Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing and Effectively Managing Infant Eczema Symptoms
This comprehensive guide explores infant eczema, detailing its symptoms, causes, and effective management strategies. It emphasizes gentle skincare, trigger avoidance, and medical treatment under professional supervision to help parents alleviate their child's discomfort. By understanding the condition thoroughly, caregivers can improve skin health and quality of life for affected infants, ultimately helping many children outgrow this common skin issue with proper care.
Understanding and Managing Infant Eczema: A Complete Guide
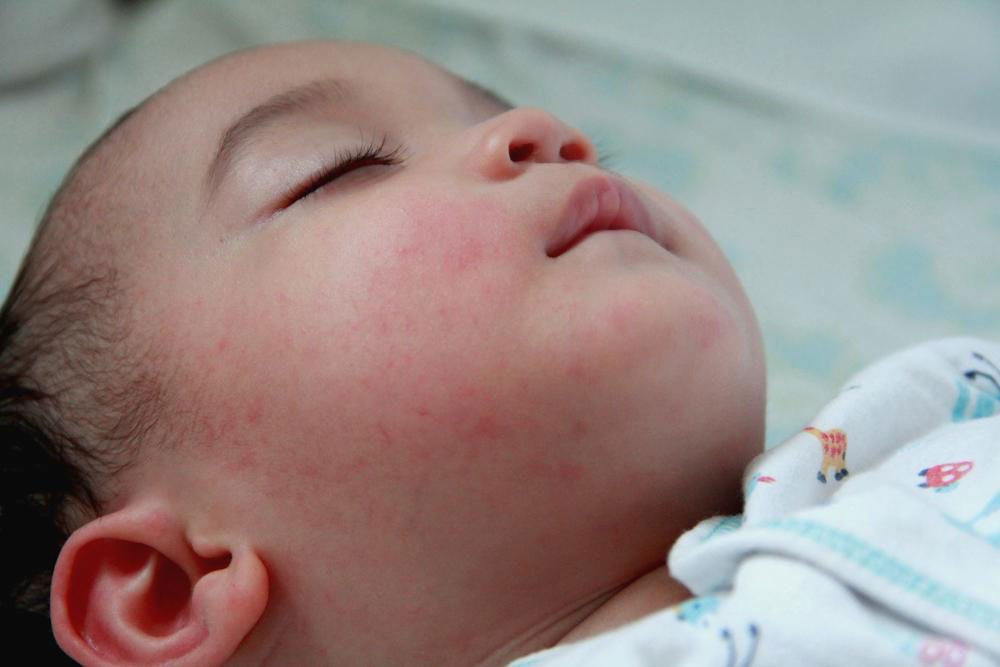
Infant eczema, medically known as atopic dermatitis, is a prevalent and often distressing skin condition that affects many babies during their early developmental stages. Characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed patches on the skin, this condition can cause significant discomfort to infants and concern to parents. Recognizing the signs early and implementing effective management strategies are crucial to alleviating symptoms, preventing secondary infections, and ensuring the child's comfort and well-being. While there is currently no definitive cure for eczema, a combination of gentle skincare routines, medication, and environmental modifications can greatly improve the quality of life for affected infants.
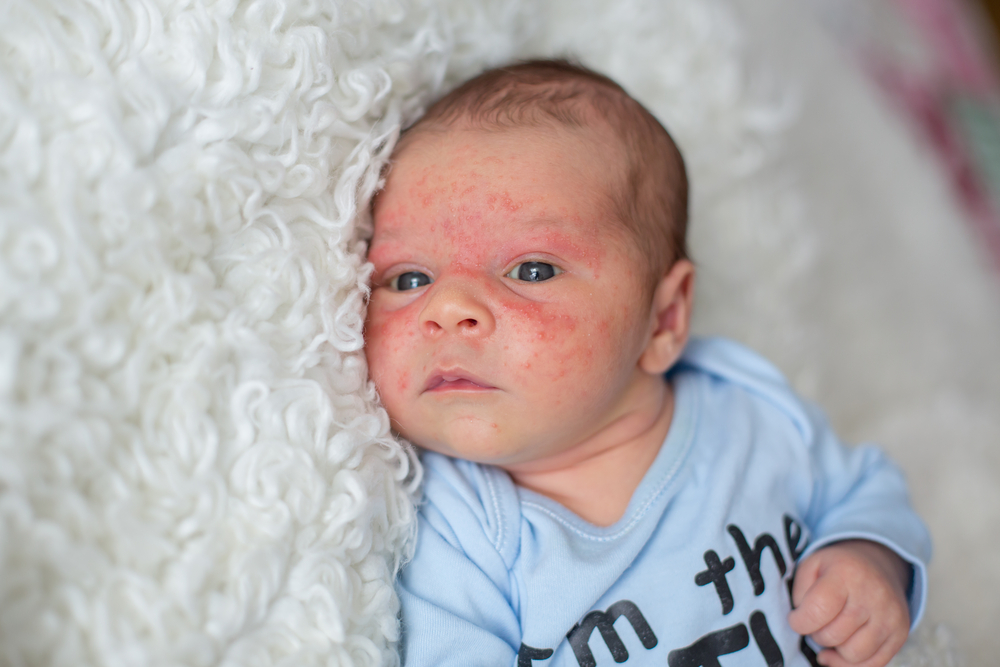
Eczema most commonly appears before the age of two, but its symptoms can sometimes be observed in older children as well. The areas most frequently impacted include the face, scalp, neck, hands, elbows, behind the knees, and sometimes on the trunk. The skin in these regions becomes dry, flaky, cracked, and reddened, often accompanied by intense itching that can disrupt sleep and feeding. In severe cases, the skin may break down, ooze, or develop crusts, increasing the risk of bacterial or viral infections. Managing these symptoms effectively requires understanding the causes and triggers, implementing proper skincare routines, and in some cases, using medications prescribed by healthcare professionals.
The exact etiology of infant eczema remains unknown, but scientists have identified several contributing factors. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, as children with a family history of eczema, allergies, or asthma are at higher risk. Environmental factors, such as exposure to irritants, allergens, harsh weather, and climatic conditions, also influence the development and severity of eczema. Increased awareness and research over recent decades suggest a complex interplay between genetic and environmental triggers.
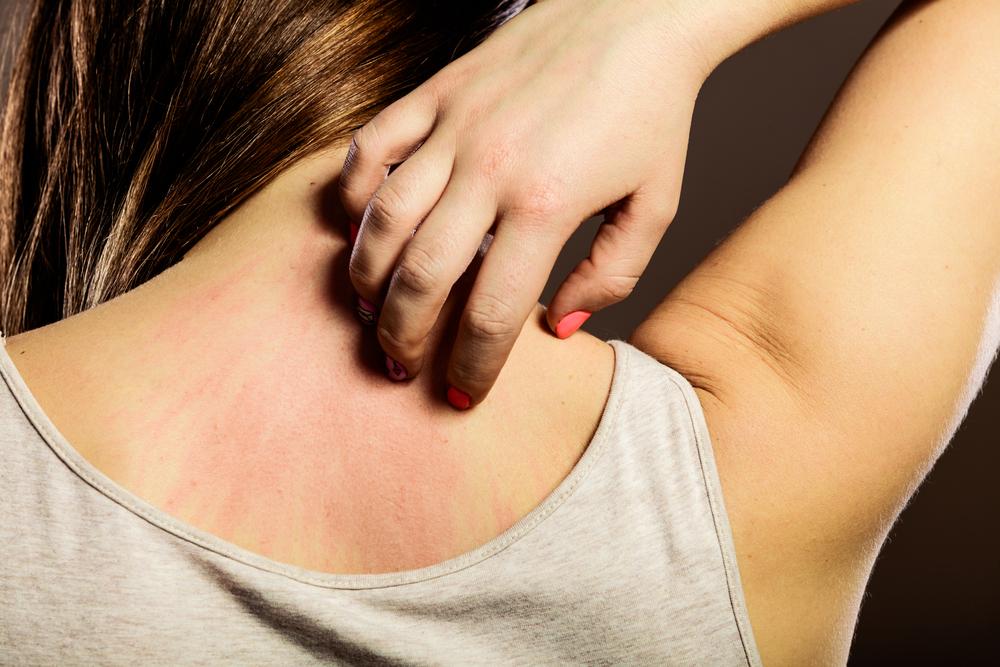
Recognizing the early signs of infant eczema is essential for prompt intervention. Parents should look for symptoms such as dry, rough, or cracked skin, redness, and persistent itching. The affected areas may become inflamed, swollen, or develop oozing lesions, especially if scratched excessively. These symptoms can cause considerable discomfort and distress for infants, leading to irritability, poor sleep, and feeding difficulties. Identifying and avoiding known triggers—like certain fabrics, soaps, detergents, or environmental allergens—play a vital role in managing eczema.
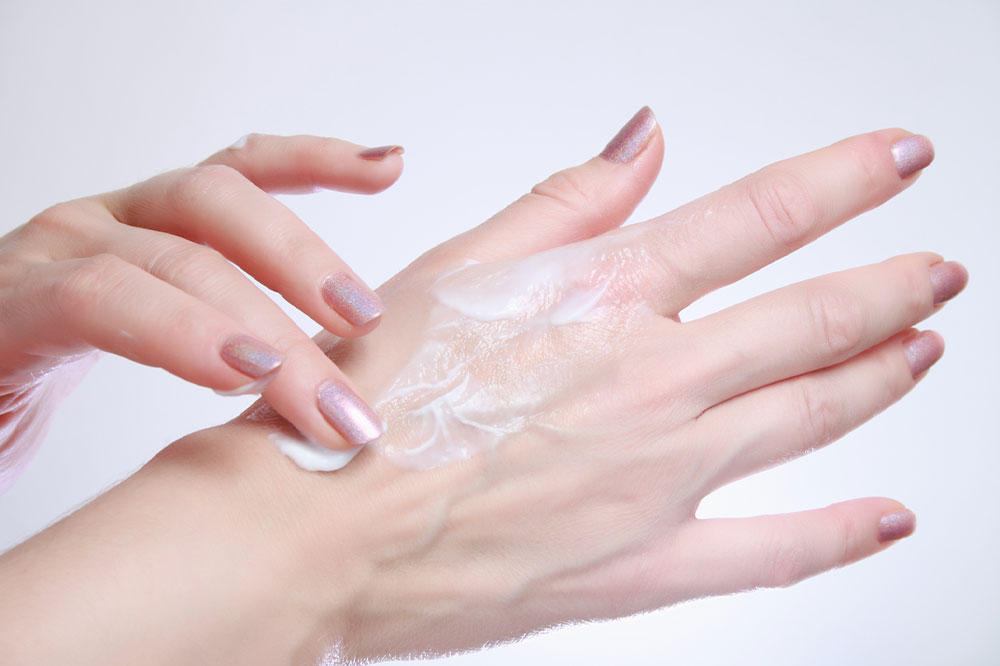
Effective management of infant eczema involves several well-established strategies. Gentle skincare routines are paramount; this includes daily bathing with lukewarm water, using mild, fragrance-free cleansers, and immediately applying emollients or moisturizers to lock in moisture. Regular use of emollients, such as petroleum jelly or specialized eczema creams, can soothe irritated skin and prevent dryness. For more severe cases, healthcare providers may recommend the judicious use of topical corticosteroids or other anti-inflammatory medications to reduce flare-ups, always under professional supervision. Parents should be cautious about over-reliance on steroids to avoid potential side effects.
Besides medication, environmental modifications are essential. Wearing soft, breathable fabrics like cotton and avoiding wool or synthetic fibers can minimize irritation. Detergents specifically formulated for sensitive skin should be used, and fragranced or dye-laden products should be avoided. Keeping the environment cool and humid can also help reduce itching and skin dryness. Managing stress and avoiding known allergens, such as pet dander or pollen, contribute to controlling eczema symptoms. Ensuring consistent skincare routines, along with early medical intervention when flare-ups occur, can significantly enhance the child's comfort and reduce the risk of infections or complications.
Most children tend to outgrow eczema as their immune systems mature, but diligent skincare and trigger avoidance are necessary to keep symptoms at bay during early childhood. It is important for parents to work closely with pediatric dermatologists or allergists to develop a tailored management plan that addresses the specific needs of their child. With proper care, many infants with eczema can lead comfortable, active lives without significant disruption.
In summary, recognizing early signs of infant eczema, understanding its triggers, and employing a comprehensive management approach are the keys to reducing discomfort and preventing complications. Patience, persistence, and professional guidance are essential components of effective treatment, improving not only the child's skin health but also their overall happiness and development.