Effective Dietary Guidelines to Manage Crohn’s Disease Symptoms and Improve Quality of Life
Discover comprehensive dietary strategies to effectively manage Crohn’s disease symptoms. Learn about foods to avoid and include, tips for reducing inflammation, and how personalized nutrition plans can improve your quality of life. This detailed guide helps patients understand the critical role of diet in controlling Crohn’s disease and provides practical advice for symptom relief and long-term health management.

Comprehensive Dietary Strategies for Controlling Crohn’s Disease Symptoms
Living with Crohn’s disease presents unique challenges, particularly in managing symptoms through diet. For many individuals, the foods they consume directly influence the severity and frequency of flare-ups. Therefore, understanding how to tailor your diet can significantly improve your comfort, reduce inflammation, and promote better digestive health. Proper nutrition is a cornerstone of managing this chronic condition, and it requires careful planning regarding portion sizes, calorie intake, and nutrient selection. Neglecting dietary considerations can exacerbate symptoms, leading to more pain, discomfort, and future complications.
Understanding Crohn’s Disease and Its Impact
Crohn’s disease is a persistent, often lifelong inflammatory condition affecting the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. It belongs to a group of disorders known as inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). The inflammation can occur anywhere along the digestive system but most commonly targets the end of the small intestine (ileum) and the large intestine (colon). The disease causes various symptoms, including abdominal pain, persistent diarrhea, weight loss, fatigue, and malnutrition. Over time, chronic inflammation can lead to serious complications such as ulcers, fistulas, strictures, and nutritional deficiencies.
Diagnosis is typically confirmed through a combination of laboratory tests, endoscopy, imaging studies like CT scans, and biopsies. Although the exact cause of Crohn’s disease remains unknown, it is believed to result from a complex interplay of genetic predisposition, immune system dysfunction, environmental factors, and microbial imbalance within the gut.
Since a cure is not currently available, focusing on an appropriate, personalized diet is essential for effective symptom management and improving quality of life.
Diet plays a pivotal role in controlling Crohn’s symptoms. Avoiding processed, high-sugar, and greasy foods can prevent unnecessary flare-ups. By selecting the right foods and following tailored eating habits, patients can mitigate inflammation and support better digestion.
Key Dietary Recommendations for Crohn’s Disease:
Limit caffeine and stimulant drinks
Caffeine can irritate the gastrointestinal tract and may exacerbate symptoms like diarrhea and cramping. It is advisable to reduce or eliminate coffee, tea, colas, and energy drinks containing caffeine. Instead, opt for decaffeinated beverages, herbal teas, or infused water to stay hydrated and soothe the digestive system.
Consume peeled, low-fiber fruits
Fruits should be selected carefully. Ripe bananas, peeled apples, watermelons, and canned fruits with no added sugars are gentle on the gut. Juices without pulp are also beneficial, as they deliver essential nutrients without irritating fiber or seeds that might worsen symptoms.
Choose easily digestible proteins
Protein sources should be gentle on the stomach. Good options include well-cooked lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, and soy-based products like tofu. Avoid fried or heavily seasoned meats, which can trigger symptoms and inflammation.
Opt for low-fiber vegetables
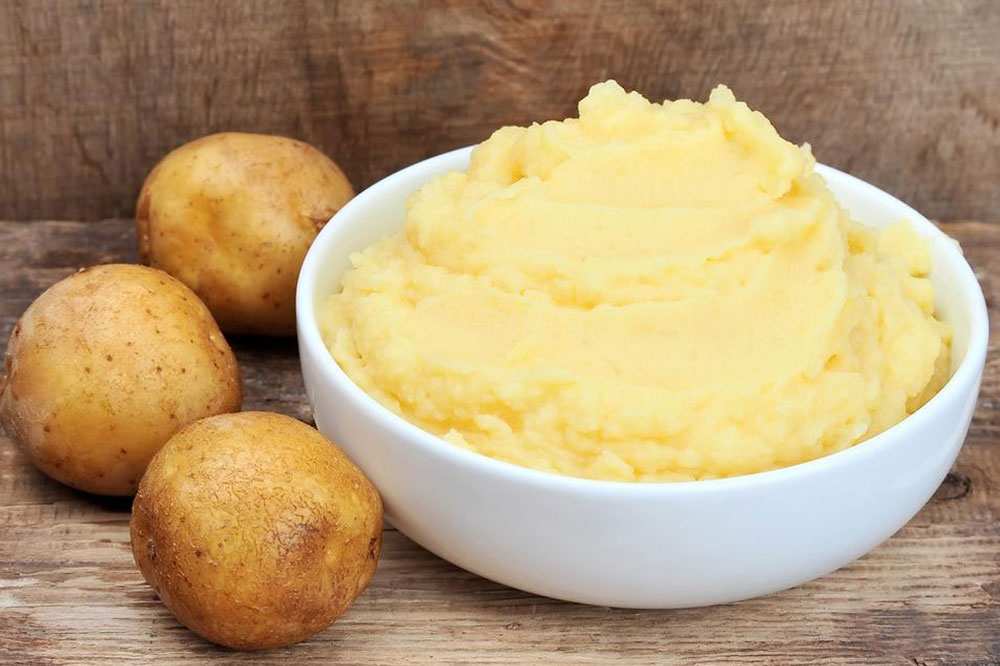
Vegetables such as potatoes, pumpkin, eggplant, and asparagus are generally well-tolerated. Raw vegetables, especially those with seeds or skins, should be avoided when symptoms flare. Vegetable juices strained to remove pulp can provide important nutrients without aggravating the digestive system.
Summary of dietary priorities
Emphasize seedless fruits and vegetables, low-sugar canned or packaged foods, and avoid dairy products if lactose intolerance symptoms are present. Monitoring individual responses to different foods is essential, as triggers vary between patients. Maintaining a food diary can help identify personal triggers and optimize diet plans tailored to your specific needs.
In conclusion, managing Crohn’s disease effectively involves a comprehensive approach centered on diet and lifestyle modifications. While medication and medical treatments play a critical role, dietary strategies can significantly reduce inflammation, lessen symptoms, and improve overall well-being. Collaborate with healthcare professionals, including dietitians, to develop a personalized nutrition plan that suits your specific condition and lifestyle. Remember, patience and consistency are key to successfully managing Crohn’s disease through diet.