Understanding the Most Common Symptoms of Asthma: A Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing Key Indicators
This comprehensive guide explores the seven most common symptoms of asthma, including breathlessness, chest tightness, and wheezing. Understanding these signs helps in early detection and effective management of the respiratory condition. From nighttime symptoms to emergency measures, learn how to identify and respond to asthma symptoms proactively for better respiratory health and quality of life.

Understanding the Most Common Symptoms of Asthma: A Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing Key Indicators
Asthma, medically known as bronchial asthma, is a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions worldwide. It is characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, which leads to difficulties in breathing. While there is no definitive cure for asthma, early detection and effective management of its symptoms can significantly improve quality of life for those affected. Recognizing the hallmark signs of asthma is essential for timely intervention, preventing severe attack episodes, and maintaining overall respiratory health.
In this detailed guide, we will explore the seven most common signs of asthma, providing insights into their causes, how they manifest, and tips for managing each symptom effectively. Whether you're a patient, caregiver, or healthcare professional, understanding these indicators can help address asthma promptly and improve patient outcomes.
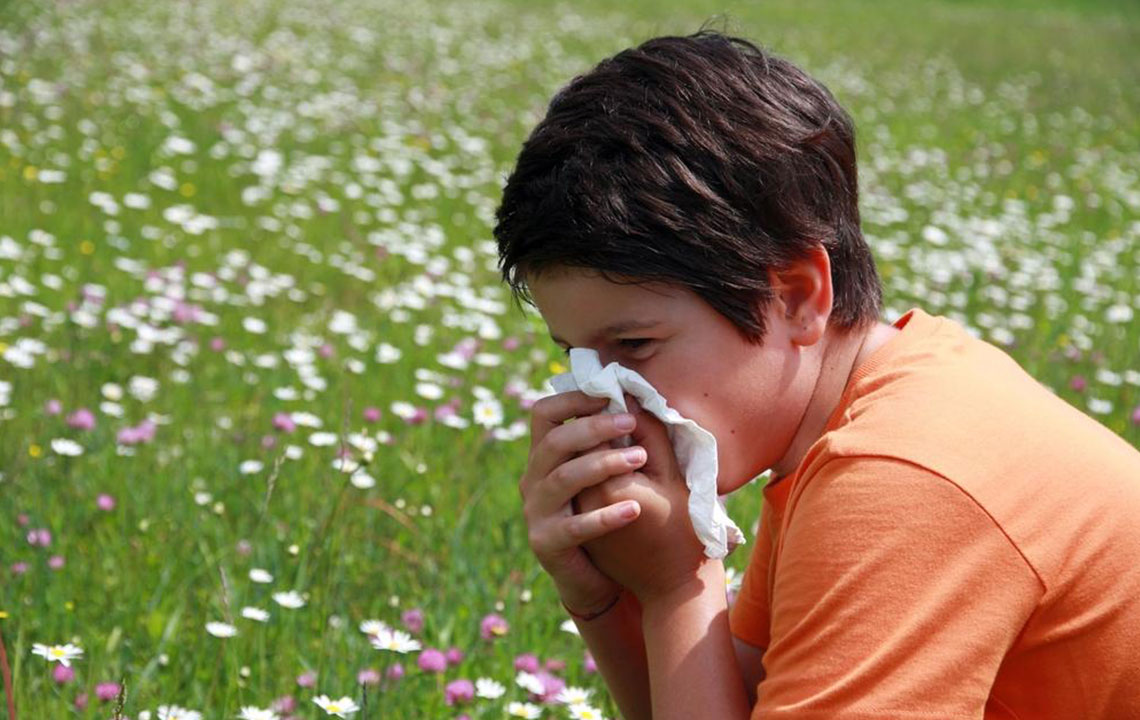
One of the primary triggers of asthma symptoms includes environmental allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and pollution. Exposure to these can cause airway muscles to tighten and the airways to become inflamed, leading to a cascade of symptoms. Understanding how these triggers influence asthma can help patients avoid exacerbations and manage their condition more effectively.
### 1. Shortness of Breath and Breathlessness
Difficulty breathing, also known as dyspnea, is often the first and most noticeable sign of asthma. Patients typically experience rapid, shallow breaths, feeling as if they can't get enough air. This sensation can be frightening and is usually associated with airway constriction caused by inflammation and muscle tightening in the bronchial tubes. During an asthma attack, the problem worsens as the airway becomes more blocked, making it difficult to breathe deeply or evenly.
When the airways narrow, oxygen intake diminishes, leading to a feeling of suffocation or a heavy chest. Patients may find themselves gasping for air, especially during physical activity or nighttime when symptoms tend to intensify. Recognizing the early signs of breathlessness enables individuals to seek immediate relief measures, such as using inhalers or seeking medical attention to prevent worsening of the attack.
### 2. Chest Discomfort and Chest Tightness
Chest tightness is a common complaint among asthma sufferers, often described as a feeling of pressure or constriction in the chest area. This symptom results from airway inflammation and mucus accumulation, which create an obstruction against normal airflow. During periods of exacerbation, the chest may feel sore or painful, and breathing can become laborious.
An overactive immune response triggers release of inflammatory mediators, which cause swelling within the airways and increased mucus production. These processes lead to the sensation of tightness, often accompanied by coughing and wheezing. Managing this symptom involves controlling airway inflammation through medication and avoiding known triggers.
### 3. Nocturnal Symptoms and Sleep Disturbances
Nighttime symptoms are a significant concern for many asthma patients. Many experience overnight wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath that disturb sleep patterns. Poor sleep quality affects overall health, mood, and daily functioning. It also increases the risk of severe nocturnal asthma attacks, which can be life-threatening.
Healthcare providers often recommend pre-bedtime inhaler use and advice on lifestyle adjustments to help improve sleep quality. This may include avoiding allergens in the bedroom, maintaining good air quality, and using medications as prescribed. Recognizing sleep disruptions as a symptom of asthma emphasizes the importance of comprehensive management to ensure restful nights for patients.
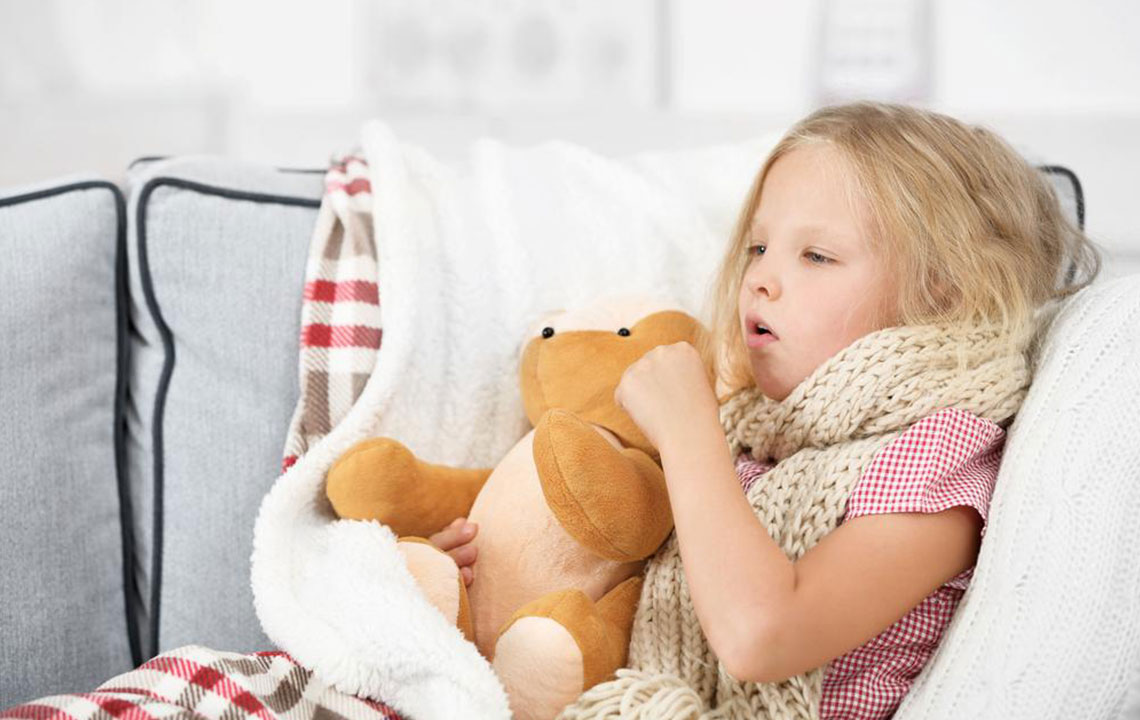
### 4. Persistent and Worsening Coughing
A chronic cough is a common symptom, especially during an asthma attack when airway inflammation and mucus buildup intensify. Coughing serves as the body's reflex to clear the constricted airways, but persistent coughing can itself become exhausting and disruptive to daily activities.
During an attack, swelling of airway tissues and the accumulation of mucus cause airway narrowing, prompting frequent bouts of coughing. Early recognition of this symptom, along with other signs such as wheezing and breathlessness, can prompt individuals to take appropriate medication or seek emergency care if necessary. Effective management of cough involves controlling inflammation and reducing trigger exposure.
### 5. Wheezing and Whistling Sounds During Breathing
Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound that occurs when air flows through narrowed or obstructed airways. It is one of the hallmark symptoms of asthma, especially during flare-ups, and indicates airway constriction and mucus secretion.
Wheezing may be more noticeable during exertion or when lying down. It reflects the degree of airway narrowing and airway hyperresponsiveness. Recognizing wheezing can help prompt early intervention with inhalers or other medications to avoid severe attack progression.
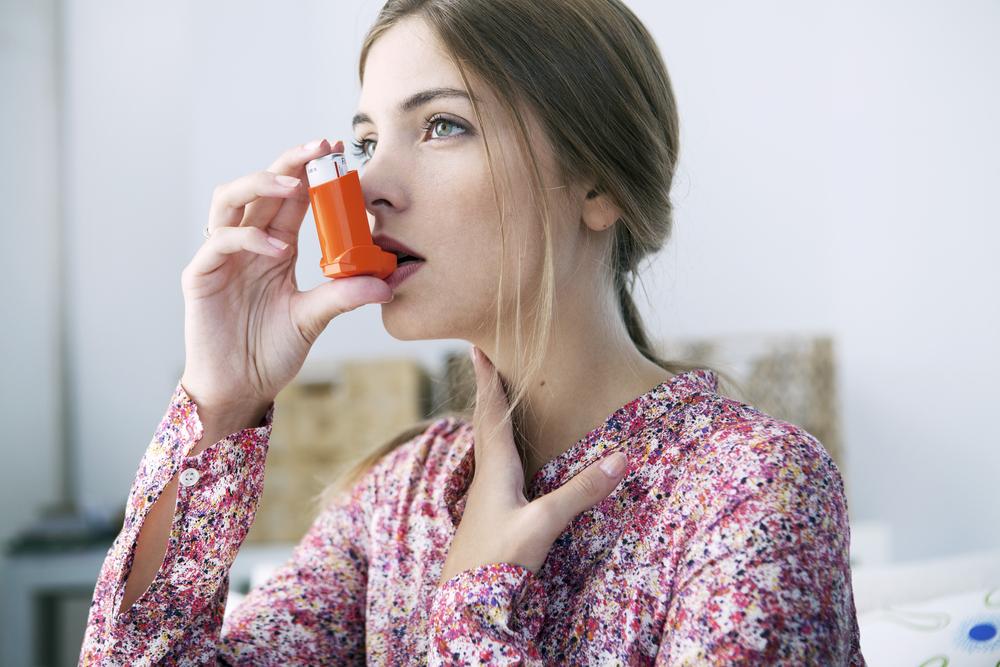
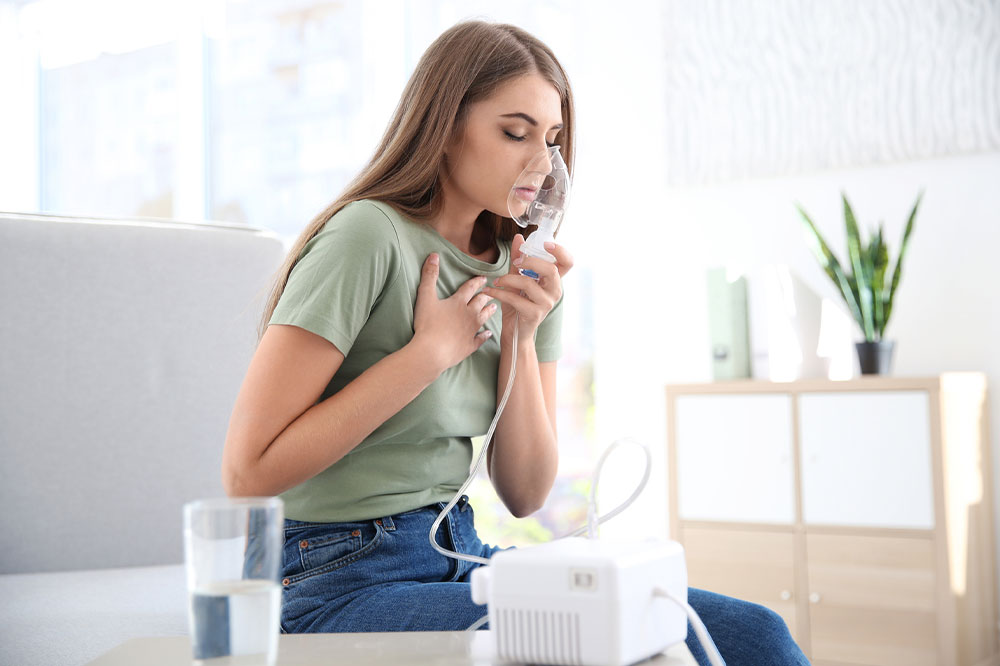
### 6. Use of Quick-Relief Inhalers and Emergency Measures
During an asthma attack, many individuals find immediate relief by using fast-acting inhalers, such as albuterol. While these inhalers are effective for rapid symptom relief, dependence on them without proper medical follow-up can lead to poor disease control.
It is essential for patients to use inhalers judiciously and under medical supervision. Overuse may mask escalating symptoms or lead to side effects, requiring alternative treatment plans or hospitalization. Educating patients about correct inhaler techniques and timing is vital for optimal asthma management.
### 7. Associated Signs: Elevated Heart Rate and Anxiety
In some cases, asthma attacks are accompanied by an increased heart rate (tachycardia) and sensations of anxiety or panic. These are physiological responses to oxygen deprivation and the body's stress response to breathing difficulty.
Elevated heart rate and blood pressure may compound the feeling of distress, intensifying the attack. Recognizing these signs is crucial, especially during severe episodes, to ensure prompt medical intervention. Managing distress and providing reassurance can also help alleviate anxiety-related symptoms associated with asthma.
In summary, understanding and recognizing these seven key signs of asthma are crucial steps toward effective disease management. Early detection allows for more timely treatment, reducing the risk of serious complications and improving overall respiratory health. Patients are encouraged to maintain regular medical check-ups, adhere to prescribed medications, and avoid known triggers to lead healthier, more comfortable lives with asthma.