Understanding the Key Causes of Pregnancy Loss and Effective Prevention Strategies
This detailed article explores the primary causes of pregnancy loss, including genetic, hormonal, physical, lifestyle, and immune factors. It offers practical prevention tips such as health management, lifestyle modifications, and medical interventions. Understanding these contributors enables women and couples to take proactive steps for a healthier pregnancy. The guide emphasizes early diagnosis, regular health check-ups, and lifestyle adjustments to minimize risks and increase the likelihood of successful pregnancies. Empower yourself with knowledge to navigate pregnancy challenges effectively and improve outcomes.

Understanding Common Causes of Pregnancy Loss and How to Prevent Them
Experiencing pregnancy loss is a difficult and emotionally charged event for many expectant parents. It often brings about a mix of feelings including grief, guilt, anxiety, and confusion. While pregnancy loss can sometimes appear unpredictable and unavoidable, gaining knowledge about the potential causes can empower women and couples to take proactive steps toward promoting a healthier pregnancy in the future. This comprehensive guide explores the major factors that contribute to pregnancy loss, including genetic, physiological, lifestyle, and immunological components, along with practical prevention tips.
Genetic Abnormalities and Chromosomal Disruptions
One of the leading causes of pregnancy loss — especially in the first trimester — is genetic abnormalities affecting the developing fetus. Chromosomes carry genetic material vital for normal growth and development. Errors during cell division can result in abnormal chromosomal numbers or structures, such as trisomy 21 (Down syndrome). These abnormalities often prevent the fetus from developing properly, leading to miscarriage. Women over 35 face increased risk due to age-related reductions in egg quality, which increases the chances of chromosomal anomalies. Genetic counseling and testing can provide insights for couples experiencing recurrent pregnancy losses, enabling informed decision-making and planning for future pregnancies.
Thyroid Function and Hormonal Balance
Thyroid health plays a crucial role in pregnancy maintenance. Both hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) and hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) can impair fertility and elevate miscarriage risks. Excess thyroid hormones may interfere with fetal support and development, while insufficient thyroid hormone production can hinder ovulation and embryo implantation. Regular thyroid function testing, alongside appropriate medical management, helps ensure hormonal stability. Women planning pregnancy should undergo thyroid evaluation and work closely with healthcare providers to manage any underlying thyroid issues effectively.
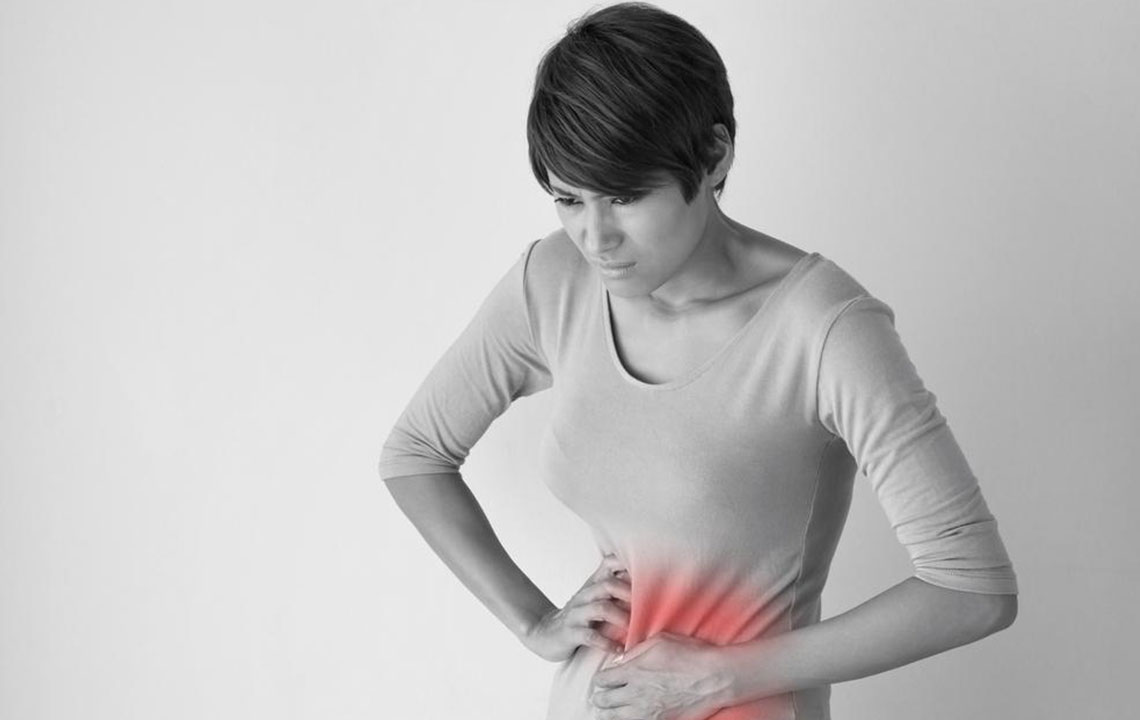
Physical Health Complications and Structural Abnormalities
Rare but impactful physical conditions can compromise pregnancy viability. Cervical weakness, often called incompetent cervix, may lead to premature cervical dilation, causing miscarriage during the second trimester. Structural uterine abnormalities such as septa, polyps, fibroids, or congenital anomalies can interfere with embryo implantation and growth. Detecting these issues through ultrasound imaging allows for surgical correction or other medical interventions to improve pregnancy outcomes, especially in women with a history of recurrent pregnancy loss.
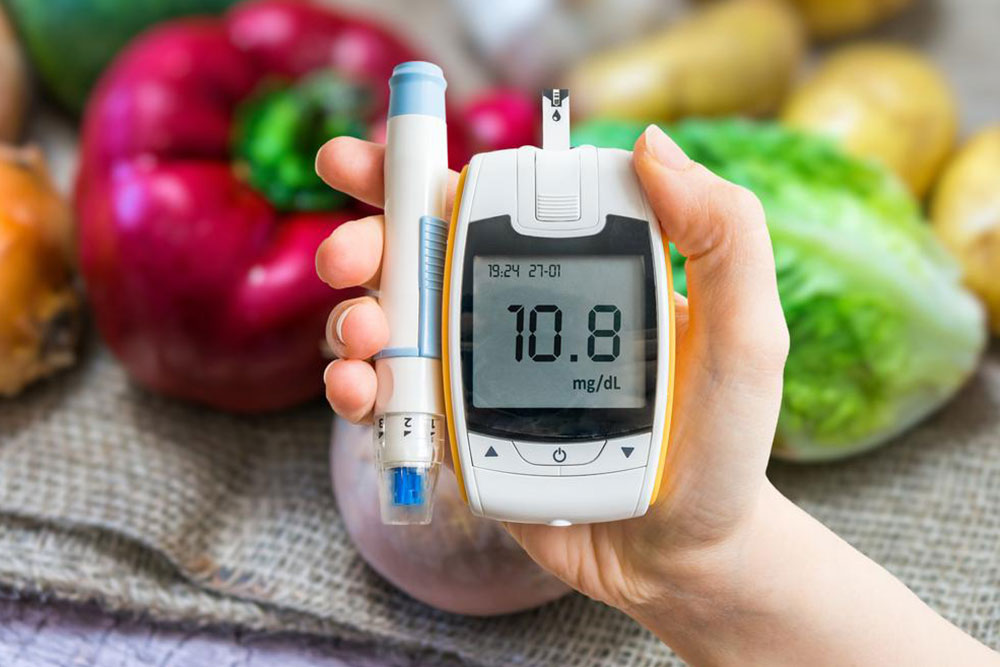
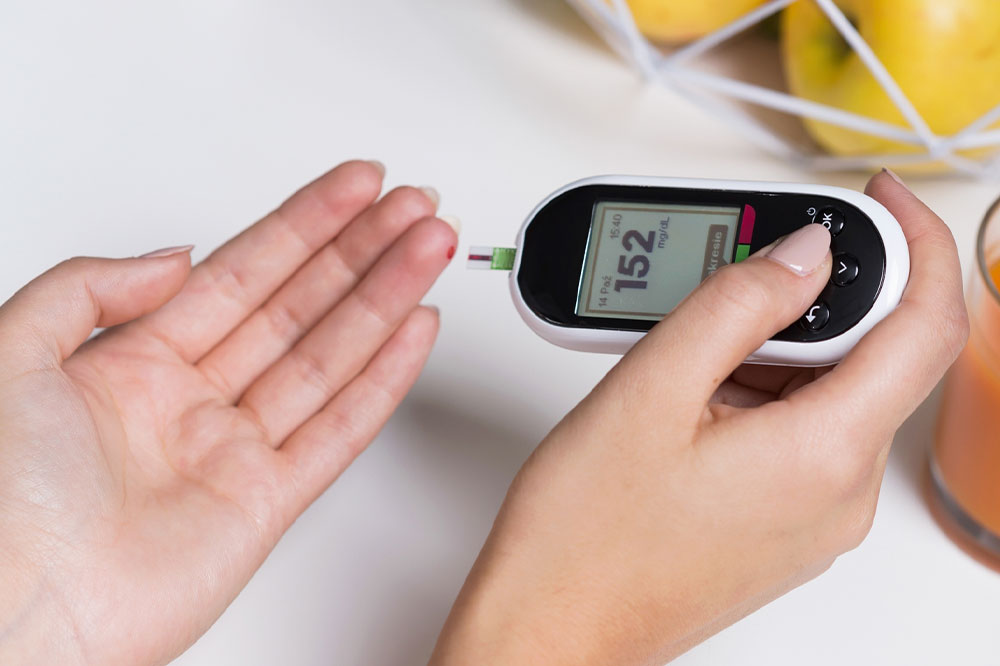
Blood Sugar Control and Diabetes Management
Uncontrolled diabetes, particularly pre-existing type 1 or type 2, poses significant risks during pregnancy. High blood sugar levels can damage the developing fetus and increase chances of miscarriage, birth defects, and complications like preeclampsia. Women planning pregnancies should optimize blood glucose management through dietary modifications, medication adjustments, and regular monitoring in collaboration with healthcare providers. Good glycemic control from preconception through pregnancy is vital for reducing miscarriage risks and supporting fetal health.
Lifestyle Choices and Their Impact
Unhealthy habits such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and illicit drug use have a detrimental effect on pregnancy viability. Tobacco contains toxins that can impair placental development and fetal growth, while alcohol and drugs can lead to developmental abnormalities or miscarriage. Women intending to conceive should prioritize cessation of harmful substances well before pregnancy and seek support if needed. Maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management are also key to promoting a healthy conception and pregnancy journey.
Blood Clotting Disorders and Thrombophilias
Certain blood conditions, like Factor V Leiden mutation, increase the risk of abnormal clot formation. These clots can obstruct blood flow to the placenta, depriving the fetus of essential nutrients and oxygen. Such disorders often lead to recurrent pregnancy losses. Testing for clotting disorders is advisable for women with multiple miscarriages. Treatments may include blood-thinning medications to reduce the risk of clot formation, thereby improving pregnancy outcomes.
Immune System Disorders and Autoimmune Conditions
Some immune system disorders, such as antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), are associated with an increased risk of miscarriage. These conditions cause the immune system to mistakenly attack the placenta or disrupt normal blood clotting processes. Women with autoimmune diseases like lupus should undergo comprehensive testing and, if necessary, receive immunosuppressive or anticoagulant medications to mitigate the risks. Proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plans significantly enhance the chance of a successful pregnancy.
Preconception planning that includes a thorough health assessment, balanced nutrition, prenatal vitamins, stable weight, and stress management practices can considerably reduce the risk of pregnancy loss. Seeking early medical consultation, adhering to prescribed treatments, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are essential steps for women aiming for a safe and healthy pregnancy. Awareness of these causes and preventive strategies empowers women and couples to approach pregnancy with confidence and preparedness, ultimately increasing the chances of a positive outcome.