The Critical Role of Dietary Fiber in Promoting Digestive Wellness and Preventing Constipation
Dietary fiber is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system, preventing constipation, and supporting gut health. This comprehensive guide explains the types of fiber, how they benefit digestion, and practical tips for increasing fiber intake. Adequate hydration is emphasized to maximize benefits and avoid side effects. Incorporating a variety of fiber-rich foods into your diet can promote long-term gastrointestinal health and reduce the risk of digestive disorders. This article offers valuable insights for anyone looking to improve their gut health naturally.

Understanding the Significance of Dietary Fiber for a Healthy Digestive System
Maintaining a healthy digestive system is fundamental to overall well-being, and an essential component of digestive health is dietary fiber. Many individuals wonder whether increasing fiber intake can effectively prevent constipation and improve gut health or if these claims are overhyped. This comprehensive guide explores how dietary fiber influences digestion, alleviates common gastrointestinal issues, and promotes long-term gut health.
What Exactly Is Dietary Fiber?
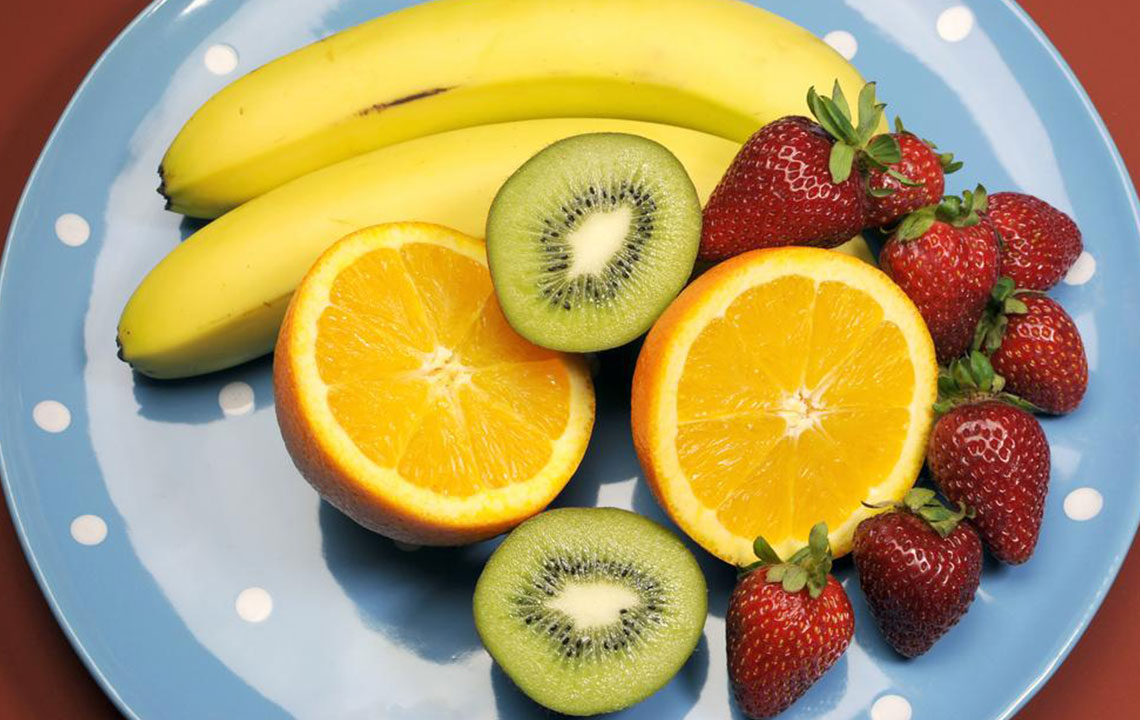
Dietary fiber refers to the indigestible parts of plant foods that pass through the gastrointestinal tract largely intact. Derived primarily from fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, and legumes, fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining normal bowel function. Unlike other nutrients, fiber isn't absorbed into the bloodstream; instead, it acts as a bulk-forming agent and aids in facilitating smooth digestion.
There are two primary types of dietary fiber:
Soluble Fiber: This type dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance. Foods rich in soluble fiber include oats, barley, fruits like apples and berries, and vegetables such as carrots. Soluble fiber helps lower cholesterol levels and stabilize blood sugar, in addition to supportingHealthy digestion.
Insoluble Fiber: This type doesn't dissolve in water and adds bulk to stool, promoting its passage through the digestive tract. Sources include wheat bran, nuts, seeds, and vegetables like cauliflower and potatoes. Insoluble fiber is especially beneficial in preventing constipation and maintaining regular bowel movements.
How Does Dietary Fiber Support Gut Health?
Incorporating adequate amounts of fiber into your daily diet offers a multitude of benefits for gut health, especially in alleviating and preventing severe constipation. Let's delve into the specific ways fiber bolsters digestive wellness:
Enhances Stool Bulk and Facilitates Regular Bowel Movements: Fiber increases the volume of stool by absorbing water, making it softer and easier to pass. This process reduces the effort required during defecation and supports consistent bowel habits.
Supports Gut Microbiota and Produces Short-Chain Fatty Acids: Fermentation of soluble fiber by beneficial gut bacteria generates short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which nourish colon cells and promote overall colon health. These SCFAs also play a role in reducing inflammation and may decrease the risk of colorectal diseases.
Reduces Risk of Gastrointestinal Disorders: A diet high in fiber helps maintain the integrity of the gastrointestinal lining and prevents the development of disorders like hemorrhoids, diverticulitis, and inflammatory bowel disease. Additionally, fiber may reduce the chances of developing colon cancer, which has been linked to chronic constipation and poor gut health.
Fiber's contribution to gastrointestinal integrity extends beyond stool regularity. It supports the healthy functioning of the entire digestive system, promotes satiety, and can assist in weight management, indirectly benefiting digestive health.
Is Excessive Fiber Intake Detrimental?
While fiber offers numerous health benefits, overconsumption can lead to undesirable side effects such as bloating, cramps, gas, and even diarrhea. To maximize the benefits of dietary fiber, sufficient hydration is essential. Drinking plenty of water helps fiber do its job effectively, softening stool and preventing constipation. It’s always recommended to increase fiber intake gradually, allowing your body to adapt without causing discomfort.
Practical Recommendations for Incorporating Fiber into Your Diet
To enjoy the full benefits of dietary fiber, aim for a balanced intake tailored to your age, gender, and activity levels. Incorporate a variety of fiber-rich foods, such as oats, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, beans, nuts, and seeds, into your daily meals. Remember to drink ample water throughout the day to support digestion. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can guide you in creating an optimal fiber plan suited to your individual needs.
Bottom Line
In summary, dietary fiber is a vital nutrient that plays a fundamental role in maintaining digestive health, preventing constipation, and supporting overall gastrointestinal function. While it’s not a miracle solution, a nutritious, fiber-rich diet combined with adequate hydration can significantly improve gut health and reduce the risk of related diseases. Understanding the different types of fiber and their benefits empowers you to make informed dietary choices that promote long-term digestive wellness.