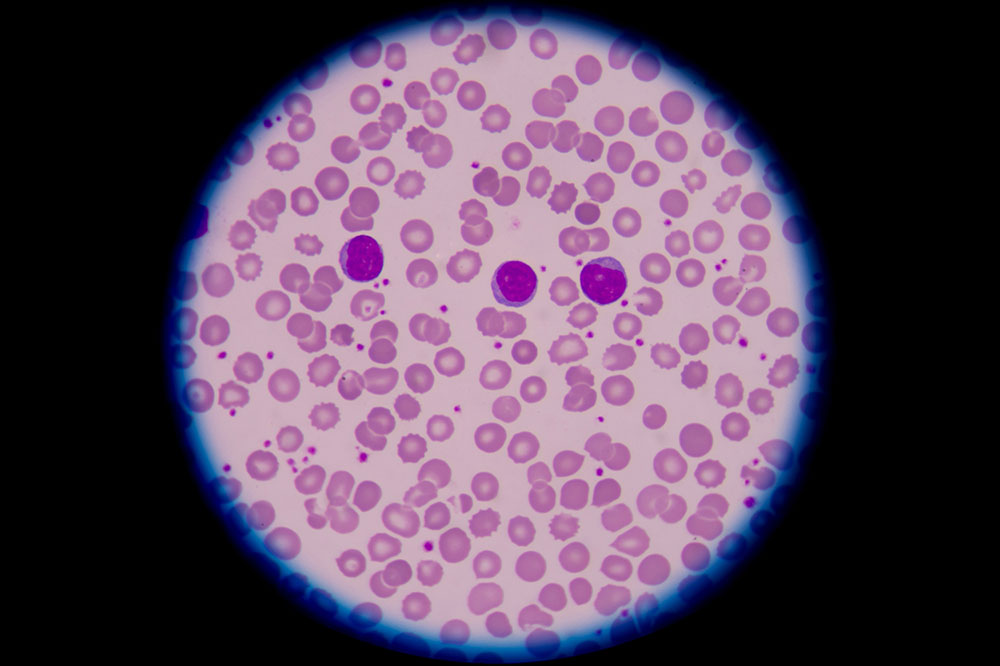
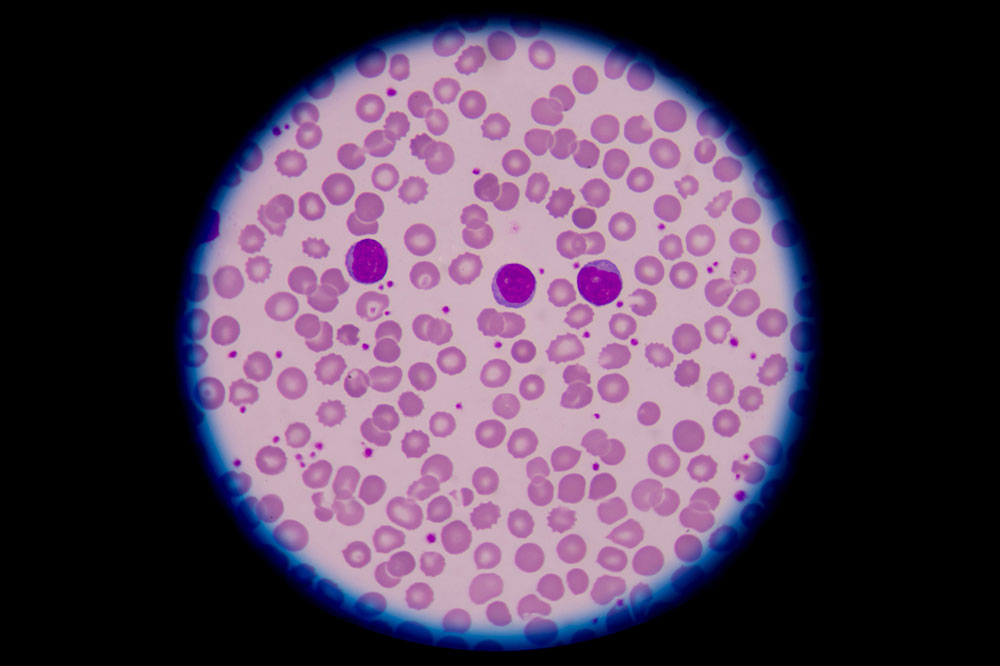
Various Types of Blood Cancer and Their Characteristics
Leukemia
Anemia
Lymphoma
Multiple Myeloma
Detailed Insights into Leukemia
Leukemia is characterized by the uncontrolled proliferation of abnormal white blood cells in the bone marrow and blood
These abnormal cells lose their ability to fight infections, leading to increased susceptibility to illnesses
Symptoms commonly include persistent high fever, fatigue, bleeding tendencies, and frequent infections
Anemia Explained
A condition marked by inadequate red blood cell production, resulting in insufficient oxygen delivery throughout the body
It often causes dizziness, pallor, chest pain, weakness, and shortness of breath
Can lead to excessive monthly bleeding in women and visible red spots caused by broken blood vessels
Weak blood cells compromise the immune system, leading to recurrent infections and spleen and lymph node swelling
Night sweats and fever are common accompanying symptoms
Bone marrow cancer, a type of blood malignancy, can cause severe bone pain and compromised bone integrity in advanced stages
Understanding Lymphoma and Its Symptoms
Lymphoma involves malignant changes in lymphocytes, key immune cells responsible for defending against pathogens
Malignant growth of lymphocytes causes swelling of lymph nodes, which are typically painless but can become large and painful
Primary signs include swollen lymph nodes in the neck, underarms, and groin, which may lead to obstruction of breathing or pain
Additional symptoms include persistent fatigue, unexplained weight loss, and itchy skin sensations
Multiple Myeloma: A Deep Dive
Originates in plasma cells within the bone marrow, affecting their ability to produce antibodies
This abnormal proliferation results in toxins that damage internal organs such as kidneys, liver, and heart
Features include persistent bone pain, fractures, and weakening of bones, leading to mobility issues
Modern Treatment Modalities for Blood Cancer
Radiation therapy: Utilized to target and destroy localized cancer cells, providing symptom relief and tumor size reduction
Stem cell transplants: Aims to replace diseased or damaged blood-forming cells with healthy stem cells, generally sourced from bone marrow or peripheral blood, to restore normal blood cell production
Chemotherapy: Employs potent drugs designed to kill or inhibit the growth of cancerous cells, often combined with other therapies for enhanced effectiveness
Advances in immunotherapy and targeted treatments are also shaping the future of blood cancer management, offering hope for more personalized and effective disease control.