The Ultimate Guide to Insulin Types and Delivery Methods for Managing Diabetes Effectively
This comprehensive guide explores the various types of insulin and their delivery devices crucial for effective diabetes management. It provides detailed insights into insulin classifications, functions, and optimal usage practices, aiding patients and healthcare providers in making informed treatment decisions. Understanding these options can help improve glycemic control, reduce complications, and enhance quality of life for those living with diabetes.
Understanding Insulin Varieties and Delivery Devices for Optimal Diabetes Control
Diabetes is a complex and long-term health condition that affects millions worldwide. According to the American Diabetes Association, diabetes is characterized by high blood sugar levels resulting from the body's inability to produce enough insulin or effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a crucial hormone responsible for facilitating the entry of glucose—derived from food—into body cells to generate energy. When insulin production or action is compromised, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to potential damage to vital organs such as the kidneys, eyes, nerves, and the heart if left unmanaged.
Different Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas. Individuals with Type 1 diabetes must rely on multiple daily insulin injections or insulin pump therapy for survival. This form of diabetes accounts for about 5-10% of total cases worldwide and is often diagnosed during childhood or adolescence.
Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form, making up approximately 90-95% of all cases. It develops when the body either does not produce enough insulin or the cells become resistant to insulin’s effects. This type often develops in adults over the age of 40 but has become increasingly prevalent among younger people due to sedentary lifestyles, poor diet, and obesity. Managing Type 2 diabetes involves lifestyle modifications such as healthy eating and physical activity, and often includes medications like metformin and insulin therapy when necessary.
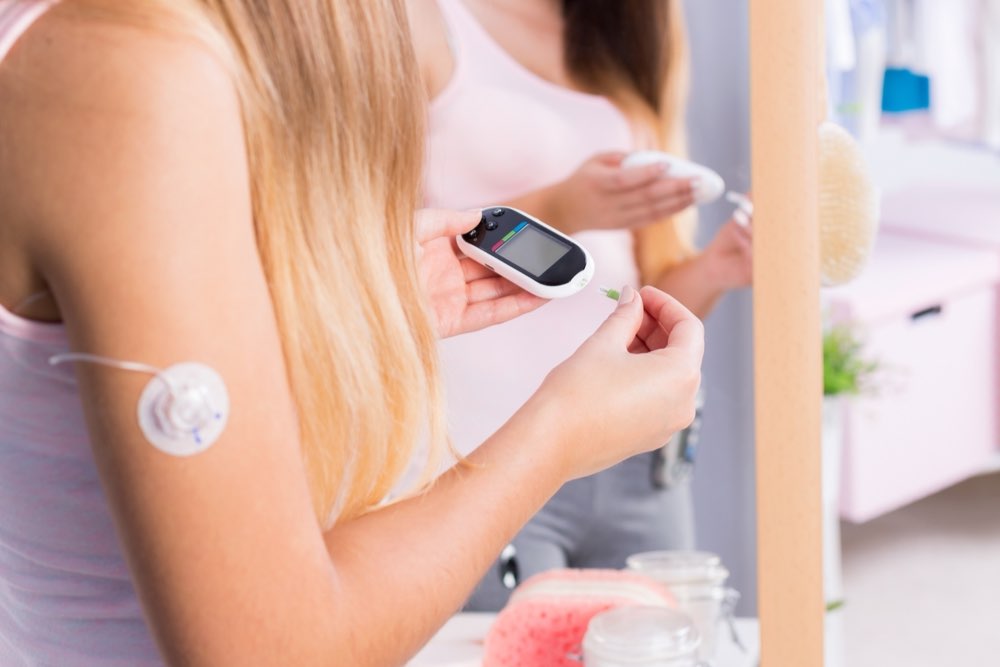
Monitoring blood glucose levels regularly is essential for effective diabetes management. Diabetic test strips are practical tools helping patients keep track of their glucose levels daily, enabling timely adjustments to treatment plans and helping prevent complications.
Varieties of Insulin and Their Uses
Insulin therapy is a cornerstone in diabetes management, with various types tailored to different needs and lifestyles. Understanding these variants can help individuals and healthcare providers select the most suitable options for stable blood sugar control.
Rapid-acting insulin: These insulins start working within 15 minutes after injection, peak around 1 hour, and last between 2 to 4 hours. Common examples include Insulin Glulisine (brand name Apidra), Lispro (Humalog), and Aspart (NovoLog). Rapid-acting insulins are typically used to control blood sugar during meals or to correct high blood sugar levels in between meals, offering flexibility and quick response.
Regular or short-acting insulin: Examples include Humulin R and Novolin R. These begin to act approximately 30 minutes after injection, peak at about 2-3 hours, and work for 3-4 hours. They are often used around meal times and in insulin pump therapy for more consistent control.
Intermediate-acting insulin: NPH insulin (Humulin N, Novolin N) typically starts working within 2-4 hours, peaks between 4-12 hours, and lasts approximately 12 to 18 hours. This insulin provides baseline coverage, often administered once or twice daily to maintain steady glucose levels.
Long-acting insulin: Insulins like Insulin Detemir (brand name Levemir) and Glargine (Lantus) are designed for continuous, steady absorption, providing consistent blood sugar control over a 24-hour period with minimal variability. These are usually injected once daily and help reduce the risk of daytime and nighttime hyperglycemia.
Inhaled insulin: Afrezza is an inhaled insulin system that begins working within 12-15 minutes, peaks around 30 minutes, and is eliminated within approximately 3 hours. It offers an alternative for those who prefer not to use injections, though it is typically used in conjunction with basal insulin therapy.
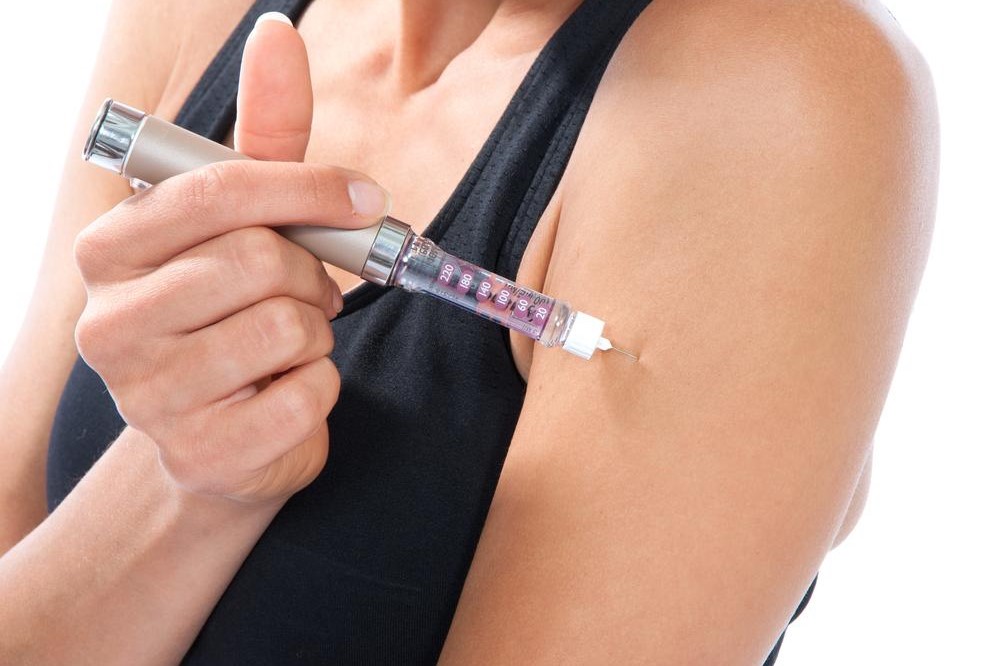
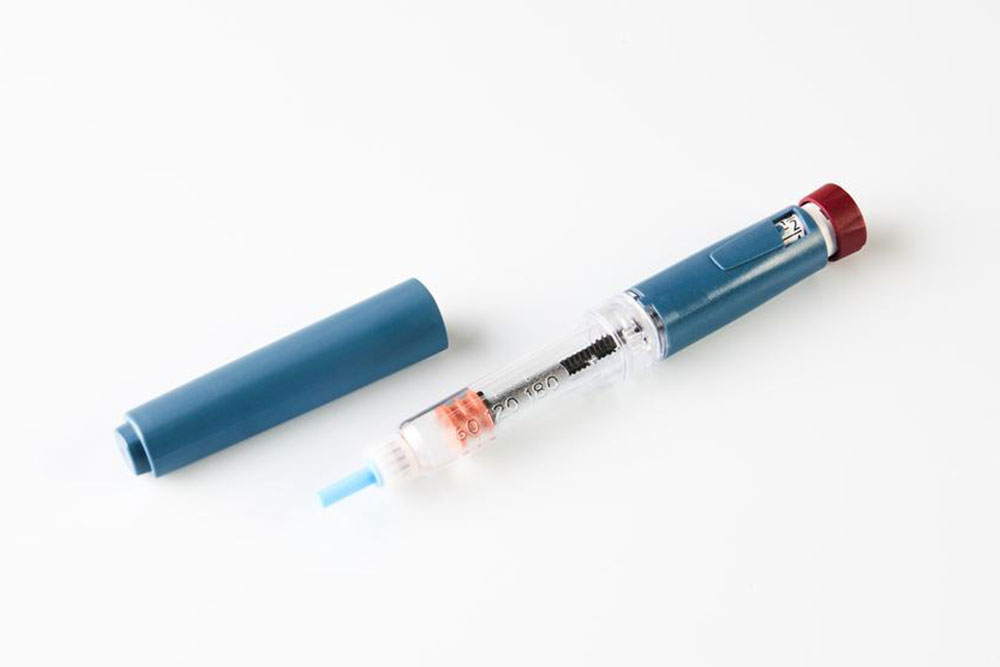
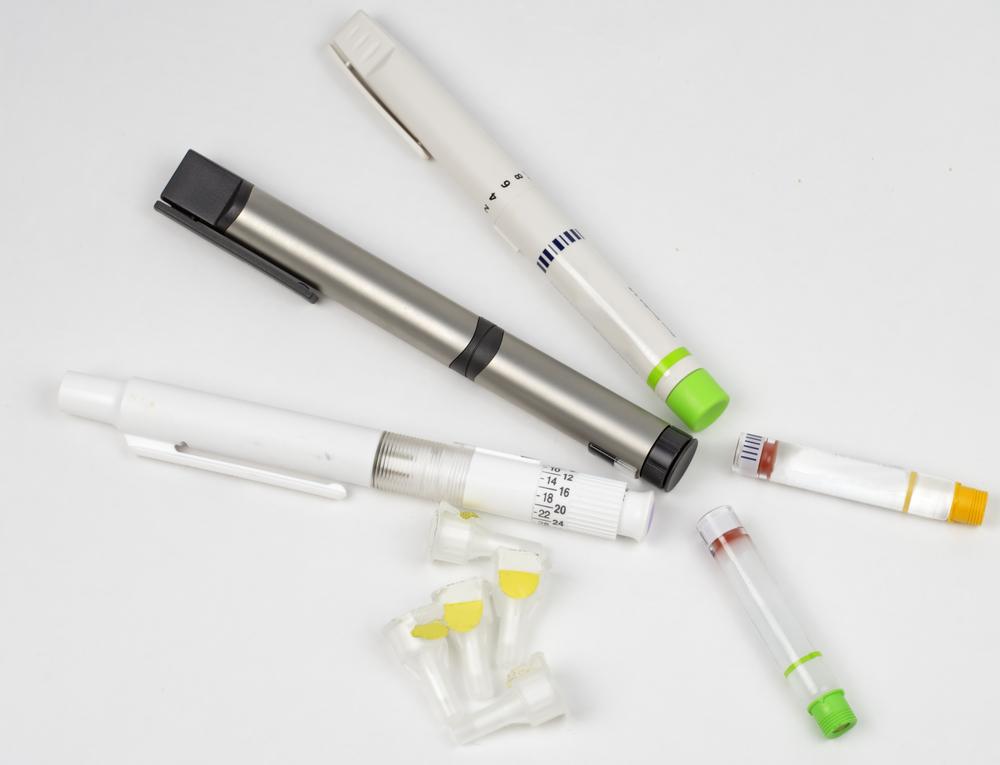
Delivery methods for insulin vary, with insulin pens being the most popular among patients for their convenience and ease of use. These pens contain pre-filled insulin cartridges or are refillable, allowing users to dial in the precise dose needed. They resemble large writing pens and are equipped with a needle at the tip for injection. Proper handling, storage, and regular replacement of insulin supplies are crucial to ensure efficacy and prevent health complications.