Comprehensive Guide to Accelerate Healing of Shin Splints
This comprehensive guide offers effective strategies to heal shin splints quickly, emphasizing the importance of rest, cold therapy, supportive footwear, physiotherapy, and prevention tips. Learn how to manage symptoms and prevent future injuries with targeted treatment and proper training habits, ensuring faster recovery and sustained injury-free activity.
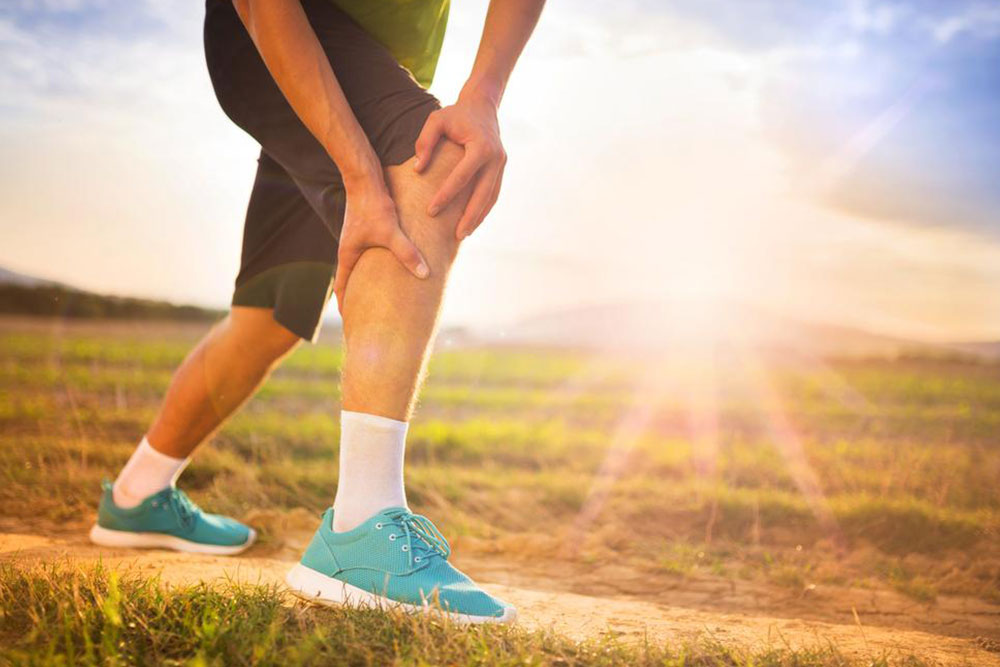

Comprehensive Strategies to Accelerate Healing of Shin Splints
Shin splints, medically known as medial tibial stress syndrome, are a prevalent injury among runners, athletes, and individuals engaged in high-impact activities. This condition manifests through pain along the inner edge of the tibia—often the result of overuse, improper training techniques, or sudden increases in activity intensity. If not addressed promptly, shin splints can lead to prolonged discomfort, diminished performance, and even more severe injuries. Therefore, understanding effective recovery methods is essential for timely rehabilitation and injury prevention.
Shin splints typically develop due to a combination of factors, including poor biomechanics, inadequate footwear, inappropriate training surfaces, muscle imbalances, and insufficient rest periods. Addressing these underlying causes alongside effective treatment strategies can significantly shorten recovery time.
Prompt and comprehensive intervention can alleviate symptoms and support the healing process. The key to successful recovery involves a multifaceted approach that combines rest with targeted therapies and gradual reconditioning. By following best practices, athletes and active individuals can return to their routines safely and prevent recurrence of this disruptive injury.
Understanding the Causes of Shin Splints
Before diving into treatment strategies, recognizing the common causes of shin splints helps in both recovery and prevention:
Poor Running Form: Improper biomechanics can place excessive stress on the tibia and surrounding tissues.
Inadequate Footwear: Worn-out shoes or those lacking arch support contribute to abnormal stress distribution.
Surface Impact: Running or exercising on hard or uneven terrains increases tibial stress.
Overtraining: Increasing intensity or duration too rapidly leaves muscles and bones ill-prepared for the workload.
Muscle Imbalances and Weaknesses: Tight calf muscles or weak tibialis anterior weaken shock absorption.
Misaligned Technique: Overpronation or supination can cause uneven stress.
Effective Treatment Strategies for Shin Splints
Recovery from shin splints requires a combination of rest and active treatment measures. The ultimate goal is to reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and restore normal function without causing further injury. Here are comprehensive strategies to promote healing:
1. Rest and Activity Modification
Taking adequate rest is vital in halting the progression of injury. Avoid high-impact activities such as running, jumping, or intense sports, at least until pain subsides. Replacing high-impact workouts with low-impact alternatives like swimming, cycling, or ellipticals allows cardiovascular activity to continue without aggravating the injury. Rest periods vary based on injury severity but typically range from several days to a few weeks.
2. Cold Therapy to Reduce Swelling and Pain
Applying ice packs or cold compresses directly to the affected area helps constrict blood vessels, reducing swelling and easing discomfort. For effective results, apply ice for 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours during the first 48 hours after pain onset. Always place a thin cloth between the ice and skin to prevent frostbite. Cold therapy is especially beneficial immediately after activity or when swelling worsens.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Over-the-counter NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen can effectively control inflammation and pain. However, these should be used judiciously and in accordance with medical advice, as long-term use can cause side effects. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any medication regimen for shin splints.
4. Gentle Mobility and Stretching Exercises
Once acute pain subsides, gentle mobility exercises aid in restoring normal joint movement. Stretching the calf muscles, Achilles tendon, and tibialis anterior strengthens tissues and prevents compensatory flaws. Examples include toe raises, calf stretches against a wall, and ankle circles. These exercises should be performed gradually and without pain, preferably under the guidance of a physiotherapist.
5. Use of Orthotics and Supportive Footwear
Proper footwear that offers adequate arch support and shock absorption can alleviate stress on the tibia. Custom orthotics designed by a podiatrist are highly effective in correcting biomechanical issues such as overpronation. Supporting the arch minimizes abnormal stress distribution, reducing the risk of future shin splints.
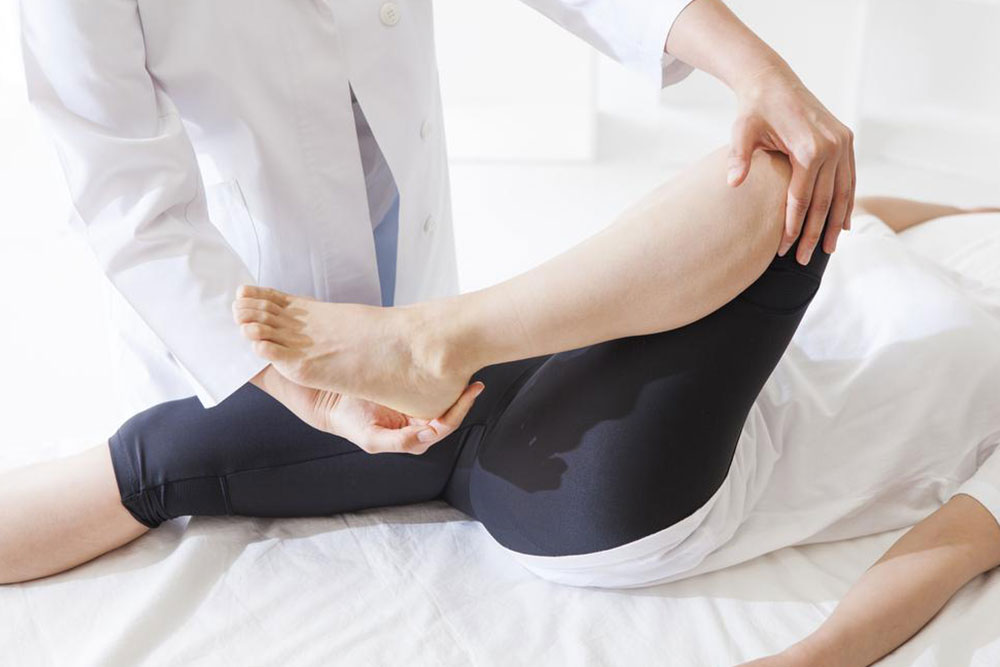
6. Physiotherapy and Tailored Rehabilitation Programs
Consulting a physiotherapist ensures a targeted approach to recovery. Therapists may employ techniques such as soft tissue massage, dry needling, ultrasound therapy, or taping. They also develop personalized exercise programs aimed at strengthening lower leg muscles, correcting gait mechanics, and improving flexibility. Consistent physiotherapy accelerates healing and enhances overall recovery outcomes.
Prevention and Long-Term Care for Shin Splints
Prevention is often more effective than treatment. Long-term management involves adopting proper training habits, equipment, and biomechanical correction:
Gradually increase workout intensity and volume, allowing tissues to adapt.
Ensure footwear is suitable for your foot type and replaced regularly.
Incorporate cross-training routines to reduce repetitive stress on specific muscle groups.
Always include proper warm-up and cool-down sessions in your exercise regimen.
Maintain calf and lower leg flexibility through regular stretching.
Address any biomechanical abnormalities with professional evaluation and correction.
By following these comprehensive strategies, you can recover from shin splints more rapidly and significantly reduce the likelihood of recurrence. Patience and adherence to a personalized rehabilitation program are key to returning to your preferred physical activities safely and efficiently.