Complete Guide to Managing Genital Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
This comprehensive guide explores genital psoriasis, covering its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and effective treatment strategies. Emphasizing medical interventions, lifestyle tips, and emotional support, it aims to empower those affected by this sensitive condition to manage symptoms and maintain their quality of life effectively. Understanding triggers and treatment options helps in proactive management and supports overall well-being.

Complete Guide to Managing Genital Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Genital psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects the sensitive skin of the genital area, leading to discomfort, itching, and emotional distress for those affected. Although psoriasis is commonly recognized for its appearance on the scalp, elbows, and knees, its manifestation in the genital region presents unique challenges due to the area's sensitivity and moisture levels. Understanding this condition thoroughly is essential for effective management and to improve quality of life.
Understanding Genital Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder characterized by an abnormal immune response that accelerates the life cycle of skin cells. Normally, skin cells mature and shed over several weeks, but in psoriasis, this process speeds up to just a few days, leading to a buildup of cells on the surface. When this overproduction occurs in the genital area, it results in what is known as genital psoriasis. This condition most often affects areas such as the groin, inner thighs, buttocks, and sometimes the genital mounds.
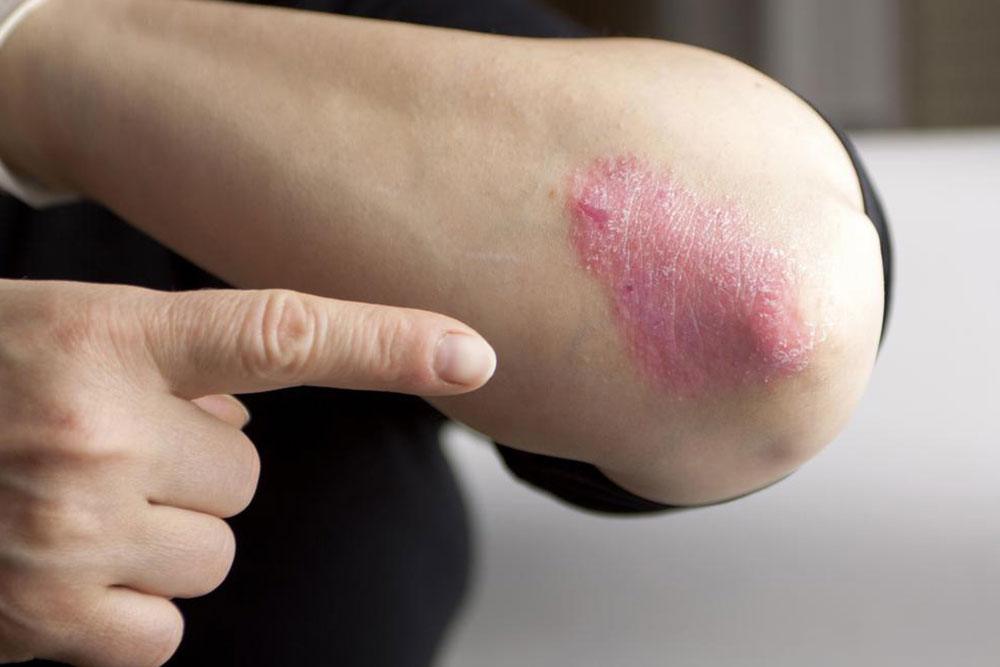
Unlike the typical psoriatic plaques seen on elbows or knees, skin lesions in the genital area tend to be smoother, less scaly, and more moist due to the natural environment of the region. The area’s moisture can influence the appearance and texture of these patches, often making them less flaky but more prone to irritation and discomfort.
Recognizing Symptoms of Genital Psoriasis
Red, smooth patches: These areas often appear as uniform, reddish patches with a smooth surface, lacking the thick, silvery scales typical of other psoriasis sites.
Persistent itching and irritation: The affected skin often itches intensely, leading to discomfort and sometimes scratching, which can worsen the condition.
Burning sensations: Many sufferers report a burning feeling, especially during physical activity, sweating, or sexual activity.
Dryness and cracking: The skin may become dry, cracked, and sometimes bleed, increasing the risk of infection and further irritation.
Underlying Causes and Triggers
The exact cause of psoriasis remains unclear; however, it involves a complex interaction between genetic predisposition, immune system dysfunction, and environmental factors. Certain triggers are known to exacerbate or initiate flare-ups, particularly in sensitive areas like the genitals. These include:
Stress: Elevated stress levels can trigger immune responses that worsen psoriasis symptoms.
Infections: Respiratory infections like strep throat are known to precipitate psoriasis outbreaks.
Skin injuries: Cuts, scrapes, or irritation from shaving or other trauma can lead to localized psoriasis flares, a phenomenon known as Koebner response.
Environmental factors: Allergens, harsh soaps, or detergents may irritate the sensitive skin further and trigger symptoms.
Hormonal fluctuations: Changes in hormone levels, such as during puberty or menopause, might influence disease activity.
Diagnosing Genital Psoriasis
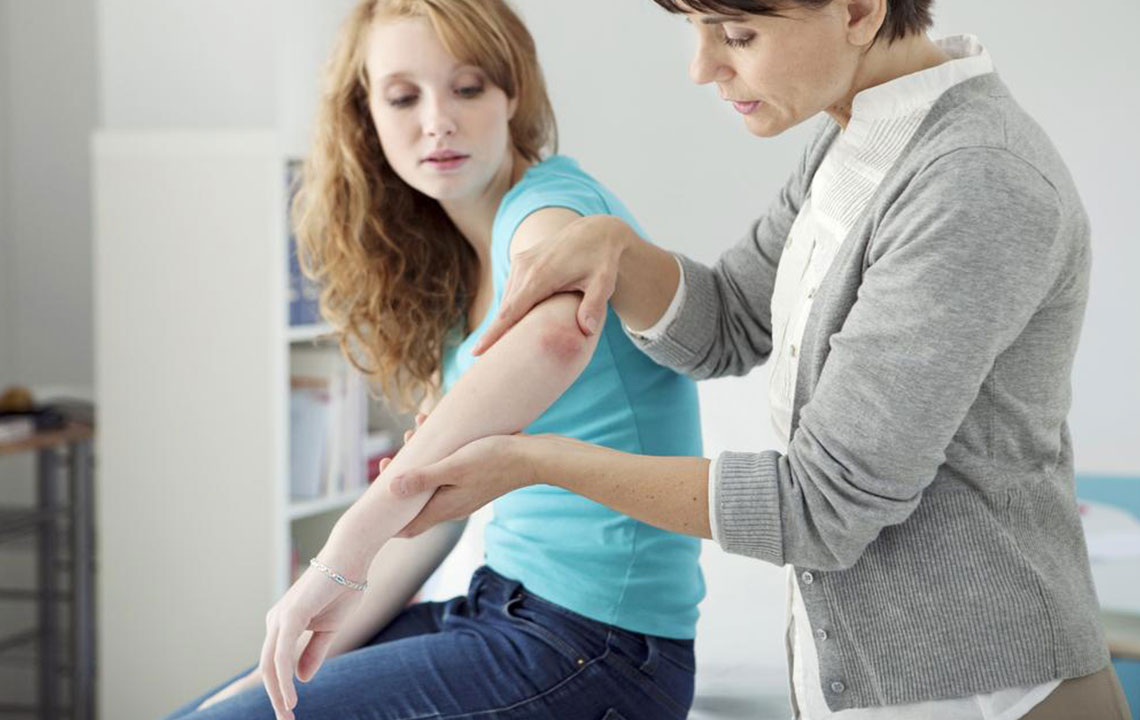
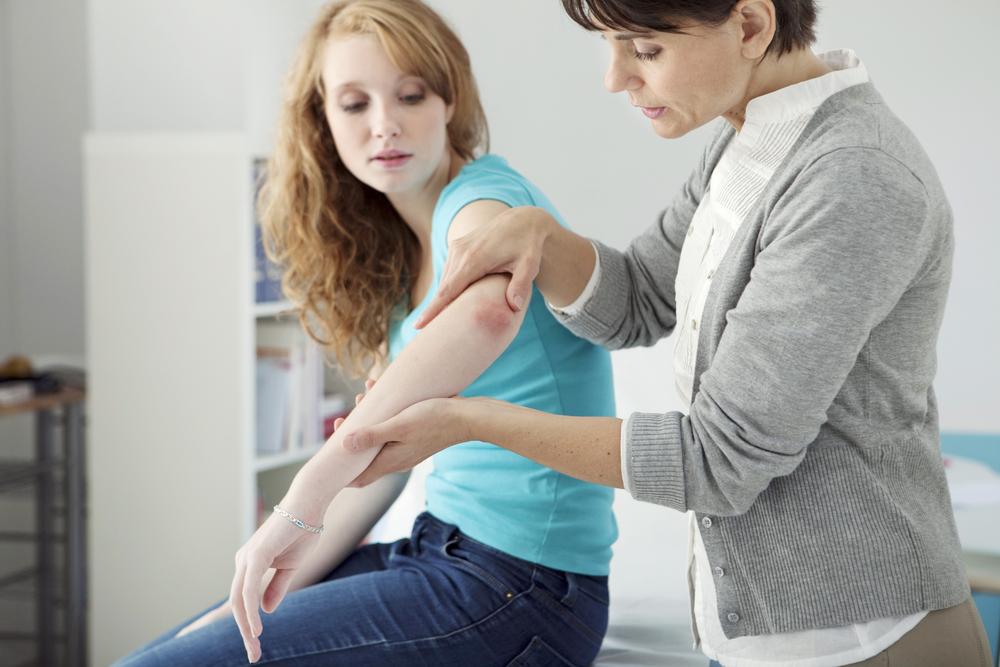
A healthcare provider typically performs a physical examination to identify psoriatic lesions based on appearance and location. To confirm the diagnosis and differentiate from other skin conditions such as eczema, lichen planus, or infections, a skin biopsy may be recommended. A biopsy involves removing a small skin sample for laboratory analysis. Proper diagnosis is essential for tailoring effective treatment strategies.
Comprehensive Treatment Options
Managing genital psoriasis involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, topical treatments, and sometimes light therapy. The goal is to reduce inflammation, control symptoms, and prevent flare-ups while maintaining comfort.
Topical medications: Corticosteroid creams are the mainstay treatment, helping to decrease inflammation and itching. Other options include vitamin D analogs (like calcipotriol), calcineurin inhibitors, and emollients.
Moisturizers: Regularly applying fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizers can help keep the skin hydrated, reducing dryness and cracking associated with psoriasis.
Avoiding triggers: Lifestyle changes such as managing stress, avoiding harsh soaps, and wearing loose, breathable clothing can significantly decrease flare-ups.
Phototherapy: Controlled ultraviolet (UV) light therapy can be effective for some patients, especially when topical treatments are insufficient. It involves exposing skin to UVB light under medical supervision.
Systemic treatments: For severe cases, doctors may prescribe systemic medications like biologics, oral immunosuppressants, or retinoids that modify or suppress the immune response.
Maintaining Emotional and Psychological Well-being
Living with genital psoriasis can have profound effects on mental health, self-esteem, and intimate relationships. Feelings of embarrassment or shame are common, which can lead to social withdrawal or depression. Seeking support from mental health professionals, joining support groups, or having open communication with partners can help cope with emotional challenges. Educating oneself about the condition fosters understanding and acceptance, which are pivotal for emotional resilience.
In conclusion, effective management of genital psoriasis requires an integrated approach that combines medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and emotional support. By staying informed, adhering to prescribed therapies, and sharing concerns with healthcare providers, individuals can lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by this chronic skin condition.