Comprehensive Guide to Vital Vitamins for Boosting Your Immune System
This comprehensive guide explores essential vitamins like A, B6, B12, C, D, and E, highlighting their crucial roles in boosting immune health. It offers dietary sources and lifestyle tips to enhance immunity naturally, emphasizing balanced nutrition, sun exposure, and lifestyle habits. Boost your body's defenses effectively by understanding how these vital nutrients support immune function and overall well-being. Ideal for those seeking to prevent illnesses and strengthen their immune resilience through informed dietary choices and healthy living practices.
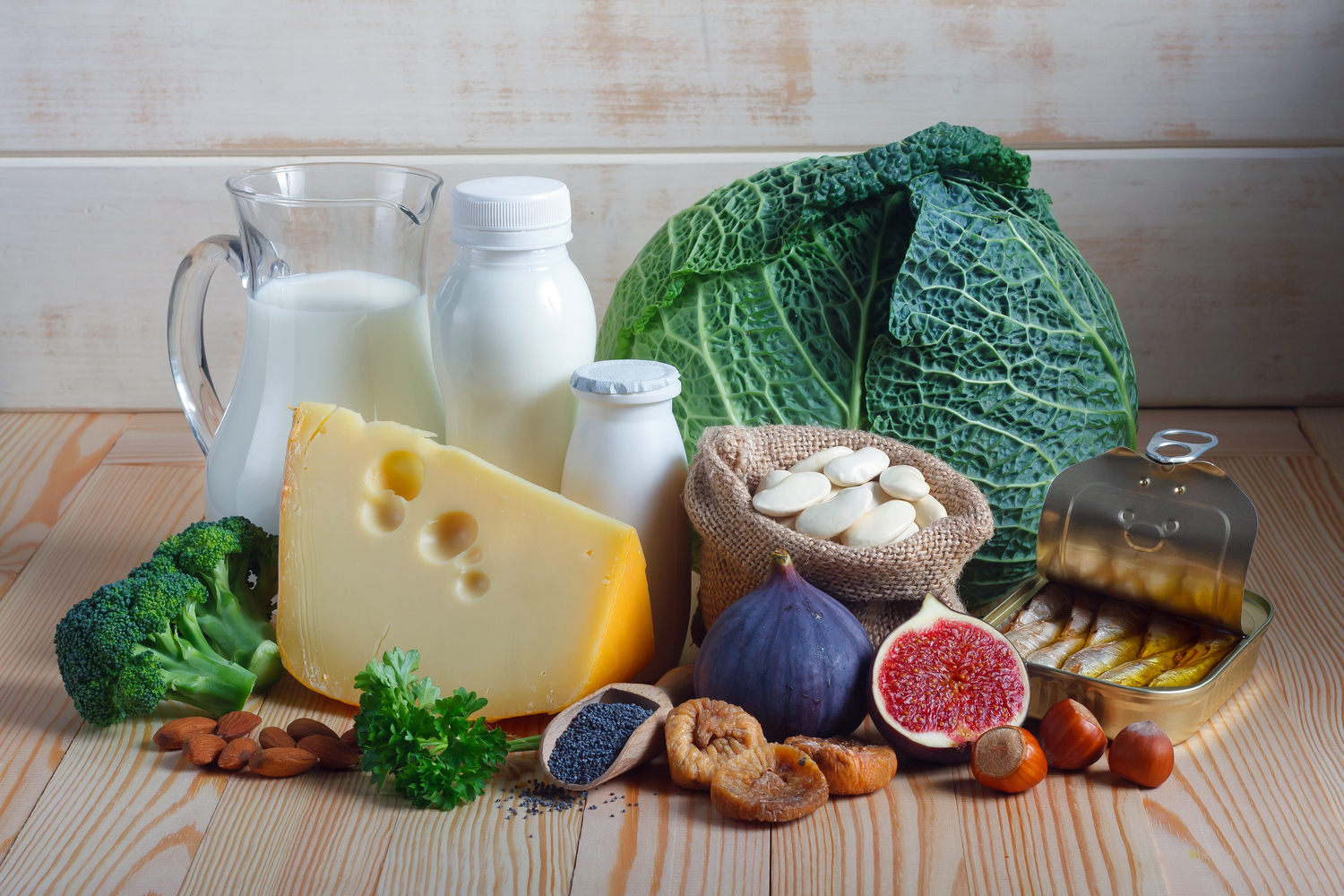

Comprehensive Guide to Vital Vitamins for Boosting Your Immune System
Your immune system serves as your body's essential defense mechanism, protecting you from a wide range of infections and illnesses. Comprising blood, tissues, and lymphatic fluids, it works tirelessly to identify and eliminate harmful pathogens. Maintaining a strong immune system is crucial for overall health and well-being, especially in today's environment where diseases can spread rapidly. A combination of proper nutrition, lifestyle habits, and good hygiene plays a vital role in ensuring your immune defenses are functioning optimally. Among these, ensuring adequate intake of key vitamins and minerals is fundamental to bolstering your immune response and reducing your susceptibility to infections.
The Critical Role of Nutrition in Immune Health
Dietary habits have a profound impact on how well your immune system functions. Consuming a diet high in processed foods, saturated fats, excessive salts, and refined sugars can lead to increased inflammation, impair your immune responses, and elevate the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular issues, and obesity. Conversely, focusing on a balanced, nutrient-rich diet supports immune resilience. Incorporating a variety of plant-based foods like colorful fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds supplies essential micronutrients including vitamins and minerals vital for immune defense. Whole grains, lean meats, and seafood not only promote gut health but also supply anti-inflammatory compounds that help maintain immune balance. Recent scientific studies emphasize the importance of specific vitamins—namely vitamins A, C, D, and E—in supporting immune function, making them integral to a health-conscious diet.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A is fundamental for maintaining good vision, supporting cellular growth, reproductive health, and functioning as a powerful antioxidant. Crucially, it plays an essential role in immune cell functions, including the activation and regulation of lymphocytes, the white blood cells that fight infections. A deficiency in vitamin A can compromise immune defenses, reducing the production of interferons—proteins that interfere with virus replication—and impairing overall immune responses. Rich dietary sources of vitamin A include leafy greens such as spinach and kale, dairy products like milk and cheese, eggs, fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, as well as liver and other meat sources. While supplementation might be necessary in severe deficiency cases, incorporating vitamin A-rich foods into your daily diet can naturally enhance your immune system’s ability to combat pathogens.
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
This water-soluble vitamin is vital for immune regulation and managing inflammation. Vitamin B6 influences the production of antibodies, which are essential for recognizing and neutralizing harmful bacteria and viruses. The recommended daily intake for adults is approximately 2 mg. You can obtain adequate B6 by eating green vegetables such as spinach and broccoli, whole grains like brown rice and oats, lean meats, fish, legumes, dairy products, and eggs. Ensuring sufficient vitamin B6 intake supports immune cell activity, aids in metabolic processes, and contributes to overall health, making it a key nutrient for immune maintenance.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is critical for the formation of red blood cells, which are responsible for transporting oxygen throughout the body—a process vital for maintaining energy levels and immune function. Naturally, B12 is found predominantly in animal-derived foods, including dairy products, eggs, fish, liver, and other meats. Vegan or vegetarian individuals might face challenges obtaining enough B12 and often need supplements or injections prescribed under medical supervision to prevent deficiency. A deficiency in B12 can result in anemia, neurological issues, and weakened immune responses, emphasizing the importance of regular intake either through diet or supplementation for maintaining resilience against illnesses.
Vitamin C
Renowned as a potent antioxidant, vitamin C plays a crucial role in neutralizing free radicals—unstable molecules that can cause cellular damage and inflammation. It supports various immune cell functions, including the proliferation of white blood cells, which are essential for fighting infections. Vitamin C also enhances the skin's barrier function, acting as the body's first line of defense against pathogens. Consuming foods abundant in vitamin C, such as oranges, lemons, kiwis, papayas, broccoli, tomatoes, and guava, helps prevent deficiencies and supports rapid immune responses during illness or stress. Regular intake of vitamin C-rich foods can shorten the duration of colds and other respiratory illnesses and improve your overall immune resilience.
Vitamin D
This fat-soluble vitamin is unique because it can be synthesized in your skin through exposure to sunlight. It also exists in certain foods, such as fortified products, fatty fish (like salmon and sardines), liver, and eggs. Vitamin D is pivotal in regulating immune responses, reducing inflammation, and modulating the activity of immune cells including macrophages and T cells. Maintaining optimal levels through a combination of sunlight exposure and dietary sources helps bolster your immune defenses. However, excessive intake through supplements can lead to toxicity, so it’s essential to monitor levels under medical supervision. Adequate vitamin D status has been linked to decreased susceptibility to respiratory infections and improved overall immune health.
Vitamin E
As a powerful antioxidant, vitamin E supports the integrity of immune cells, helping to prevent the oxidative damage caused by free radicals. It is especially important in older adults, whose immune responses tend to weaken with age. Sources of vitamin E include nuts like almonds and hazelnuts, seeds such as sunflower seeds, vegetable oils (like sunflower and olive oil), avocados, mangoes, and leafy greens such as spinach and Swiss chard. While supplements are available, it is generally safer to achieve adequate vitamin E intake through diet, as high doses can have adverse effects. Ensuring sufficient vitamin E levels can enhance immune cell function and reduce the risk of infections.
In addition to focusing on vitamins, maintaining a balanced intake of zinc and iron—minerals essential for immune cell proliferation and function—supports overall immunity. Engaging in regular physical activity, ensuring at least six hours of quality sleep nightly, staying well-hydrated with eight glasses of water daily, and practicing good hygiene are critical lifestyle factors that complement nutritional strategies. Before starting any supplements, always seek advice from healthcare professionals to confirm appropriate dosages and product safety. Opt for licensed, high-quality supplements to avoid contaminants and ensure efficacy.