Comprehensive Nutritional Strategies for Managing Crohn's Disease Symptoms Effectively
This comprehensive guide offers practical nutritional strategies for managing Crohn's disease symptoms. It emphasizes the importance of choosing easily digestible foods like refined grains, oatmeal, low-fiber fruits, cooked vegetables, and probiotic-rich dairy. Proper dietary care can alleviate flare-ups, reduce discomfort, and support overall health. Expert tips and food choices are highlighted to help individuals maintain balanced nutrition while managing this chronic digestive condition effectively.

Key Dietary Practices to Support Crohn's Disease Management
Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, leading to a range of uncomfortable and disruptive symptoms such as persistent fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, bloating, and frequent episodes of diarrhea. These symptoms can significantly diminish a person's quality of life, interfere with daily activities, and complicate overall health. While medical treatments are essential, dietary modifications play a crucial role in managing flare-ups and minimizing symptom severity. Making informed food choices can help soothe the inflamed gut, reduce the frequency of flare-ups, and promote better nutritional status.
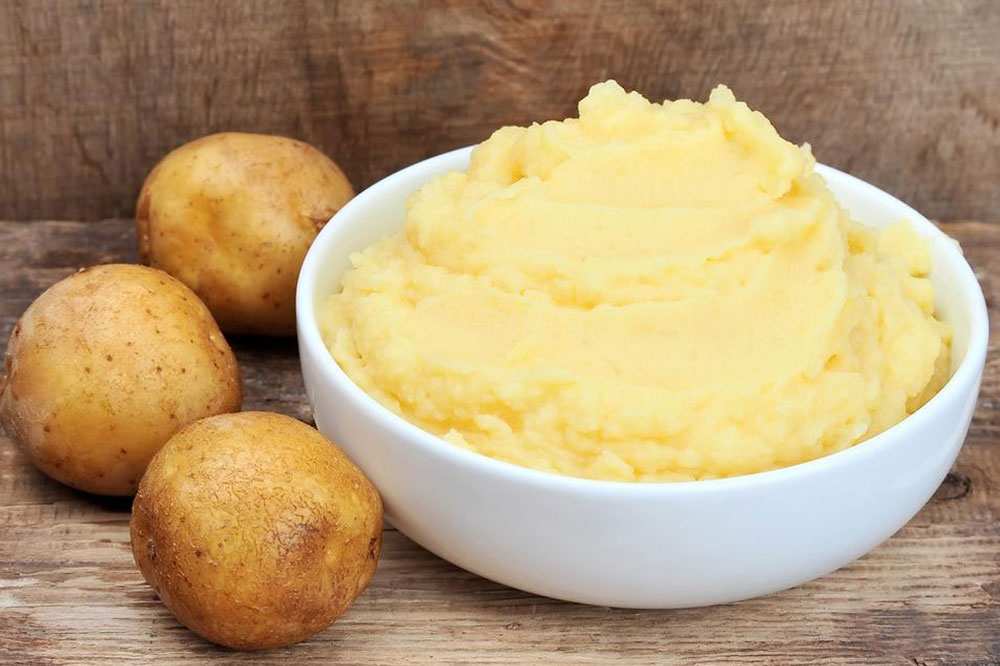
Choosing the Right Carbohydrates: Emphasizing Refined Grains
During flare-ups, it's important to select easily digestible carbohydrates that are gentle on the digestive system. Refined grains such as pasta, white rice, bread, and crackers are often recommended because they contain less fiber, which means they are less likely to irritate the gut. These foods pass more quickly through the digestive system, helping to reduce inflammation and discomfort. Including these in your diet can contribute to better nutrient absorption and less gastrointestinal stress.
Examples of suitable refined grain products include rice snacks, waffles, pancakes made with refined flour, white bread, and cereals fortified with essential vitamins and minerals. Incorporating these foods can help maintain energy levels and support overall health during periods of gastrointestinal flare-ups.
Incorporating Oatmeal for Gentle Nutrition
Oatmeal, made from rolled or quick oats, is a versatile and gentle food option suitable for those managing Crohn’s disease symptoms. It contains soluble fiber, especially beta-glucan, which helps solidify stool, reduces diarrhea, and absorbs excess water in the intestines. These properties can help soothe an inflamed gut and promote regular bowel movements.
To maximize benefits, try adding oats to smoothies with peeled, low-fiber fruits such as bananas or melons. This can make oatmeal easier to digest while still providing essential nutrients.
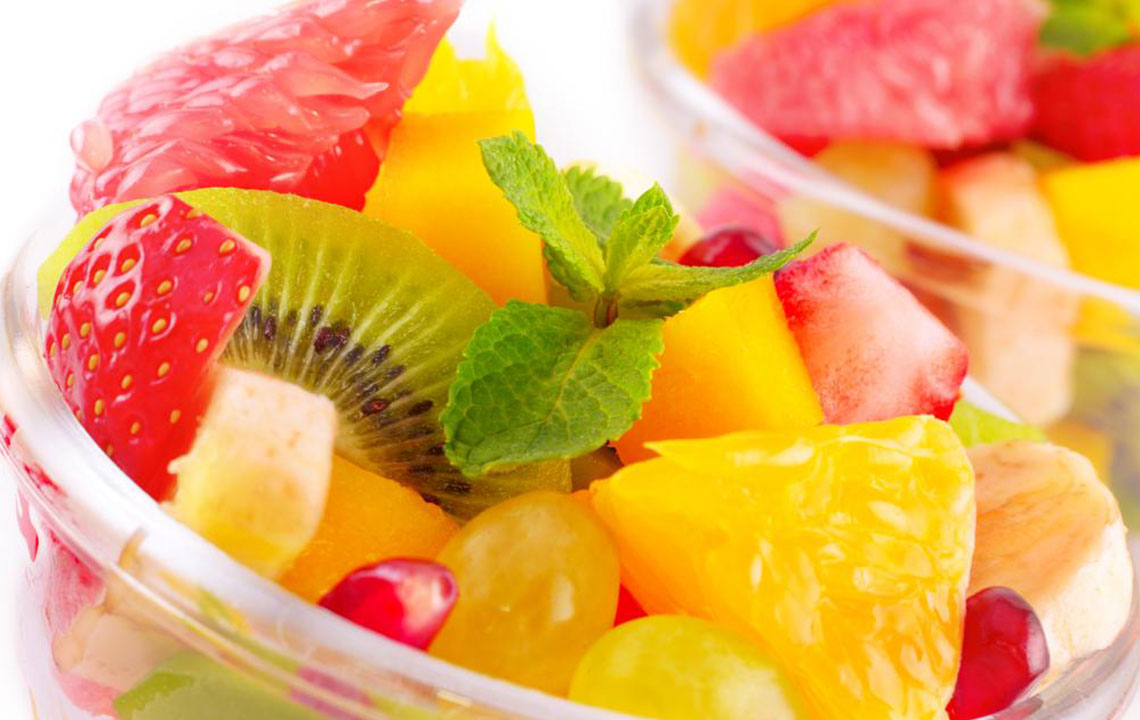
Low-Fiber Fruits for Digestive Comfort
When managing Crohn’s symptoms, selecting low-fiber fruits minimizes digestive stress. Fruits like bananas, cantaloupe, watermelon, honeydew, and peaches are good options. Smaller servings of these fruits are recommended during flare-ups, as they are easier to digest and less likely to cause irritation.
Peeling and Cooking Fruits for Better Tolerance
Removing skins from fruits or cooking them reduces insoluble fiber, making them gentler on the digestive tract. Canned fruits or cooked fruits tend to be lower in fiber but should be consumed in moderation due to their natural sugar content. This practice helps prevent additional strain on inflamed intestines while still allowing you to enjoy fruits’ nutritional benefits.
Cooked and Peeled Vegetables for Reduced Irritation
Peeling vegetables such as carrots, potatoes, squash, and zucchini effectively reduces the insoluble fiber that can irritate your digestive system. Cooking vegetables through methods like steaming, boiling, or gentle sautéing softens them, further aiding digestion. It’s best to avoid frying or roasting vegetables in fats and oils during flare-ups, as these methods can further irritate the gut.
Inclusion of Dairy and Probiotics
Dairy products, especially yogurt rich in probiotics, may help decrease inflammation within the gut and support a healthy microbial balance. Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can enhance gut health, although research results are mixed regarding their effectiveness for all individuals with Crohn’s disease. Dairy products also provide vital nutrients such as calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin C, which are important for overall health. Since lactose intolerance is common among those with Crohn’s, consulting a healthcare provider about potentially reducing or eliminating lactose from the diet can be beneficial.
Overall, a tailored diet focusing on easily digestible, nutrient-rich foods can significantly improve quality of life for individuals with Crohn’s disease. Consulting with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians can help create personalized meal plans that accommodate specific needs and sensitivities, ensuring optimal nutritional intake while minimizing gastrointestinal discomfort.