Understanding How Lifestyle Choices Elevate Gout Risk and How to Prevent It
This comprehensive article explores the top lifestyle habits that increase the risk of gout, including diet, hydration, weight, and alcohol consumption. It offers practical tips for reducing risk through healthier routines, such as balanced dieting, proper hydration, and weight management. Understanding these links helps individuals make informed lifestyle choices to prevent gout flare-ups and manage symptoms effectively, leading to improved joint health and overall well-being.

Understanding How Lifestyle Choices Elevate Gout Risk and How to Prevent It
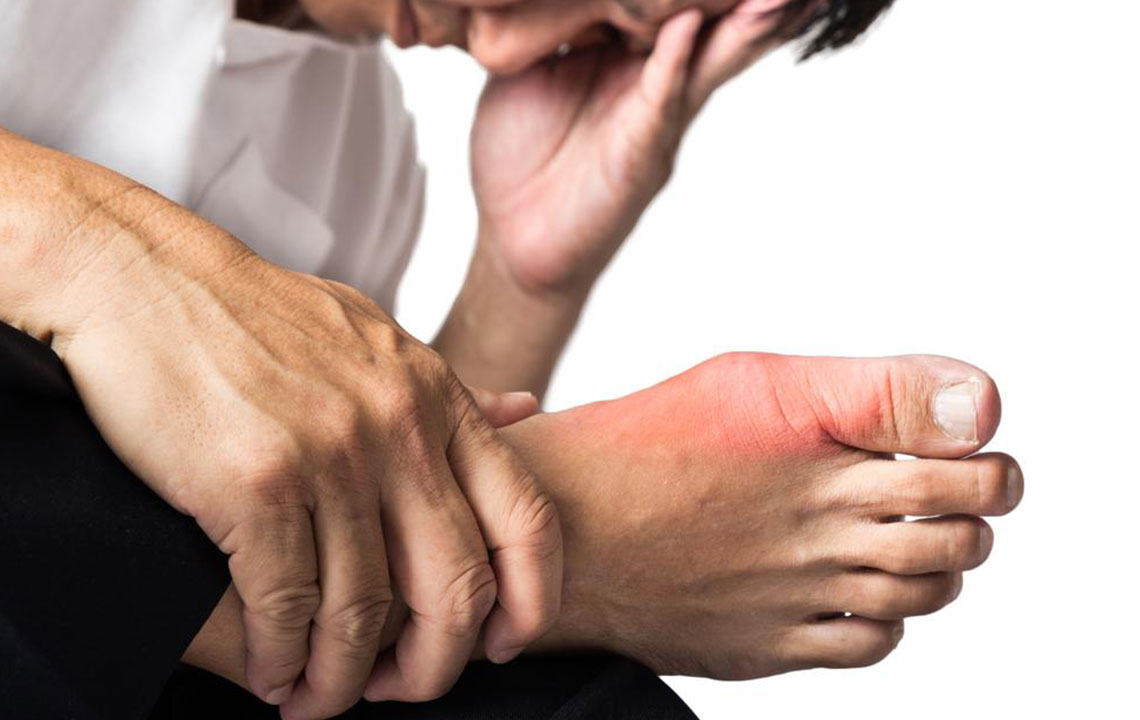
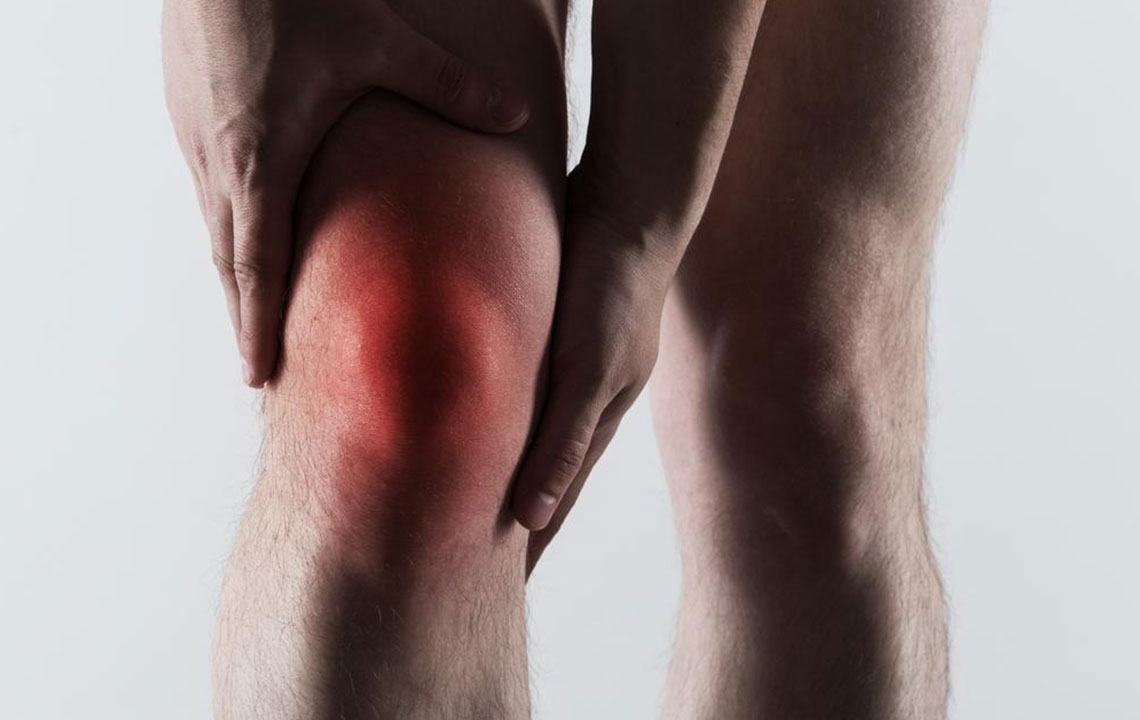
Gout is a common and often painful form of inflammatory arthritis that affects millions worldwide. In the United States alone, approximately 8.3 million adults suffer from this condition, characterized by sudden and intense pain, swelling, and stiffness typically occurring in the big toe but sometimes affecting other joints. The disease results from the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, which leads to inflammation and severe discomfort. While genetics and certain medications play a role in gout development, lifestyle factors significantly influence the likelihood of experiencing gout attacks. Understanding and modifying these habits can be crucial in reducing the risk and managing symptoms effectively.
Several habitual behaviors are linked to increased uric acid levels, thus raising the chances of gout episodes. These behaviors often revolve around dietary choices, hydration status, body weight, and consumption of certain substances like alcohol. By making informed lifestyle modifications, individuals can greatly minimize their risk of developing gout or experiencing flare-ups. Here, we explore the top habits that contribute to gout risk and offer practical advice on how to adopt healthier routines.
1. Extreme Dieting and Fasting: Causes and Consequences
While maintaining a healthy weight is essential, extreme dieting or prolonged fasting can paradoxically elevate gout risk. During severe calorie restriction, the body starts breaking down muscle tissue and other stores for energy, which increases the production of purines—substances found in certain foods and tissues. This breakdown leads to an excess of uric acid, increasing the likelihood of crystal formation in joints. Additionally, fasting can disrupt normal metabolic processes, impairing the body's ability to eliminate uric acid efficiently. Therefore, it's vital to approach weight management gradually and under medical supervision, avoiding drastic dieting measures that may do more harm than good.
2. Dehydration: The Hidden Trigger
Dehydration is a common but often overlooked factor that can trigger gout attacks. When the body does not consume enough fluids, uric acid becomes more concentrated in the bloodstream. This increased concentration raises the chances of uric acid crystals forming and depositing in the joints. Staying well-hydrated by drinking adequate amounts of water and avoiding excessive caffeine or sugary beverages can significantly lower the risk. Experts recommend drinking at least 8-10 glasses of water daily, especially during hot weather or physical activity, to maintain optimal kidney function and facilitate uric acid excretion.
3. Excess Weight and Obesity
Obesity is a well-documented risk factor for gout. Excess body weight promotes increased production of uric acid due to higher cell turnover and metabolic activity. Moreover, adipose tissue impairs the kidneys' ability to eliminate uric acid efficiently, leading to hyperuricemia—the elevated levels of uric acid in the blood. Weight loss through a balanced diet and regular exercise has been shown to significantly reduce uric acid levels and prevent gout attacks. Even a modest reduction of 5-10% of body weight can have substantial benefits, making weight management a cornerstone of gout prevention strategies.
4. Dietary Habits High in Purines
What we eat greatly influences uric acid levels. Foods rich in purines—such as red meats (beef, lamb), organ meats (liver, kidney), and certain types of seafood (sardines, anchovies, scallops)—are known to increase uric acid production. Frequent consumption of these foods can push uric acid levels beyond the threshold, precipitating gout attacks. It is advisable for individuals at risk to limit intake of high-purine foods and incorporate more low-purine options like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and dairy. Moreover, reducing intake of processed foods and sugary snacks can help maintain balanced uric acid levels and overall health.
5. Alcohol Consumption’s Impact on Gout Development
Alcohol consumption is another major lifestyle factor contributing to gout risk. Alcohol interferes with the kidneys' ability to clear uric acid from the body and stimulates increased purine breakdown in the liver. Beer, in particular, contains significant purines and is often linked with higher gout incidence. Additionally, alcohol can lead to dehydration, further compounding the risk. Limiting or abstaining from alcohol, especially during flare-ups, can markedly reduce the likelihood of gout attacks. For those who choose to drink, moderation and awareness of the triggers are essential to maintaining control over uric acid levels.
Conclusion: Proactive Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Gout
Gout is a manageable condition, especially when identified early and accompanied by lifestyle modifications. Adopting healthy habits such as staying well-hydrated, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet low in purines, and limiting alcohol intake can significantly reduce the risk of gout attacks. It is equally important to avoid extreme dieting and be mindful of overall health to ensure optimal management of the condition. Consulting healthcare providers for personalized advice and regular monitoring of uric acid levels can provide an effective strategy in controlling gout and improving quality of life. By making these informed adjustments, individuals can minimize painful flare-ups and enjoy a healthier, gout-free life.