Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Controlling Asthma Symptoms Effectively
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for managing asthma symptoms, emphasizing medication, trigger avoidance, and lifestyle modifications. It offers valuable tips for controlling asthma and preventing attacks, enabling individuals to lead healthier lives despite this respiratory condition.
Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Controlling Asthma Symptoms Effectively
Asthma is a widespread chronic respiratory condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While the exact cause of asthma remains elusive, research indicates that a combination of genetic predisposition and exposure to environmental triggers plays a critical role in its development. Understanding how asthma impacts the respiratory system, recognizing its symptoms, and implementing effective management strategies are essential steps for patients seeking a better quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the nature of asthma, its triggers, treatment options, and advanced management techniques to help individuals live full and active lives despite this condition.
Asthma primarily involves inflammation of the bronchial tubes—the passageways that carry air in and out of the lungs. When these airways become inflamed, their lining swells, and the surrounding muscles tighten. This results in a narrowing of the airways, which significantly impairs airflow and causes the characteristic symptoms of asthma. These symptoms typically include chest tightness, wheezing with a high pitch, persistent coughing, especially at night or early morning, and shortness of breath. The severity and frequency of symptoms can vary greatly among individuals and may fluctuate with specific seasons, exposure to allergens, or physical activity.
The symptoms of asthma often worsen in response to specific triggers, which can be broadly categorized into environmental factors and personal health conditions. Common triggers include airborne allergens such as pollen, dust mites, mold spores, pet dander, and airborne pollutants like smoke and vehicle emissions. Cold air, strenuous exercise, respiratory infections, and strong odors may also precipitate asthma attacks. Recognizing personal triggers is vital in developing a proactive management plan tailored to individual needs.
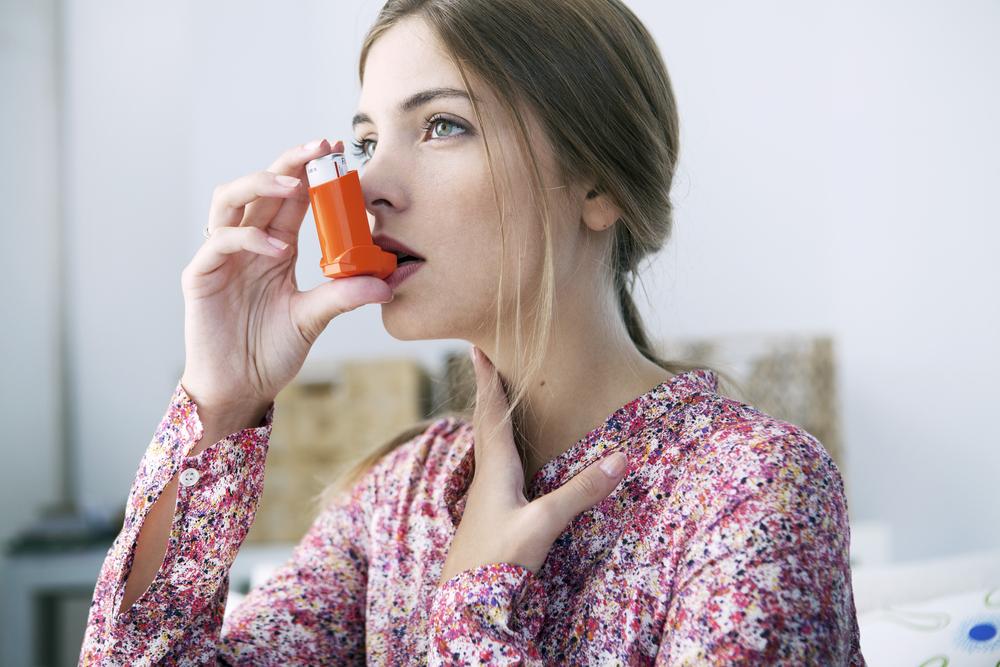
Effective asthma management hinges on a comprehensive understanding of the disease’s nature and a personalized approach to treatment. The cornerstone of controlling asthma is the use of prescribed inhalers, which serve two primary purposes: long-term control and quick relief. Long-term control medications aim to reduce airway inflammation and prevent severe attacks, while reliever inhalers provide rapid symptomatic relief during an attack. Mastering the correct use of these inhalers, maintaining regular medication schedules, and avoiding known triggers significantly reduce the risk of asthma exacerbations.
The primary long-term control medications include inhaled corticosteroids, which reduce airway inflammation, and long-acting beta-agonists, which keep airways open over extended periods. These medications are generally well-tolerated and pose fewer side effects than oral medications. Adherence to prescribed inhaler routines and consistent follow-up with healthcare providers are crucial for optimal outcomes. In addition to medication, lifestyle adaptations such as avoiding identified triggers, maintaining a healthy weight, and engaging in regular, appropriate physical activity contribute to better management.
Reliever inhalers, often containing short-acting beta-agonists, offer immediate relief during asthma flare-ups by relaxing airway muscles rapidly. Although effective, these should be used cautiously, as overuse can lead to decreased effectiveness and potential side effects such as tremors, rapid heartbeat, or feelings of anxiety. In severe or poorly controlled cases, healthcare providers might recommend additional therapies, including allergen immunotherapy or biologics, to better control symptoms and reduce attack frequency.
Beyond medication, identifying and minimizing exposure to asthma triggers is a central pillar of management. This may involve measures such as using air purifiers, reducing dust and mold, avoiding tobacco smoke, and implementing allergen desensitization protocols when appropriate. Regular monitoring of lung function through spirometry tests and maintaining an asthma action plan developed with a healthcare professional are essential components of ongoing care.
Living with asthma requires a proactive and informed approach. Patients should educate themselves about their condition, recognize early warning signs of worsening symptoms, and ensure they have access to emergency inhalers at all times. Lifestyle modifications, such as quitting smoking, managing stress, and maintaining good hygiene and respiratory health, further empower individuals to control their symptoms effectively and reduce the likelihood of severe attacks.
In summary, optimal asthma management involves a combination of appropriate medication, trigger avoidance, and lifestyle adjustments. Advances in treatment options and a better understanding of asthma’s underlying mechanisms continue to improve outcomes for individuals affected by this condition. Working closely with healthcare professionals to develop personalized management plans is key to maintaining healthy, active lives despite asthma.





