7 Worst Foods That Can Worsen Respiratory Health Issues and How to Avoid Them
This comprehensive guide explores the top seven foods that can worsen respiratory issues such as asthma. It offers insightful advice on avoiding triggers like eggs, soda, bread, dried fruits, dairy, shellfish, and mushrooms to better manage breathing difficulties. Learn how diet impacts respiratory health and discover practical tips to promote healthier choices for improved lung function and overall well-being.

Respiratory health problems, including conditions like asthma, chronic bronchitis, and other airway-related disorders, significantly impact millions of individuals worldwide. These conditions are characterized by breathing difficulties, wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness, often triggered or worsened by various environmental and dietary factors. While medication, inhalers, and lifestyle modifications are key components of managing respiratory illnesses, emerging research indicates that diet also plays a critical role in either alleviating or exacerbating symptoms. Recognizing and avoiding foods that may trigger respiratory distress is vital for those affected.
Understanding the link between diet and respiratory health can help individuals better control their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Certain foods contain components that can provoke allergic reactions, increase mucus production, or cause inflammation—all of which can impair normal breathing. Below is an in-depth exploration of the top seven foods that are commonly associated with worsening respiratory problems, alongside practical tips for identification and avoidance.
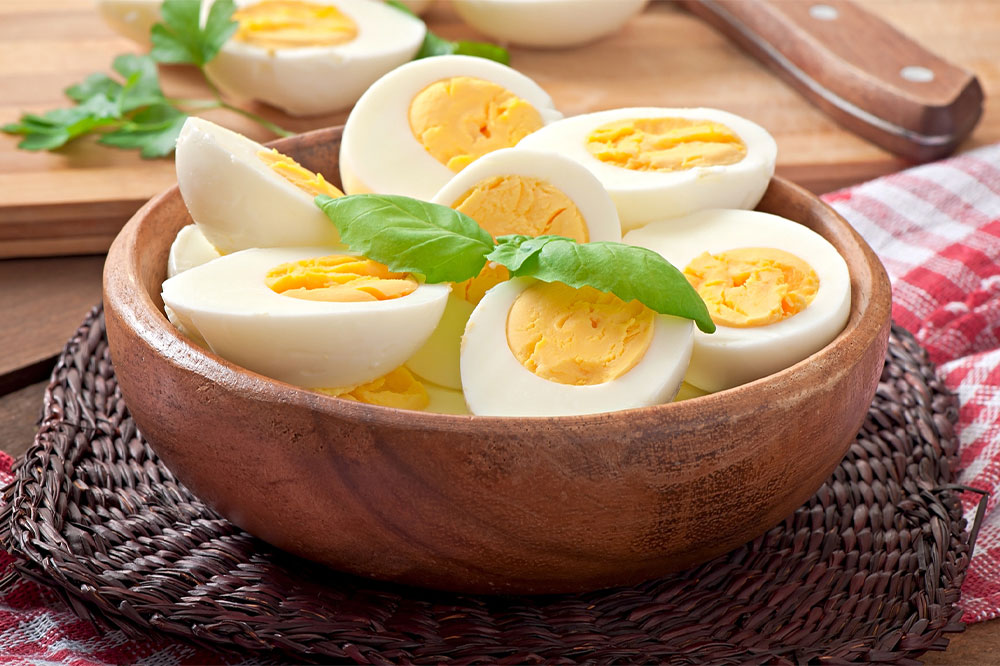
1. Eggs: Nutrient-Rich but Potentially Problematic for Allergic Individuals
Eggs are a highly nutritious food, packed with high-quality protein, vitamins, and minerals. They are a staple in many diets due to their versatility and nutritional value. However, eggs are also a common allergen, particularly in children, and some adults may develop sensitivities over time. For those with egg allergies or sensitivities, consuming eggs can lead to inflammatory responses, which may exacerbate respiratory conditions such as asthma.
For susceptible individuals, ingestion of eggs can trigger airway inflammation, swelling, and increased mucus secretion, which aggravates breathing difficulties. Symptoms may include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, or even asthma attacks. It is essential for people with known egg allergies to strictly avoid eggs and egg-containing products, including baked goods or processed foods that may contain egg derivatives.
2. Carbonated Beverages: How Sodas Can Impact Lung Function
Soda and other carbonated drinks are popular beverages globally, often consumed for their taste and stimulating effect. Despite their popularity, these effervescent drinks pose risks for individuals with respiratory problems. The carbonation process releases carbon dioxide gas, which can lead to bloating and excess gas in the stomach, putting pressure on the diaphragm. This pressure can hinder proper lung expansion and complicate breathing, especially for asthmatics.
Additionally, many sodas are high in sugar and artificial additives, which can promote systemic inflammation—a factor linked to worsening respiratory conditions. The presence of caffeine in certain sodas may also serve as a stimulant that impacts respiratory health. For those with asthma or other airway issues, it's advisable to limit or avoid sugary carbonated beverages and opt for healthier alternatives like water or herbal teas.
3. Wheat and Bread: Gluten Sensitivities and Respiratory Inflammation
Wheat-based products, including bread, pasta, and baked goods, are dietary staples for many. Rich in carbohydrates, they provide energy and comfort foods for countless people. However, in individuals with gluten sensitivity, wheat consumption can induce immune responses leading to inflammation not only in the gut but possibly throughout the body, including the respiratory system.
For susceptible individuals, consuming bread and other gluten-containing products may trigger airway inflammation, increase mucus production, and exacerbate asthma symptoms. Some people might also experience allergic reactions to grains, which can present with respiratory symptoms as part of their manifestation. For these reasons, those with known gluten sensitivities or celiac disease should consider gluten-free alternatives to manage their respiratory health effectively.
4. Dried Fruits: Nutritional Powerhouses with Hidden Risks
While dried fruits like raisins, apricots, and cranberries are often promoted for their health benefits—such as providing fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants—they also contain preservatives and chemical additives, notably sulfites. Sulfites are commonly used as preservatives to prolong shelf life and prevent oxidation but can be problematic for individuals sensitive to these chemicals.
For those with asthma, sulfites can act as potent triggers, potentially causing bronchospasm, inhalation reactions, and worsening respiratory symptoms. Symptoms may include coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, or even a full-blown asthma attack. To mitigate such risks, it is advisable for susceptible individuals to limit or avoid dried fruits with added sulfites and opt for fresh fruits or sulfite-free dried options.
5. Milk and Dairy Products: Mucus Production and Respiratory Discomfort
Dairy products such as milk, cheese, yogurt, and butter are common dietary components that provide calcium and other vital nutrients. However, many individuals report that dairy consumption leads to increased mucus thickening and production within the respiratory tract. Although scientific evidence on this matter remains mixed, anecdotal reports and some studies suggest that dairy can exacerbate symptoms in people with asthma or bronchitis.
Excess mucus can clog airways, make breathing more difficult, and increase the frequency of coughing and respiratory infections. People prone to respiratory issues are encouraged to monitor their responses to dairy intake and consider reducing or eliminating dairy products if they notice a pattern of increased congestion or breathing difficulties.
6. Shellfish and Seafood: Allergens That Trigger Respiratory Attacks
Shellfish, including shrimp, crab, oysters, clams, and lobster, are highly nutritious sources of protein and omega-3 fatty acids. However, they are also among the most common food allergens, especially for individuals with seafood allergies. Reactions to shellfish can be severe and include respiratory symptoms such as wheezing, throat tightness, nasal congestion, and even asthma attacks.
Moreover, some shellfish contain sulfites and other preservatives that can trigger bronchospasms in sensitive individuals. It's crucial for seafood-allergic persons to avoid shellfish entirely and be cautious about contamination or cross-contact in restaurants or processed foods. If you have a known seafood allergy and respiratory issues, carrying an epinephrine auto-injector and consulting with an allergist are essential steps toward safety.
7. Mushrooms: Mold-Related Respiratory Irritants
Mushrooms are fungi that are part of many cuisines worldwide. While they are low in calories and high in nutrients, they pose a specific risk for respiratory health because of their association with mold and mildew. Mushrooms can release spores and airborne allergens that can irritate the respiratory system, particularly in sensitive individuals.
People with mold allergies or respiratory conditions like asthma may experience worsened symptoms after consuming mushrooms or being exposed to mushroom spores in the environment. Therefore, they should limit their intake of mushrooms and avoid mushroom-derived products like powders, extracts, or supplements if they are prone to mold sensitivities.
Practical Strategies for Managing Diet-Related Respiratory Triggers
Identifying which foods may negatively impact respiratory health requires attentive observation and possibly consultation with healthcare professionals. Keeping a food diary can help track reactions and pinpoint problematic foods. Reading labels carefully is essential, especially since many processed foods contain hidden allergens or preservatives.
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fresh fruits (excluding dried varieties with sulfites), vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can support respiratory health. Hydration also plays a key role in thinning mucus and maintaining optimal lung function.
Consulting with a registered dietitian or allergist can provide personalized guidance and ensure nutritional adequacy while avoiding specific triggers. For individuals with known allergies or sensitivities, strict avoidance is crucial to prevent severe reactions and improve overall respiratory well-being.
Conclusion
While respiratory conditions like asthma involve complex factors including genetics, environment, and lifestyle, diet remains an influential component that should not be overlooked. By understanding which foods can aggravate symptoms and making informed dietary choices, individuals can better manage their respiratory health and improve their quality of life. Awareness and prevention are key steps toward breathing easier and living healthier lives amidst these dietary considerations.