Comprehensive Guide to Preventing Heartburn and Acid Reflux During Pregnancy
This comprehensive guide covers effective strategies for preventing and managing heartburn and acid reflux during pregnancy. It emphasizes dietary modifications, lifestyle tips, and understanding causes, helping expectant mothers achieve a more comfortable pregnancy experience by reducing common digestive discomforts safely and effectively.

Effective Strategies for Managing Heartburn and Acid Reflux in Pregnant Women
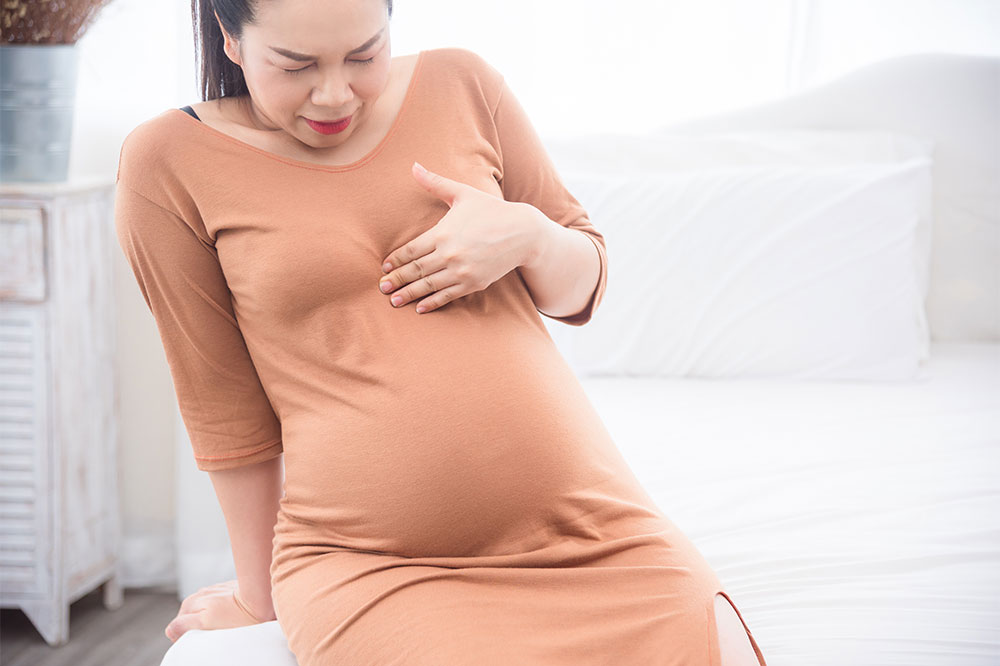
Pregnancy is a beautiful journey, but it often comes with uncomfortable symptoms such as heartburn and acid reflux. These issues are very common among expecting mothers and can significantly impact daily comfort and well-being. Understanding the underlying causes and implementing practical, safe remedies can make a noticeable difference. Fortunately, there are various dietary and lifestyle modifications that can help alleviate these symptoms without compromising the health of the mother or the developing baby. This comprehensive guide explores the causes of heartburn during pregnancy, effective preventive strategies, food choices, and lifestyle tips to ensure a more comfortable pregnancy experience.
Many pregnant women experience episodes of indigestion characterized by a burning sensation that occurs in the chest or throat. This discomfort is often mistaken for heart-related issues but is actually related to digestive processes and hormonal changes. With proper awareness and proactive habits, managing and reducing these symptoms becomes achievable, allowing for a more enjoyable pregnancy journey.
In this guide, we delve into why heartburn and acid reflux are more common during pregnancy, highlighting hormonal and physical factors. We also provide detailed dietary and lifestyle tips tailored specifically for pregnant women to prevent and manage these symptoms effectively.
Understanding Why Heartburn Is Common During Pregnancy
The primary reason for increased heartburn and acid reflux during pregnancy is linked to hormonal fluctuations, particularly the increased production of progesterone. This hormone relaxes smooth muscles, including the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which is responsible for preventing stomach acids from flowing back into the esophagus. When the LES relaxes inappropriately, acid can leak upward, causing the burning sensation known as heartburn.
Another contributing factor is the physical pressure exerted by the expanding uterus on the stomach, which displaces its position and reduces its capacity, leading to increased pressure and a higher likelihood of reflux. Combined with the hormonal influence, these physical changes make pregnant women more susceptible to indigestion and acid reflux symptoms.
Key Dietary and Lifestyle Modifications for Relief
Simple adjustments in eating habits and daily routines can significantly reduce the occurrence of heartburn and acid reflux during pregnancy. Here are some detailed tips:
Eat Small, Frequent Meals
Consuming large meals can cause the stomach to become overly full, increasing pressure on the LES and promoting reflux. Adopting a pattern of smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day helps keep stomach pressure low, thereby reducing the likelihood of acid leakage. Aim for 5-6 small meals instead of three big ones, spreading them evenly during waking hours.
Avoid Known Trigger Foods
Certain foods are notorious for aggravating heartburn. These include spicy dishes, fried foods, citrus fruits, tomato-based products, chocolate, caffeine, and carbonated drinks. These items relax the LES or increase stomach acidity, making reflux more likely. Pregnant women should monitor their personal reactions and eliminate or limit these triggers accordingly. It's also advisable to abstain from alcohol, which can exacerbate symptoms and pose risks during pregnancy.
Manage Fluid Intake Wisely
Drinking plenty of fluids is essential, but the timing and type of fluids matter. Opt for smoothies, yogurt, clear soups, and herbal teas that are gentle on digestion. Drinking slowly and avoiding gulping can prevent bloating and pressure on the stomach. It's best to avoid excessive liquid intake during meals; instead, hydrate between meals to reduce the volume in the stomach at any given time.
Schedule Meals Thoughtfully and Maintain Upright Position
Eating right before bed can lead to nighttime reflux, disturbing sleep and causing discomfort. Plan to have your last meal at least 2-3 hours before bedtime, ensuring the stomach has time to digest food. After eating, remain upright for about 30 minutes to an hour to facilitate digestion and prevent acid from flowing back into the esophagus. Elevating the head of the bed slightly can also help reduce nighttime symptoms.
Additional Tips for a Reflux-Free Pregnancy
Maintain a healthy weight gain as recommended by your healthcare provider; excessive weight increases abdominal pressure.
Wear loose-fitting clothing that does not constrict your abdomen.
Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or prenatal yoga to reduce stress, which can worsen symptoms.
Avoid smoking and exposure to cigarette smoke, as it aggravates reflux and is harmful during pregnancy.
Consult your healthcare provider before taking any medications or herbal remedies for heartburn, ensuring they are safe for pregnancy.
In conclusion, managing heartburn and acid reflux during pregnancy is achievable through a combination of dietary adjustments, lifestyle practices, and awareness of triggers. By adopting these strategies, expecting mothers can significantly reduce discomfort and enjoy a healthier, more comfortable pregnancy journey.
Remember, if symptoms persist or worsen, always seek medical advice. A healthcare professional can provide personalized treatment options and ensure both mother and baby remain healthy and safe throughout pregnancy.