Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing and Preventing Hearing Loss
This comprehensive guide explores the signs and prevention strategies for hearing loss. It emphasizes early detection, identifies key risk factors, and discusses effective techniques to safeguard auditory health. From protective measures like earplugs to advanced treatments such as cochlear implants, learn how to maintain healthy hearing throughout your life. Understanding these aspects can help you take proactive steps to prevent irreversible damage and improve your quality of life. Stay informed and protect your hearing today.
Understanding the Signs and Prevention Strategies for Hearing Impairment
Hearing health is a vital aspect of overall well-being, yet many individuals overlook the gradual decline in auditory function that can occur over the years. Even those who once had perfect hearing are susceptible to age-related changes and environmental factors that can impair their ability to hear clearly. Early detection of hearing impairment plays a crucial role in effective management and preservation of hearing abilities. This comprehensive guide delves into the common signs of hearing loss, the risk factors involved, and practical steps to prevent or mitigate auditory damage.
Hearing loss is often a gradual process, and identifying early symptoms can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes. Modern technology offers various solutions, such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, and surgical interventions, which can dramatically improve quality of life for those affected. The key to maintaining healthy hearing lies in awareness, protective measures, and timely medical attention.
Factors Influencing Hearing Loss
Numerous factors can influence an individual's risk of developing hearing impairment. Understanding these factors allows you to take proactive steps to reduce your risk and seek appropriate medical advice when necessary.
Age – Natural aging (presbycusis) causes the degeneration of inner ear structures. As the tiny hair cells in the cochlea wear out over time, hearing diminishes, especially at higher frequencies.
Loud noise exposure – Prolonged or repeated exposure to loud noises, typically above 80-85 decibels, can damage delicate hair cells and auditory nerve fibers. Occupational hazards such as construction work, factory environments, or frequent concerts increase risk.
Sudden loud sounds – Explosive noises or intermittent loud impacts can cause immediate damage to the ear structures, leading to sudden hearing loss.
Additional Risk Factors
Genetics – Family history of hearing loss can predispose individuals to similar issues, especially congenital or early-onset forms.
Medications – Ototoxic drugs like certain antibiotics (aminoglycosides), chemotherapy agents, high-dose aspirin, and pain relievers can adversely affect cochlear health.
Health conditions – Diseases such as meningitis, Meniere’s disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders can impair auditory function.
Recognizing Early Signs of Hearing Loss
Being vigilant about the early signs of hearing impairment allows for prompt intervention, potentially halting or reversing progression. Common indicators include:
Muffled or distorted sounds – Hearing conversations or environmental noises becomes unclear or fuzzy.
Difficulty understanding speech – Especially in noisy surroundings, distinguishing words becomes challenging.
Increased volume requirements – The need to turn up the volume on radios, televisions, or phones beyond normal levels.
Frequent ask for repetitions – Asking people to repeat themselves or clarify statements often.
Struggling in social situations – Avoiding conversations or social gatherings due to difficulty in hearing can lead to social isolation.
Impacts of Ignoring Hearing Issues
If untreated, hearing loss can have profound effects beyond difficulty hearing. It may cause social withdrawal, reduce cognitive engagement, and lead to mental health issues such as depression and anxiety. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve quality of life.
Preventive Measures and Treatment Options
Prevention is key to maintaining healthy hearing. Some effective strategies include:
Using ear protection – Earplugs or earmuffs should be used in noisy environments like construction sites, concerts, or during heavy machinery operation.
Limiting exposure to loud sounds – Take regular breaks from noisy environments and adhere to safe listening levels.
Managing health conditions – Keeping chronic illnesses under control to prevent complications affecting hearing.
Avoiding ototoxic medications when possible – Discuss alternatives with your healthcare provider if medications are known to affect ear health.
When signs of hearing loss are detected, medical interventions can significantly improve auditory functions. These include:
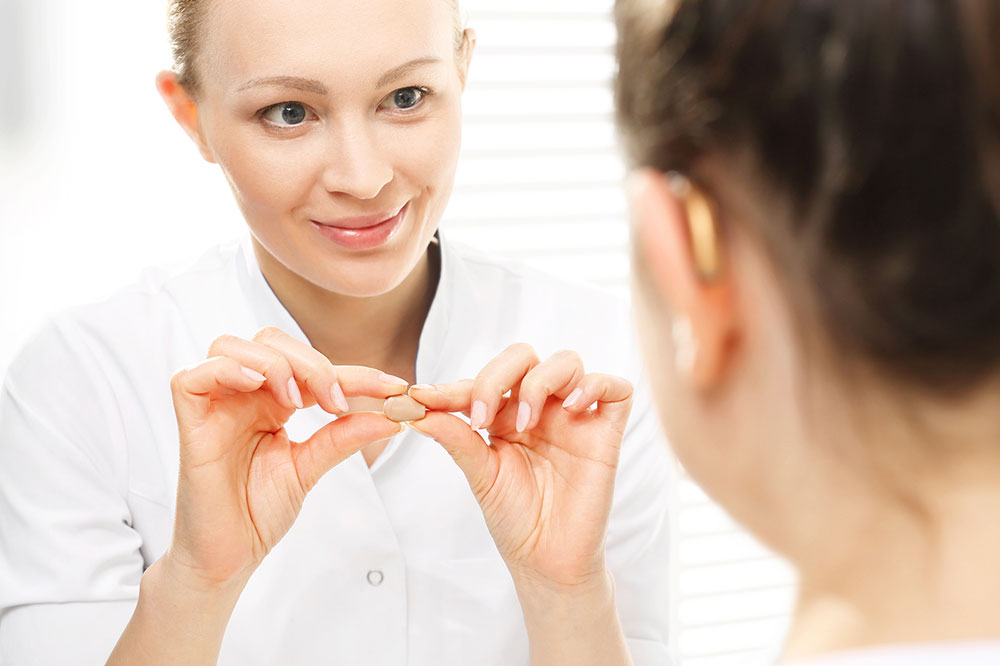
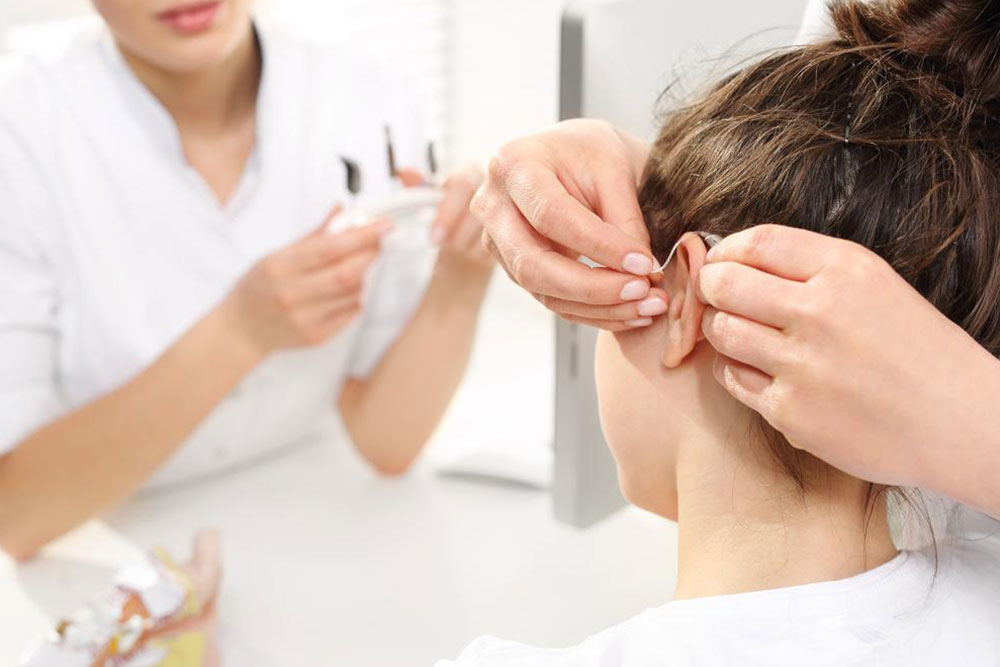
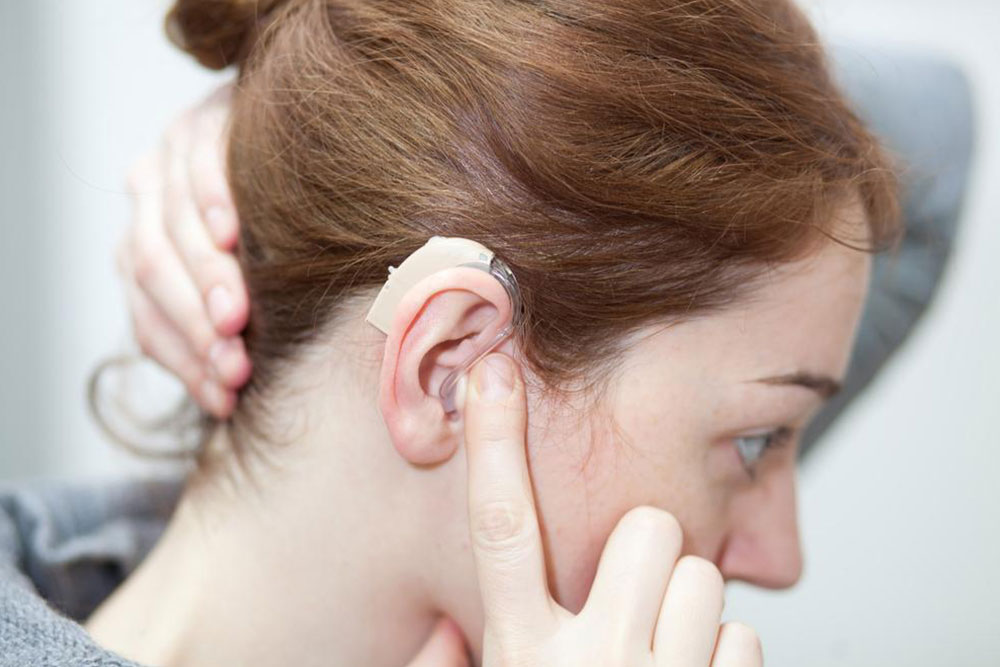
Hearing aids – Modern devices are discreet and offer customizable sound enhancement tailored to individual needs.
Surgical procedures – Options like tympanoplasty or removal of growths can address specific issues.
Cochlear implants – For severe to profound hearing loss, these devices bypass damaged parts of the inner ear, directly stimulating auditory nerves.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Hearing for the Future
Maintaining hearing health is a proactive process that involves understanding the risk factors, recognizing early signs, and taking preventive actions. Regular hearing assessments are recommended, especially for individuals exposed to occupational or environmental hazards. Educating yourself and others about noise safety and ear health can prevent irreversible damage and preserve auditory function for years to come. Remember, early intervention is your best defense against hearing impairment, ensuring you stay connected to the sounds and conversations that enrich your life.