Understanding Bursitis: Causes, Prevention Strategies, and Tips for Maintaining Joint Health
Bursitis is a common joint condition caused by various factors such as injury, repetitive pressure, and infections. This detailed article explores the main causes of bursitis, risk factors, and effective prevention tips. Understanding how to maintain healthy joints through proper ergonomics, weight management, and injury prevention can significantly reduce your chances of developing this painful condition. Prompt medical attention is essential if symptoms persist, helping avoid complications. Stay informed about bursitis causes and take proactive steps to safeguard your joint health and enjoy a pain-free, active lifestyle.
Understanding Bursitis: Causes, Prevention Strategies, and Tips for Maintaining Joint Health
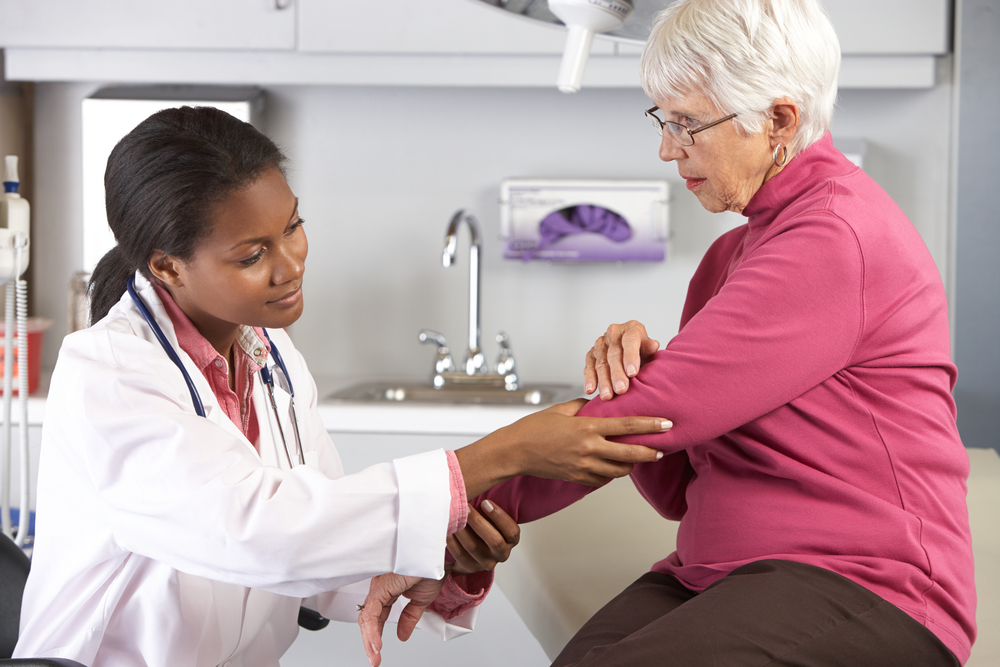
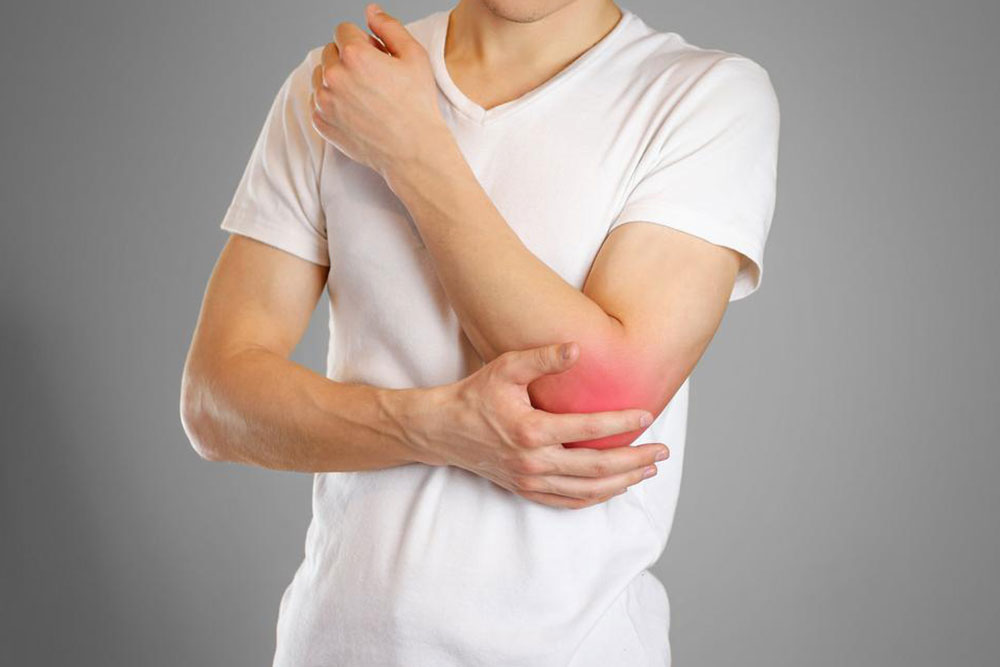
Bursae are tiny, fluid-filled sacs situated around our joints, serving as natural cushions that enable smooth and painless movement between bones, tendons, and skin. These sacs play a crucial role in reducing friction and absorbing shock during joint activities. However, when bursae become inflamed, it results in a condition known as bursitis. This condition can cause significant discomfort, swelling, warmth, redness, and in some cases, limited mobility. Understanding the various causes of bursitis is essential for effective prevention and management. Bursitis can affect any joint in the body, especially areas subjected to repeated stress or trauma, such as knees, elbows, hips, and heels.
While bursitis can develop unexpectedly due to injuries, repetitive motions, infections, or underlying health issues, proactive measures can significantly reduce your risk of developing this painful condition. Recognizing the common causes and adopting preventive strategies can promote healthier joints and improve quality of life.
Bursitis is classified into various types, each with specific causes related to the affected joint. A detailed understanding of these types helps in identifying risk factors and implementing targeted preventive measures.
Prepatellar bursitis - Often referred to as kneecap bursitis, this type commonly results from frequent kneeling (such as in certain sports or occupational activities), direct trauma or injury to the knee, or infections that enter through cuts or abrasions over the knee cap.
Olecranon bursitis - Typically affects the elbow, caused by prolonged resting on hard surfaces, repetitive elbow movements, or impact injuries. It may also occur due to infections or inflammation resulting from cuts near the elbow.
Trochanteric bursitis - Involves inflammation of the bursae near the hip's outer part, triggered by falls, hip injuries, prolonged lying on one side, poor posture, or systemic conditions like arthritis, gout, or infections.
Retrocalcaneal bursitis - Also known as Achilles bursitis, caused by repetitive activities like running or jumping, especially if done without proper warm-up, or by wearing tight shoes that exert pressure on the heel.
Understanding additional risk factors is vital for prevention. Systemic diseases such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and diabetes can predispose individuals to bursitis. Obesity and a sedentary lifestyle increase joint stress, raising the likelihood of inflammation. Certain occupations that require frequent kneeling, lifting heavy objects, or repetitive motions, like construction work or cleaning, are more prone to bursitis development. Recognizing these risk factors enables individuals to take proactive measures to safeguard their joint health.
Prevention Tips and Strategies for Bursitis
Preventing bursitis involves moderate lifestyle adjustments, maintaining proper joint function, and avoiding activities that cause excessive pressure or trauma. Here are some practical tips to reduce your risk:
Proper Ergonomics: Use supportive footwear and ergonomic furniture to reduce pressure on knees, elbows, hips, and heels.
Gradual Training: Engage in warm-up exercises before intense physical activity, and gradually increase the intensity of workouts to prevent trauma.
Protective Gear: Wear pads or braces during sports or occupational tasks that involve kneeling, lifting, or impact.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts additional stress on joints, increasing inflammation chances.
Avoid Repetitive Movements: If your work involves repetitive motions, take frequent breaks and stretch regularly.
Injury Management: Treat cuts, abrasions, or impact injuries promptly to prevent infections that may lead to bursitis.
Manage Underlying Conditions: Control systemic illnesses like gout, arthritis, or diabetes through appropriate medical care.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience persistent joint pain, swelling, warmth, redness, or reduced mobility, consult a healthcare professional promptly. Accurate diagnosis often involves physical examination, imaging tests, and sometimes joint fluid analysis. Early intervention can prevent bursitis from becoming chronic or leading to complications like infections or joint damage.
In summary, bursitis is a common but preventable condition that affects many individuals, especially those engaged in physical activities, certain occupations, or with underlying health issues. Recognizing the causes and risk factors empowers you to take vital steps toward protecting your joints. Maintain an active lifestyle, adopt proper ergonomic practices, and seek timely medical advice when needed to keep bursae healthy and prevent painful episodes.