Comprehensive Guide to Exercise Strategies for Osteoporosis Management
This comprehensive guide offers essential strategies for managing osteoporosis through safe and effective exercise routines. It covers diagnosis, medical treatments, and specific workout types like weight-bearing, low-impact, strength, and balance exercises, providing a holistic approach for better bone health, fracture prevention, and improved quality of life for older adults.

Comprehensive Guide to Exercise Strategies for Osteoporosis Management
Osteoporosis is a widespread health condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide, particularly impacting older adults. According to recent statistics, approximately 53 million people in the United States alone are living with osteoporosis or are at increased risk of fractures due to weakened bones. This condition predominantly affects the wrist, spine, hip, and ribs, significantly increasing the risk of fractures that can severely impact quality of life. Early detection and effective management are crucial for improving outcomes and maintaining independence among those affected.
Understanding Osteoporosis: Causes and Symptoms
Osteoporosis develops when bone mineral density decreases, and the bones become fragile and more prone to fractures. Women face a higher risk, especially after menopause due to hormonal fluctuations that accelerate bone loss. Men, though less commonly affected, can also develop osteoporosis, particularly with aging or other health conditions. Typical early signs include reduced grip strength, brittle nails, receding gums, and sometimes, unnoticed small fractures. As the disease progresses, individuals may experience severe fractures after minor falls or stresses.
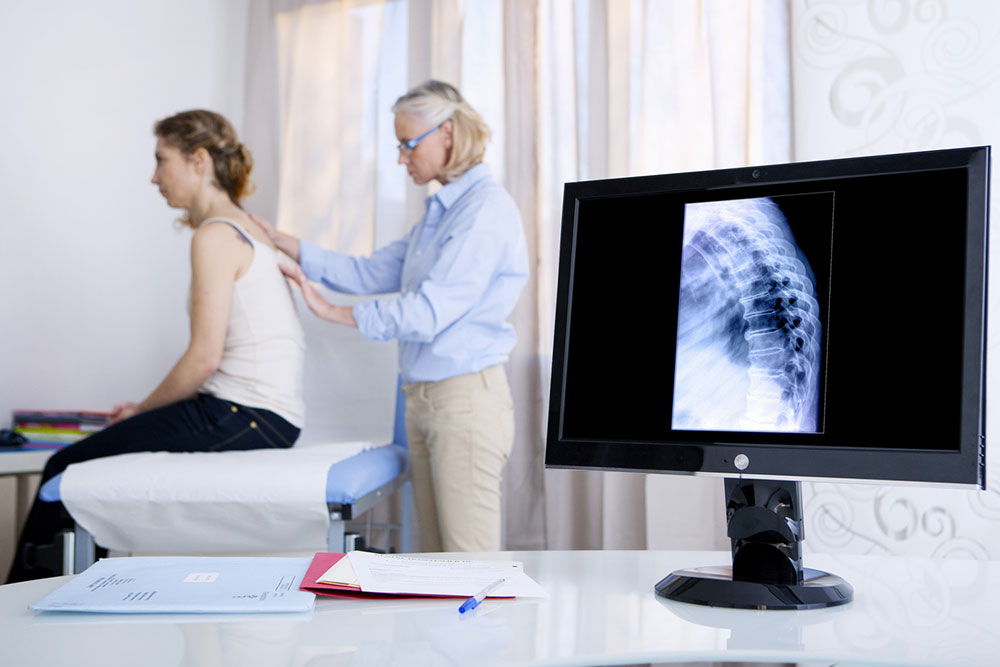
Diagnosing Osteoporosis
Early and accurate diagnosis is essential for effective management. Healthcare providers utilize a combination of physical examinations, laboratory tests—including blood and urine analyses—and detailed family medical histories. A key diagnostic tool is the Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) scan, a quick, non-invasive procedure that measures bone mineral density at high-risk sites such as the hips, spine, and wrists. A DEXA scan can typically be completed in under 30 minutes and provides critical information for diagnosing osteoporosis, assessing fracture risk, and tailoring treatment plans.
Comprehensive Treatment Approaches
While prevention remains challenging, current treatments focus on slowing disease progression, alleviating symptoms, and promoting bone regeneration. Medical interventions often involve a combination of medications, nutritional supplements, and customized exercise routines tailored to individual needs. Hormone replacement therapies, such as estrogen for women and testosterone for men, are utilized to counteract hormonal deficits that contribute to bone loss, especially around menopause. Additionally, calcitonin-salmon injections are prescribed to reduce spinal fractures, although they do not significantly impact hip fracture risk.
Exercise and Physical Activity: Cornerstones of Osteoporosis Management
Engaging in regular exercise is essential for managing osteoporosis effectively. However, it requires careful planning and professional supervision to minimize fracture risk. Proper exercise routines help strengthen muscles, improve balance, enhance flexibility, and stimulate bone growth, thereby reducing the likelihood of falls and fractures. Here, we explore various safe and effective workout strategies suitable for individuals with osteoporosis.
Weight-Bearing Exercises
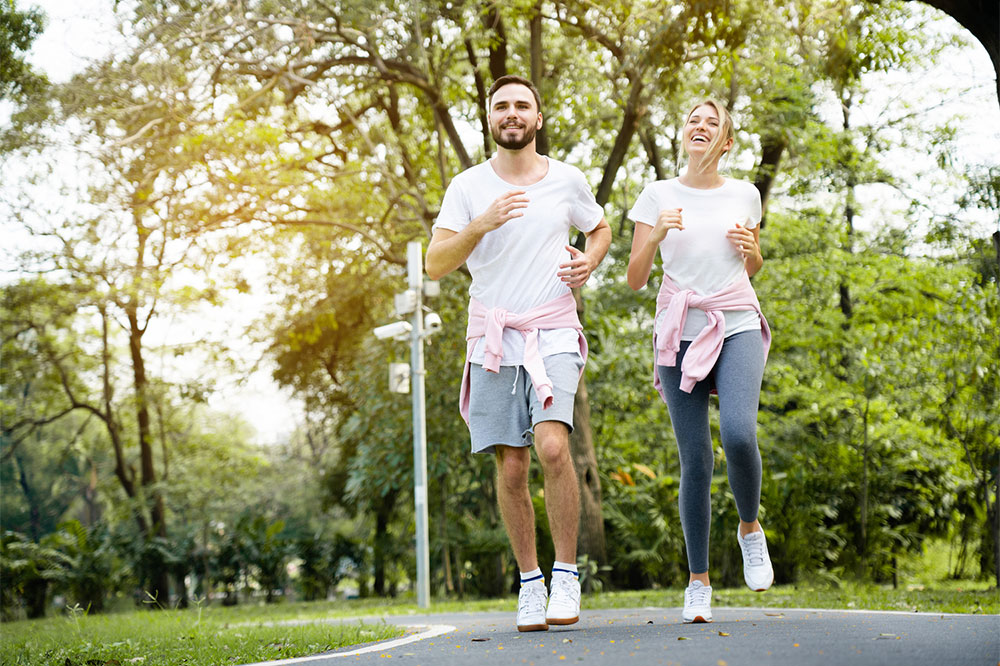
Despite the fragility of osteoporotic bones, weight-bearing activities are vital because they help stimulate bone remodeling and growth through hormonal responses. Incorporating activities such as walking, jogging, stair climbing, hiking, and low-impact aerobic exercises can promote increased bone density and muscular strength. These activities, when performed consistently—ideally several times a week—can make a significant difference in maintaining bone health and preventing further deterioration.
Low-Impact and Gentle Exercises
For individuals with advanced osteoporosis or those who are particularly vulnerable to fractures, low-impact exercises are safer and still highly beneficial. Consulting with healthcare providers is essential to ensure exercises are appropriate. Suitable options include elliptical trainer workouts, water aerobics, modified aerobic routines, stair steppers, and treadmill walking. These activities should ideally be performed for about 30 minutes per session, five days a week, to attain health benefits while minimizing risks.
Muscle Strengthening and Resistance Training
Enhancing muscle strength not only improves overall stability but also positively influences bone density. Resistance training exercises using resistance bands, light weights, dumbbells, or weight machines can be integrated into weekly routines. Engaging in strength training at least twice a week can dramatically improve muscle mass, support joints, and reduce fracture risk. Strengthening exercises also help improve balance and coordination, which are crucial for fall prevention.
Flexibility and Balance Exercises
Activities that promote flexibility and improve balance play a vital role in osteoporosis management. Practices such as Tai Chi, gentle yoga, and Pilates can help enhance posture, stability, and overall coordination. These exercises are gentle on bones but effective in reducing fall risk. Additionally, cycling and swimming can be incorporated for cardiovascular health benefits without putting undue strain on fragile bones. Regular participation in these activities can significantly enhance quality of life and independence among osteoporotic individuals.
In summary, a multifaceted approach combining medical treatments, nutritional support, and a well-structured exercise regimen is essential for managing osteoporosis. Tailored physical activity programs, guided by healthcare professionals, can improve bone health, reduce fracture risk, and enhance overall well-being. Living with osteoporosis requires ongoing attention, but with proper management strategies, individuals can maintain active and fulfilling lives well into their senior years.