Comprehensive Guide to Modern Strategies for Managing Hearing Loss
This comprehensive guide explores modern strategies for managing deafness, including hearing aids, cochlear implants, surgical options, and preventive measures. It emphasizes early detection, technological advancements, and lifestyle adjustments to improve hearing health and quality of life for individuals with hearing loss.
Comprehensive Guide to Modern Strategies for Managing Hearing Loss
Hearing impairment can manifest through common signs such as frequent misunderstandings during conversations, asking others to repeat themselves, or a perceived difficulty in hearing sounds clearly. While these issues are often associated with advanced age, they are not exclusive to seniors and can affect individuals across all age groups. Recognizing the signs early and exploring effective management options is crucial for improving quality of life. Although currently there is no permanent cure for sensorineural hearing loss, advancements in medical technology and audiology services have made it possible to significantly compensate for hearing deficits, enabling individuals to lead more active and communicative lives.
This extensive guide explores the various treatment options and preventive strategies available today, providing valuable insights for individuals experiencing hearing challenges or those seeking to protect their auditory health.
Key Treatment Options for Hearing Loss
1. Hearing Devices: Enhancing Auditory Perception
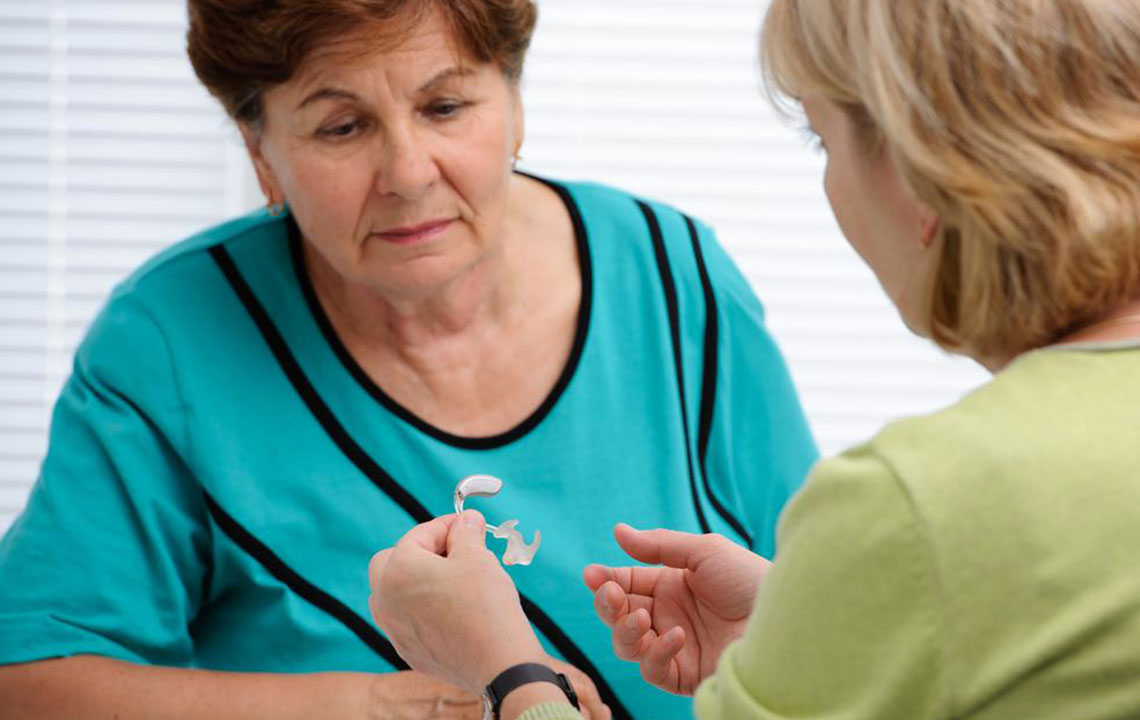
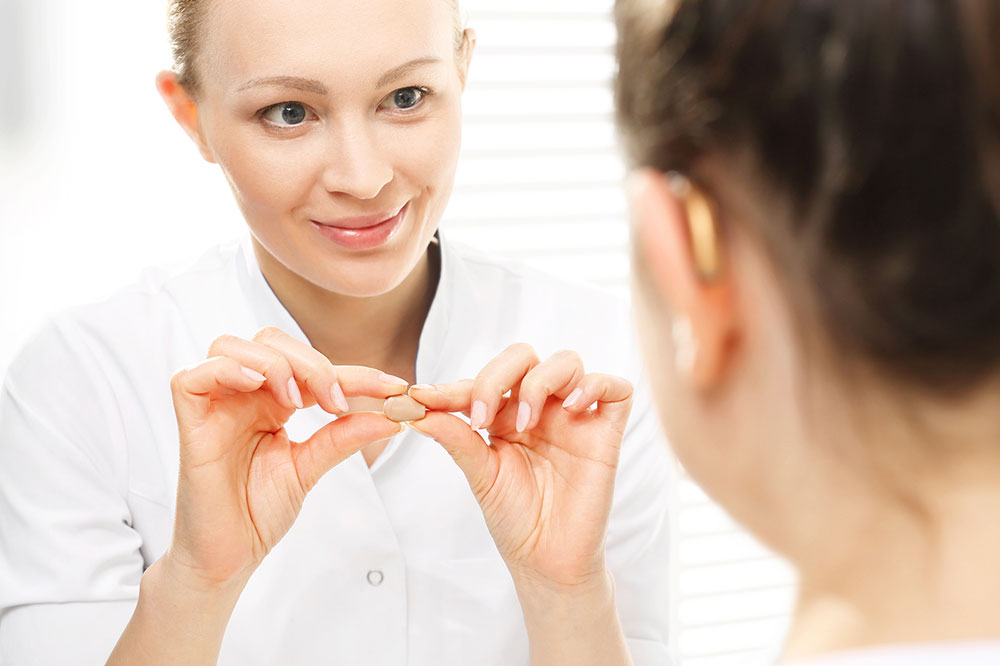
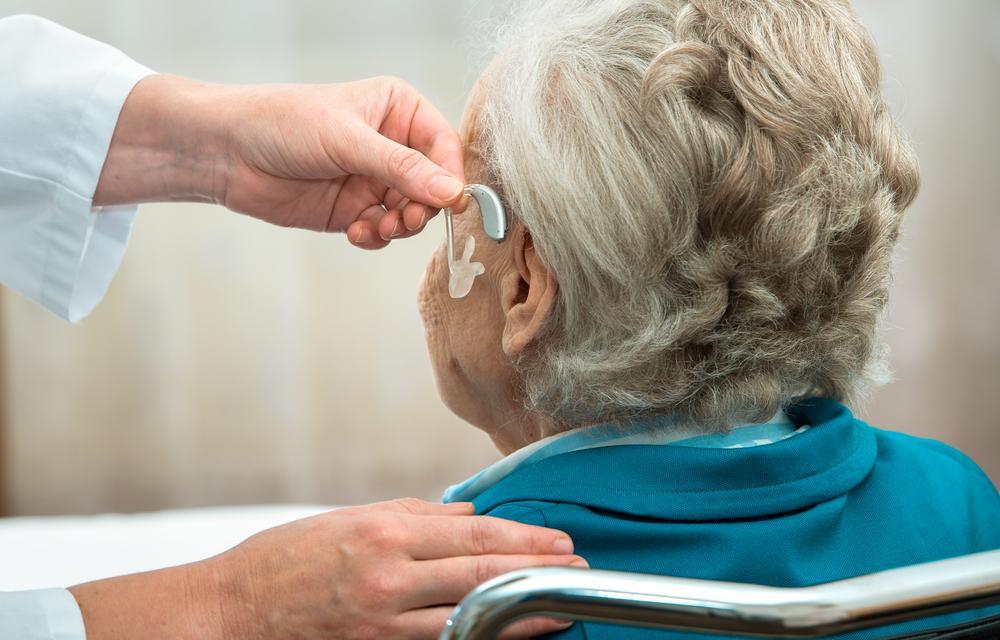
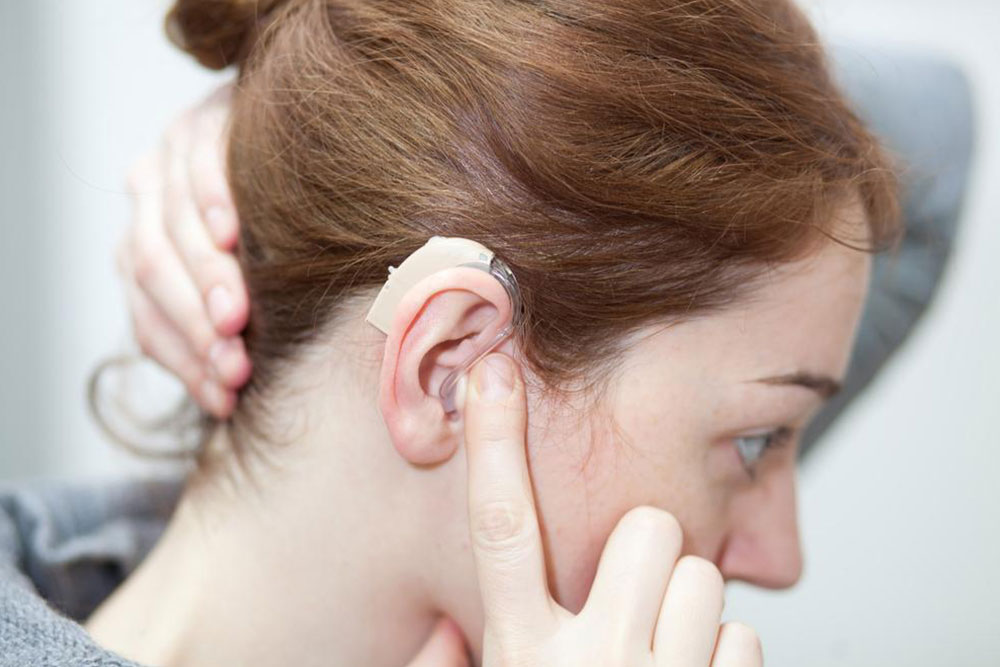
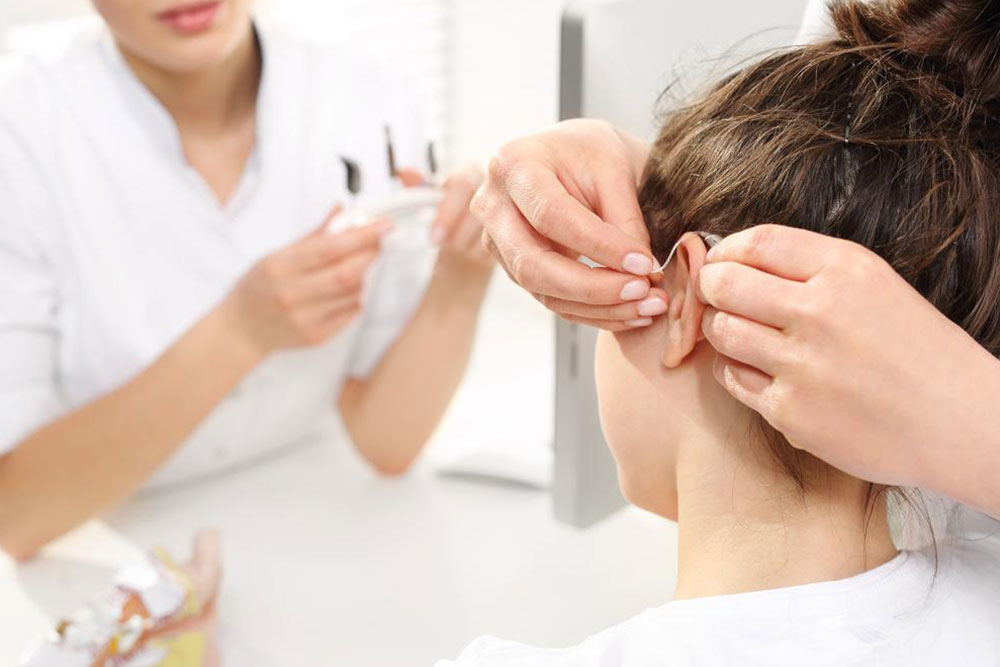
Hearing aids remain one of the most effective and accessible solutions for individuals with mild to moderate hearing impairment. Designed to amplify sound, these devices help users distinguish speech and environmental sounds more clearly. Modern hearing aids come in various styles to suit individual preferences, including discreet models that fit inside the ear canal, behind-the-ear options, and those that rest on the ear's outer edge. Many models incorporate advanced noise filtering technology, which reduces background noise and emphasizes conversations, making it easier for users to participate in social interactions. Selecting the right hearing aid requires professional evaluation by an audiologist who considers factors such as hearing loss type, lifestyle, and aesthetic preferences. With proper adjustment and early use, individuals typically adapt quickly, experiencing noticeable improvements in their hearing abilities.
2. Cochlear Implants: Restoring Hearing Through Advanced Technology
Cochlear implants are revolutionary devices designed for individuals with moderate to profound sensorineural hearing loss when traditional hearing aids no longer provide satisfactory results. These sophisticated electronic devices bypass damaged inner ear structures by directly stimulating the auditory nerve, thereby restoring a sense of sound. The implant comprises an internal component surgically placed in the cochlea and an external processor that captures sound signals and converts them into electrical impulses. Implantation requires careful evaluation by specialized audiologists and ENT surgeons. Post-surgical rehabilitation and auditory training are essential to help recipients interpret new sounds effectively, especially in complex acoustic environments. Cochlear implants have transformed countless lives by enabling users to engage more fully in social, educational, and professional activities, offering a renewed connection to the auditory world.
3. Middle Ear Devices: Enhancing Sound Transmission for Mild to Moderate Loss
For individuals with mild to moderate hearing loss unresponsive to traditional hearing aids, middle ear devices (MEDs) present an innovative alternative. These devices consist of miniature microphones placed near the ear canal, which pick up sounds and send amplified signals to an implant situated in the middle ear. The implant enhances vibrations of the ossicles—the tiny bones in the middle ear—thereby improving sound transmission to the inner ear. MEDs are especially beneficial for patients who experience discomfort with conventional aids or have specific anatomical considerations. As the technology continues to evolve, MEDs are becoming more efficient and less invasive, providing another layer of choice for managing hearing impairment.
4. Surgical Procedures: Restoring Hearing Through Medical Interventions
Stapedectomy is a common surgical treatment for conductive hearing loss caused by abnormalities such as otosclerosis, where abnormal tissue growth locks the stapes bone, preventing sound from transmitting properly. This procedure involves removing the affected stapedial footplate and replacing it with a prosthesis, restoring normal movement and sound transmission. Surgery is typically successful with minimal recovery time and offers a permanent solution for eligible candidates. Other surgical options include repairing tympanic membrane perforations or removing ossicular chain dislocations, further expanding the array of medical interventions available for hearing restoration.
Preventive Measures: Protecting Your Hearing for the Future
Preventing further hearing loss is equally important as treatment. To safeguard auditory health, avoid exposure to excessively loud sounds—generally noise levels exceeding 85 to 90 decibels—whenever possible. Use protective gear such as earplugs or earmuffs in noisy environments like concerts, construction sites, or during shooting activities. Maintaining ear hygiene through regular cleaning, either at home using appropriate techniques or with assistance from healthcare professionals, helps prevent wax buildup and infections that could impair hearing. Routine hearing evaluations are essential, especially for individuals exposed to risk factors such as prolonged noise exposure or ototoxic drugs. Early detection and intervention enable better management and can slow or prevent further deterioration of hearing functions, ensuring longer-term auditory health.
Summary: Embracing a Future of Better Hearing Management
Understanding the comprehensive range of available treatments and preventive strategies empowers individuals with hearing difficulties to take proactive steps toward improved auditory health. From advanced hearing aids and cochlear implants to surgical interventions and lifestyle modifications, modern technology and medical science continue to enhance options for those with hearing impairment. Early detection and consistent management are key to maintaining effective hearing and communication abilities. As research progresses, new solutions are expected to emerge, promising even more effective and less invasive methods for managing hearing loss in the future. Ultimately, embracing these strategies can help individuals preserve their hearing health, participate actively in social environments, and enjoy the sounds of life with greater clarity and confidence.