Understanding the Top 5 Autoimmune Diseases That Can Affect Anyone
Explore the comprehensive guide to the top 5 autoimmune diseases affecting millions worldwide. Learn about their symptoms, diagnosis, and modern treatment options, emphasizing the importance of early intervention for better health outcomes.

Comprehensive Insights into the Top 5 Autoimmune Diseases Impacting People Worldwide
Autoimmune diseases represent a significant category of health conditions that can affect individuals across all age groups and backgrounds. These diseases occur when the body's immune system, which normally protects us from infections and harmful invaders, mistakenly targets and damages healthy tissues and organs. This misguided immune response can lead to chronic inflammation, tissue destruction, and a variety of serious health complications. Understanding these conditions is vital for early diagnosis, effective management, and improved quality of life.
The human immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs working harmoniously to defend the body against pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and other foreign substances. Typically, the immune system distinguishes between self and non-self. However, in autoimmune diseases, this self-tolerance mechanism fails, leading to the immune system attacking the body's own cells and tissues. These attacks can vary widely depending on the specific disease, the organs involved, and the severity of the immune response.
According to data presented by the American Autoimmune Related Diseases Association (AARDA), approximately 50 million Americans, which is about 1 in 5 people, live with at least one autoimmune condition. These statistics highlight the substantial impact of autoimmune diseases on public health, underscoring the necessity for increased awareness, research, and tailored treatments. While the exact causes of autoimmune diseases remain complex and multifactorial—often involving genetic, environmental, hormonal, and lifestyle factors—their prevalence is rising globally, affecting diverse populations regardless of age, gender, or ethnicity.
This article aims to shed light on five of the most common and impactful autoimmune diseases that affect a significant portion of the population. Each condition presents unique challenges but also offers insights into the importance of early diagnosis and innovative management strategies.
1. Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Chronic Autoimmune Joint Disorder
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is one of the most recognizable autoimmune diseases, primarily affecting the joints. It is characterized by persistent inflammation of the synovial membrane— the lining of the joints— leading to swelling, pain, and stiffness. Over time, the chronic inflammation can damage cartilage, bone, and surrounding tissues, potentially resulting in joint deformity and loss of function.
RA affects individuals differently, but it is most common among women over 40. Symptoms often include symmetrical joint pain, morning stiffness lasting more than an hour, swollen joints, and fatigue. Certain biomarkers, such as rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies, aid in diagnosis.
Modern treatments focus on controlling inflammation and preventing joint damage. These include disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologic agents, corticosteroids, and NSAIDs. Early diagnosis and tailored therapeutic strategies are crucial for managing symptoms and improving long-term outcomes.
2. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (Lupus): A Multi-Organ Autoimmune Disorder
Lupus, scientifically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is a complex autoimmune condition that can affect virtually any organ or tissue in the body. It results from the immune system producing autoantibodies that attack healthy cells, leading to widespread inflammation and tissue damage. The disease is characterized by periods of exacerbation (flares) and remission, making it unpredictable and challenging to diagnose and treat.
Symptoms of lupus vary widely but often include fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes, fever, and photosensitivity. A hallmark skin manifestation is the butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and nose. Other common issues involve kidney inflammation (lupus nephritis), cardiovascular problems, and neurological involvement.
Diagnosis relies on a combination of blood tests, clinical criteria, and imaging studies. Treatment strategies aim to suppress the immune response and reduce inflammation. Common medications include corticosteroids, antimalarials like hydroxychloroquine, and immunosuppressants. Regular monitoring and personalized treatment plans are vital for managing this chronic condition effectively.
3. Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis: Autoimmune Disease in Children
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA), also known as juvenile idiopathic arthritis, is an autoimmune disorder affecting children and adolescents under 16 years of age. It causes persistent joint inflammation, pain, swelling, and stiffness, similar to adult rheumatoid arthritis, but with different subtypes and presentation patterns.
JRA can significantly impact a child's growth, development, and daily functioning. Symptoms may include fever, rash, and eye inflammation, depending on the subtype. Untreated, JRA can lead to joint erosion, deformities, and long-term disability.
Diagnosis involves clinical examination, lab tests, and imaging studies. Treatment approaches focus on controlling joint inflammation, alleviating pain, and preventing joint damage. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, physical therapy, and sometimes biologic agents are employed in managing JRA. Early intervention is essential for maintaining the child's quality of life and preventing permanent joint damage.
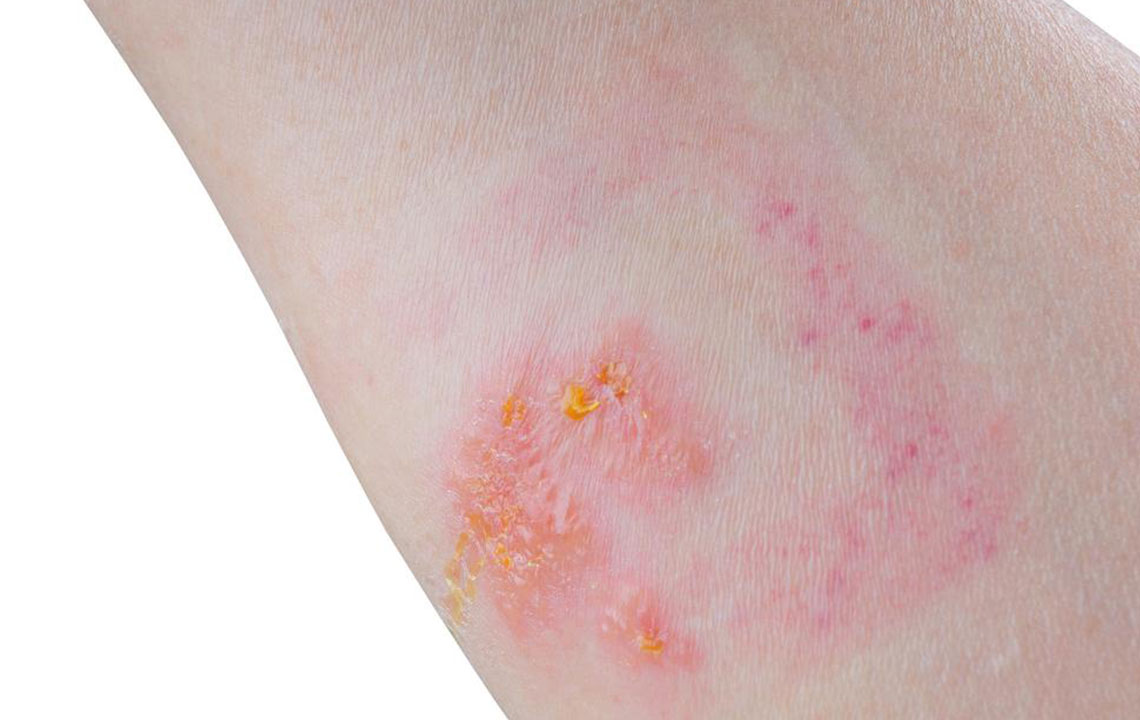
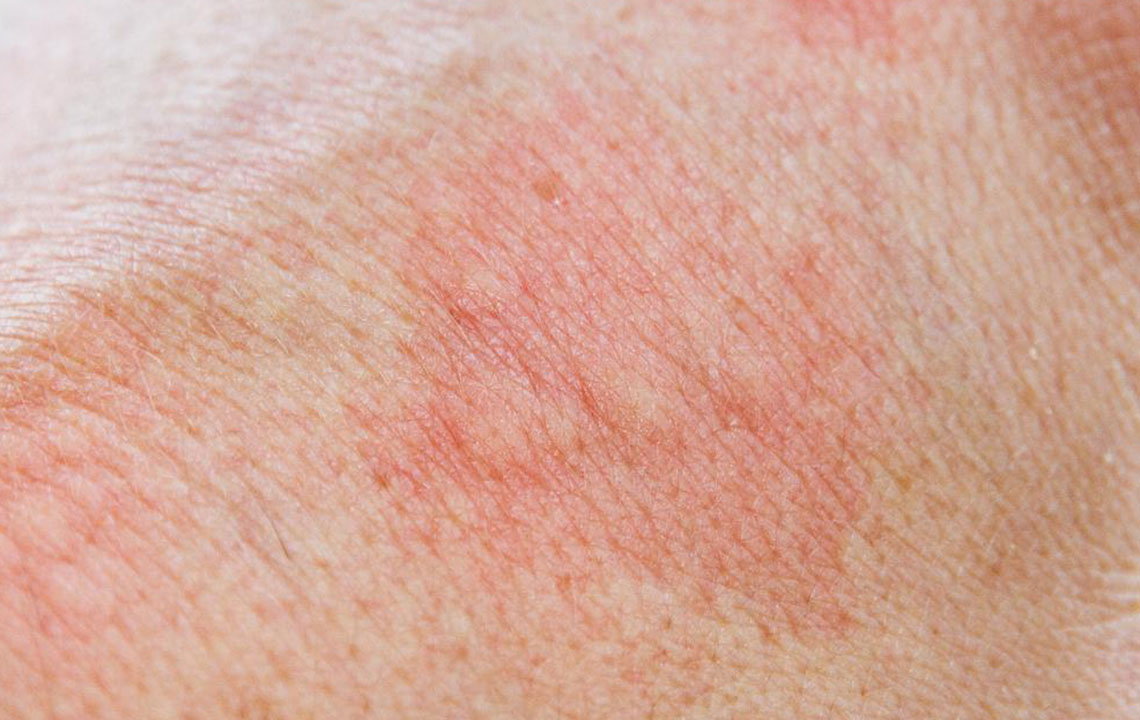
4. Psoriasis: An Autoimmune Skin Condition
Psoriasis is a common autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the skin, leading to rapid skin cell proliferation and inflammation. This results in characteristic scaly, silvery patches or plaques that may appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
While psoriasis is primarily a skin condition, it is also associated with systemic inflammation and can increase the risk of psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic syndrome. The exact cause involves a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers such as stress, infections, injury, or medications.
Treatments include topical agents like corticosteroids and vitamin D analogs, phototherapy, and systemic medications like biologics targeting specific immune pathways. Maintaining skin hydration, avoiding triggers, and regular dermatologist consultations are essential for managing psoriasis effectively.
5. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Crohn’s Disease & Ulcerative Colitis): Autoimmune Disorders of the Digestive Tract
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) encompasses a group of chronic autoimmune conditions primarily affecting the gastrointestinal tract. The two main types are Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Both involve an abnormal immune response that causes ongoing inflammation of the gut lining, leading to symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, weight loss, and fatigue.
Crohn’s disease can involve any part of the digestive tract—from the mouth to the anus— and often causes transmural inflammation, affecting all layers of the intestinal wall. Ulcerative colitis, on the other hand, typically confines itself to the colon and rectum, with inflammation limited to the mucosal layer.
Diagnosis involves endoscopic, histological, and imaging evaluations. Treatment plans include aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and biologic agents. Surgery may be necessary in severe cases. Managing diet, reducing stress, and regular medical monitoring are crucial for controlling disease progression and maintaining quality of life for sufferers.
Understanding these autoimmune diseases is essential for early detection and effective treatment. Advances in medical research continue to improve the outlook for patients, offering hope for better management strategies and improved life quality. If you suspect you or a loved one may have an autoimmune condition, consulting healthcare professionals promptly is vital for personalized care.