Comprehensive Guide to the Human Immune System: Functions, Types, and How to Strengthen It
Discover everything about the human immune system in this comprehensive guide. Learn how it functions, the types of immunity, and strategies to boost immune health. From the roles of key organs to lifestyle tips, this article provides valuable insights for maintaining optimal immunity and preventing illness, emphasizing the importance of a holistic approach to immune support for overall well-being.
The human immune system is an intricate and highly effective defense mechanism that protects the body from a wide array of harmful invaders, including viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. Its primary function is to detect these foreign substances, known as antigens, and initiate an immune response to neutralize or eliminate them. Understanding how the immune system works is essential for maintaining health and preventing disease. This detailed guide explores the components, types, and ways to strengthen your immune defenses for optimal health.
What Is the Human Immune System?
The immune system is a sophisticated network of cells, tissues, organs, and molecules that work together to defend the body against pathogens. It recognizes molecules that are foreign to the body, such as parts of viruses, bacteria, or other microorganisms, and triggers immune responses to combat these threats. It also plays a role in identifying and destroying abnormal cells, including those that could become cancerous.
Key Components of the Immune System
White Blood Cells (Leukocytes): These are the primary soldiers of the immune system. They include lymphocytes (such as B cells and T cells), macrophages, neutrophils, monocytes, and others that identify and attack pathogens.
Lymphatic System: This network of vessels transports immune cells throughout the body and includes lymph nodes, which act as filters trapping harmful substances.
Spleen: An organ that filters blood, removing old or damaged blood cells and helping to fight infection.
Thymus: A small organ where T lymphocytes mature, essential for adaptive immunity.
Bone Marrow: The site of hematopoiesis, where all blood cells, including immune cells, are produced.
Types of Immunity
Immunity can be broadly classified into two categories:
Active Immunity: This occurs when the body produces its own immune response, either naturally through infection or artificially via vaccinations. Active immunity tends to be long-lasting and sometimes lifelong.
Passive Immunity: Acquired through medical interventions, such as antibody transfer from mother to baby or through antibody injections. Passive immunity provides immediate protection but is temporary.
The Immune Response: How the Body Fights Off Invaders
When a pathogen invades, the immune system responds through several steps:
Recognition: Immune cells detect antigens on the pathogen’s surface.
Activation: This triggers the proliferation of specific immune cells tailored to target the invader.
Response: Effector cells, such as cytotoxic T cells and antibodies, attack and neutralize the pathogen.
Memory Formation: The immune system creates memory cells that enable faster and more effective responses to future infections by the same pathogen.
How to Keep Your Immune System Healthy
A strong immune system is vital for overall health. Here are some effective ways to support and maintain immune function:
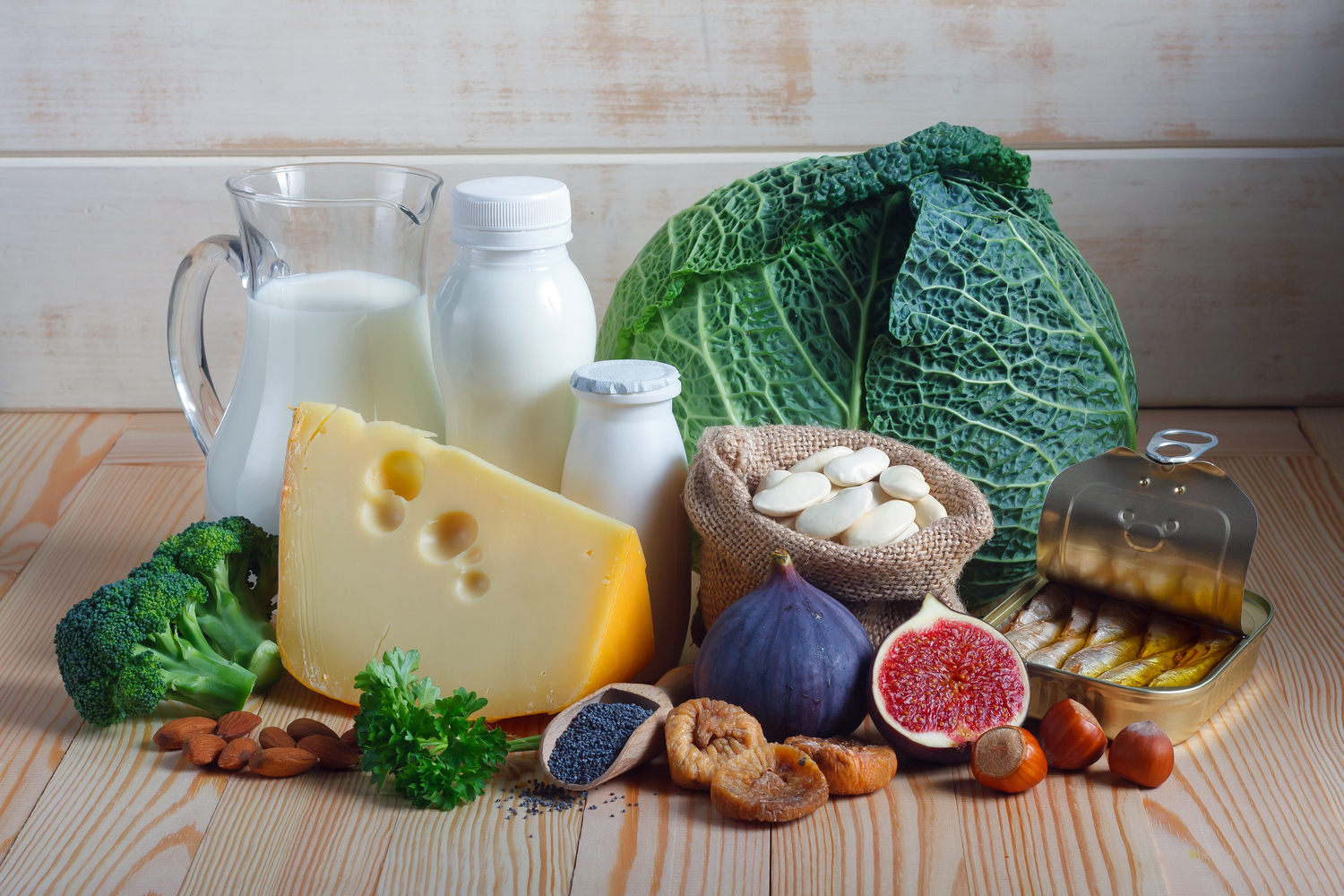
Eat a Balanced Diet: Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. Nutrients like vitamins C, D, E, and zinc are particularly important for immune health.
Regular Exercise: Engaging in moderate physical activity boosts circulation and immune cell activity.
Get Adequate Sleep: Sleep is essential for immune regulation. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
Practice Good Hygiene: Regular handwashing and proper sanitation reduce exposure to pathogens.
Stay Up-to-Date with Vaccinations: Vaccines are a crucial preventive measure against many infectious diseases.
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can weaken immune function. Techniques like meditation, yoga, and mindfulness can help manage stress levels.
The Role of Modern Medicine and Vaccines
Advancements in medicine have dramatically improved our ability to bolster immune defenses. Vaccines stimulate the production of specific antibodies and memory cells, providing protection against diseases like influenza, hepatitis, measles, and COVID-19. In addition to vaccinations, immunotherapies and targeted treatments are being developed to empower the immune system in fighting chronic illnesses and cancers.
Common Immune System Disorders
While a healthy immune system is beneficial, immune dysfunction can lead to disorders:
Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues.
Immunodeficiency: Conditions such as HIV/AIDS or genetic disorders impair immune response, increasing susceptibility to infections.
Allergies: Excessive immune reactions to harmless substances like pollen, foods, or pet dander.
Conclusion
Understanding the human immune system's complexity is key to adopting healthier lifestyles that support immune health. From maintaining a balanced diet and regular exercise to staying current with vaccinations and managing stress, each step enhances your body's natural defense mechanisms. As medical science progresses, new therapies and vaccines continue to offer hope for combating infections and immune-related disorders. Invest in your immune health today for a healthier, more resilient life.