Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Preventing Asthma Triggers for Better Respiratory Health
Managing asthma effectively requires identifying personal triggers and implementing comprehensive strategies such as avoiding allergens, reducing exposure to pollutants, and adhering to proper medication use. Lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, and professional guidance are key to controlling symptoms and preventing attacks, ultimately improving quality of life for asthma patients.

Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Preventing Asthma Triggers for Better Respiratory Health
Asthma is a prevalent chronic respiratory condition that affects millions worldwide, impairing lung function and causing episodes of wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing. The condition is driven by inflammation of the airways, which become hyperresponsive to specific triggers. These triggers can vary widely from person to person but commonly include allergens, environmental pollutants, respiratory infections, and lifestyle factors. While there is currently no cure for asthma, effective management strategies focus on controlling symptoms, reducing the frequency of attacks, and enhancing quality of life through proactive measures.
Understanding the key factors that trigger asthma episodes is critical for individuals seeking to maintain optimal respiratory health. Identifying personal triggers involves close observation and sometimes medical testing, allowing for tailored management plans. Once identified, avoiding or minimizing exposure to these triggers forms the cornerstone of effective asthma control.
Environmental allergens such as pollen, pet dander, dust mites, and mold are among the most common triggers. Implementing measures like regular cleaning, using air purifiers, and keeping indoor spaces dry can significantly reduce exposure. For outdoor allergens, monitoring local pollen forecasts and limiting outdoor activities during high pollen seasons can help prevent exacerbations.
Air pollution, tobacco smoke, and strong odors also pose significant risks for asthma sufferers. Staying indoors during smog alerts, avoiding cigarette smoke, and using natural or scent-free cleaning products can mitigate these risks. Physical activity is beneficial, but activities should be tailored to avoid overheating or excessive exertion that may trigger symptoms.
Infections, particularly respiratory viruses like the flu or common cold, can worsen asthma symptoms. Vaccinations, good hygiene practices, and prompt treatment of infections are essential preventative strategies.
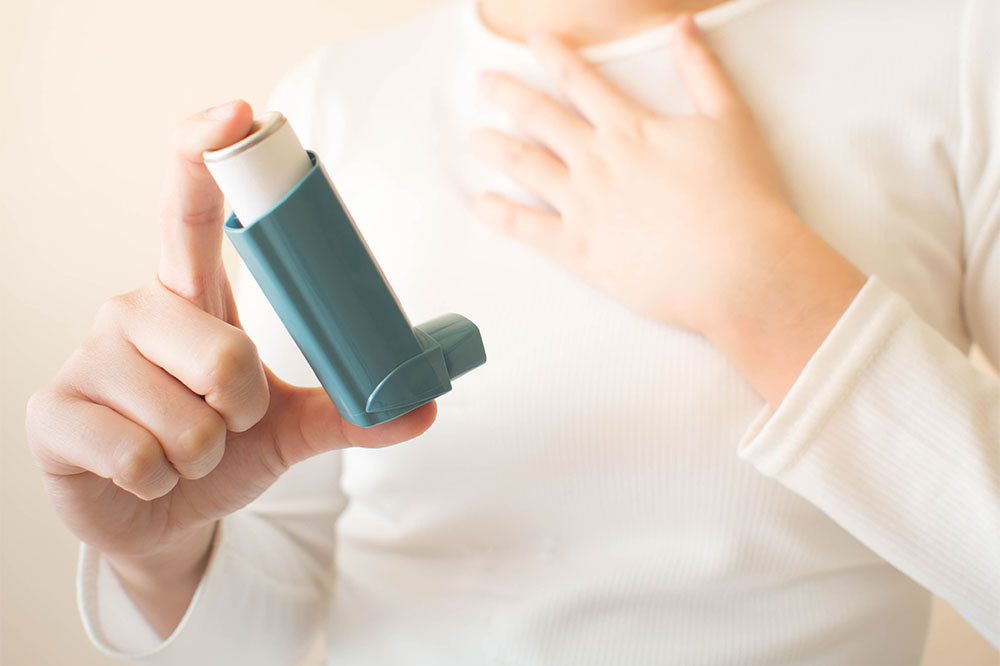
Effective use of inhalers and medications, as prescribed by healthcare professionals, is vital. Proper inhaler technique ensures optimal delivery of medication into the lungs. Regular medical check-ups enable adjustments to treatment plans based on symptom fluctuations and lung function tests.
Beyond medical management, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular exercise reduces overall inflammation and stress on the respiratory system. Avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke is essential as these are potent asthma triggers.
Daily symptom monitoring helps individuals recognize early signs of worsening asthma and take appropriate action promptly. This proactive approach empowers patients to manage their condition effectively and reduces emergency hospital visits.
Asthma management is an ongoing process that involves education, environmental control, appropriate medication use, and lifestyle adjustments. Support from healthcare providers, asthma education programs, and community resources can further enhance disease control and improve prognosis. By adopting these comprehensive strategies, individuals with asthma can lead healthier, more active lives with fewer limitations caused by their condition.