Essential Home Environment Factors That Impact Lung Health and How to Mitigate Risks
Discover the top indoor environmental factors affecting lung health and learn practical strategies to mitigate risks. From mold and allergens to indoor air pollutants, this comprehensive guide provides valuable insights for creating a healthier home environment and promoting respiratory wellness.
Understanding How Your Home Environment Influences Lung Well-being
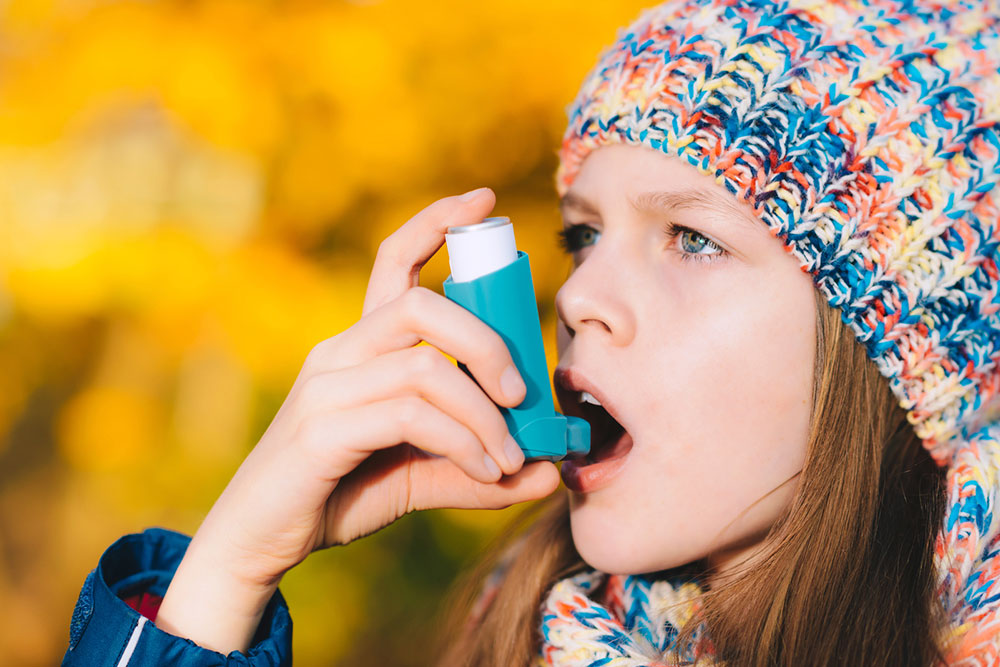
Our lungs are vital organs responsible for breathing and oxygenating our bodies. Maintaining optimal lung health is fundamental for overall vitality and wellness. However, various indoor environmental factors can adversely affect respiratory functions, leading to allergies, asthma, or more severe lung conditions. Recognizing these elements can help you take proactive steps to create a healthier living space. This comprehensive guide explores the top indoor environmental factors that influence lung health and offers practical solutions for mitigation.
Mold Growth in Homes
Mold is a common indoor contaminant that thrives in damp, poorly ventilated areas such as basements, bathrooms, and behind wallpaper. Mold spores are microscopic and easily become airborne, leading to respiratory irritation and allergic reactions. For individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions like asthma, mold exposure can exacerbate symptoms significantly. Long-term mold exposure has also been linked to decreased lung function and other chronic respiratory issues. To prevent mold proliferation, ensure proper ventilation in humid areas, fix leaks promptly, and use dehumidifiers to maintain indoor humidity levels below 60%. Regular cleaning with mold-inhibiting solutions and addressing water intrusion issues are essential steps for mold prevention.
Carpets as Allergens Traps
Carpeting enhances comfort and aesthetic appeal but tends to trap dust mites, pet dander, mold spores, and other airborne allergens. These allergens can be inhaled, causing or aggravating respiratory diseases such as asthma, bronchitis, and allergic rhinitis. To reduce indoor allergen levels, vacuum carpets regularly using HEPA filters, consider replacing carpets with hard flooring where possible, and schedule professional deep cleaning periodically. Maintaining a clean and allergen-free carpet environment is crucial for individuals sensitive to airborne irritants.
Flour Dust in Household and Commercial Kitchens
Flour dust is a significant health concern in bakeries and homes baking bread or pastries. Inhalation of fine flour particles can lead to baker's asthma, a type of occupational asthma characterized by wheezing, coughing, and difficulty breathing. Even non-professional bakers or family members nearby can be affected due to airborne flour dust. It's vital to ensure proper ventilation during baking, use protective masks, and clean up flour dust thoroughly to minimize inhalation risks. Implementing dust extraction systems and using low-dust flour varieties can also help protect respiratory health.
Candles and Indoor Air Quality
Many households enjoy candles for ambiance and scent, yet paraffin candles release fumes containing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and particulate matter when burned. These emissions can contribute to indoor air pollution, causing respiratory irritation and aggravating allergies or asthma attacks. Opting for natural candles made from beeswax or soy reduces exposure to harmful chemicals. Always ensure proper candle burning practices by trimming wicks and providing adequate ventilation, especially in small or poorly ventilated spaces.
Humidifiers and Indoor Microbial Growth
Humidifiers are beneficial for relieving dry air, but if not maintained correctly, they can become breeding grounds for bacteria, mold spores, and other microorganisms. These microbes are dispersed into the air during humidifier operation, posing risks for respiratory infections and allergies. Regular cleaning, disinfecting, and using distilled or filtered water are essential to prevent microbial growth. Air conditioners and heaters that cause fluctuations in humidity levels can also promote mold growth if not properly managed. Maintaining a balanced indoor humidity of around 40-50% can help safeguard lung health and prevent microbial proliferation.





