Comprehensive Nutritional Guidelines for Managing Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST)
This comprehensive guide provides essential nutritional strategies for managing GIST, emphasizing a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. It highlights the importance of mindful food choices, cooking methods, and protein sources to support recovery, boost immunity, and reduce cancer risk. Tailored dietary guidelines help patients improve quality of life and health outcomes during and after treatment, making nutrition a key component of effective GIST management.
Comprehensive Nutritional Guidelines for Managing Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST)
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors, commonly referred to as GIST, are relatively rare types of tumors that develop within the digestive tract. These tumors can originate anywhere along the gastrointestinal tract but are most frequently found in the stomach. Occasionally, they can be present in other parts such as the small intestine, esophagus, colon, or rectum. Due to their location and potential health implications, managing GIST requires a multifaceted approach, combining surgical intervention, targeted therapies, and crucially, dietary and nutritional strategies to support patient recovery and overall health.
Proper nutrition is a cornerstone in the treatment plan for GIST patients. It not only aids in healing and recovery post-surgery but also contributes significantly to maintaining a strong immune system, reducing inflammation, and enhancing the body's natural defenses against disease progression. Here, we delve into detailed dietary considerations and strategies that can help individuals with GIST optimize their health outcomes and improve their quality of life.
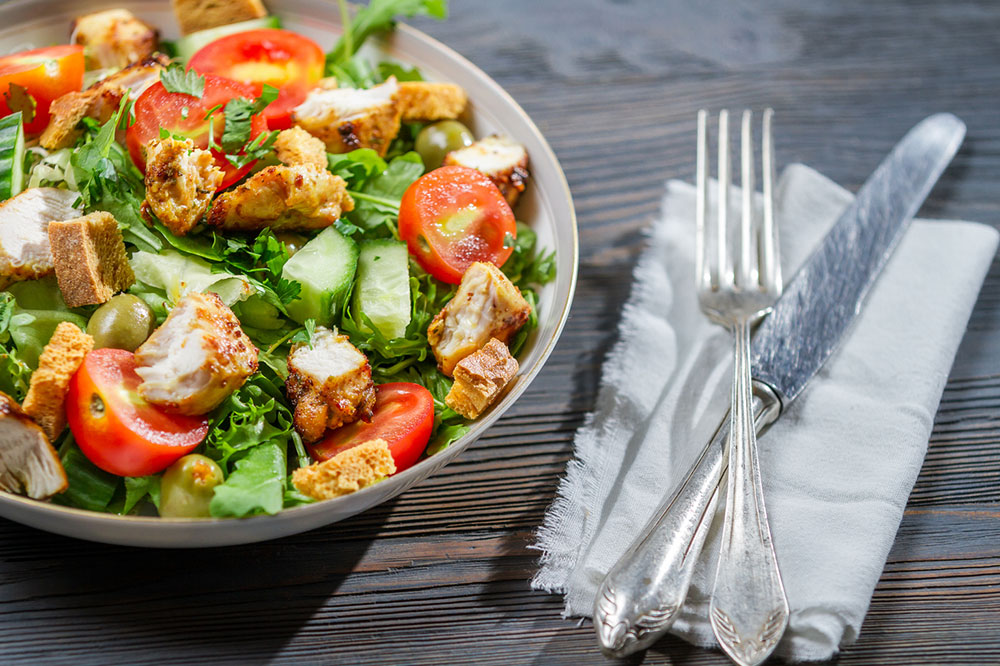
Emphasize a colorful array of fresh fruits and vegetables - Incorporating a wide variety of produce ensures a rich intake of antioxidants, vitamins, and phytochemicals that bolster the immune response and help combat cancerous cell growth. Berries such as blueberries, strawberries, and blackberries are particularly potent sources of antioxidants. Vegetables like bell peppers, spinach, kale, and broccoli provide essential nutrients that support cellular repair and immune health.
these nutrient-dense foods provide a foundation to strengthen the body's defenses during recovery and ongoing health maintenance.
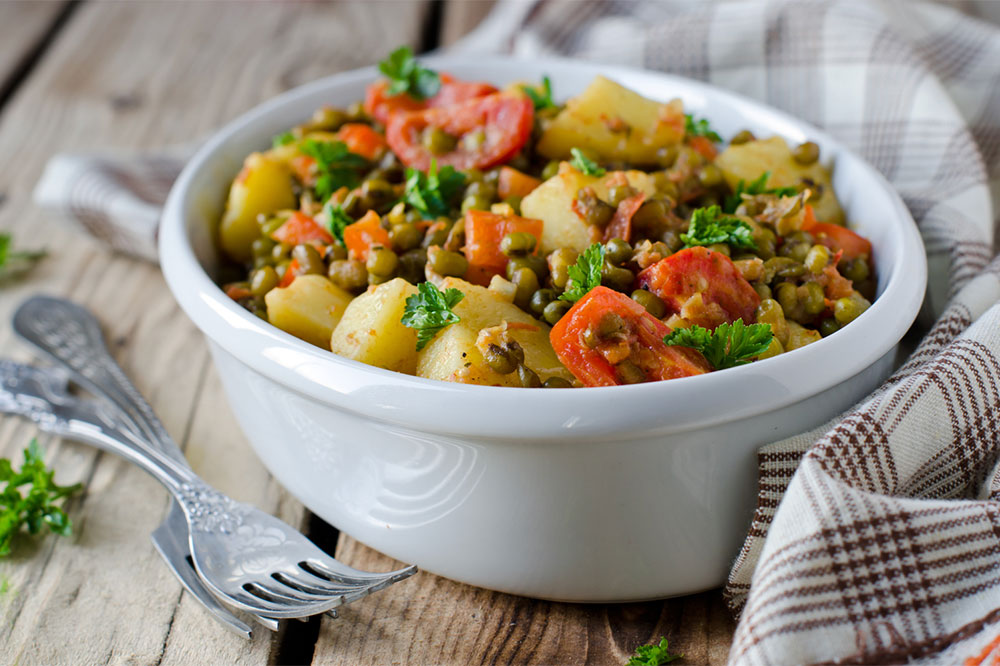
Incorporate legumes and whole grains into daily meals - Legumes such as beans, chickpeas, and lentils, alongside whole grains like quinoa, oats, and rye, are high in dietary fiber. Dietary fiber is crucial for supporting gastrointestinal health, promoting regular bowel movements, and reducing the risk of colon-related complications. Including these foods can also help maintain steady blood sugar levels and prevent constipation, which is particularly important for GIST patients post-treatment.
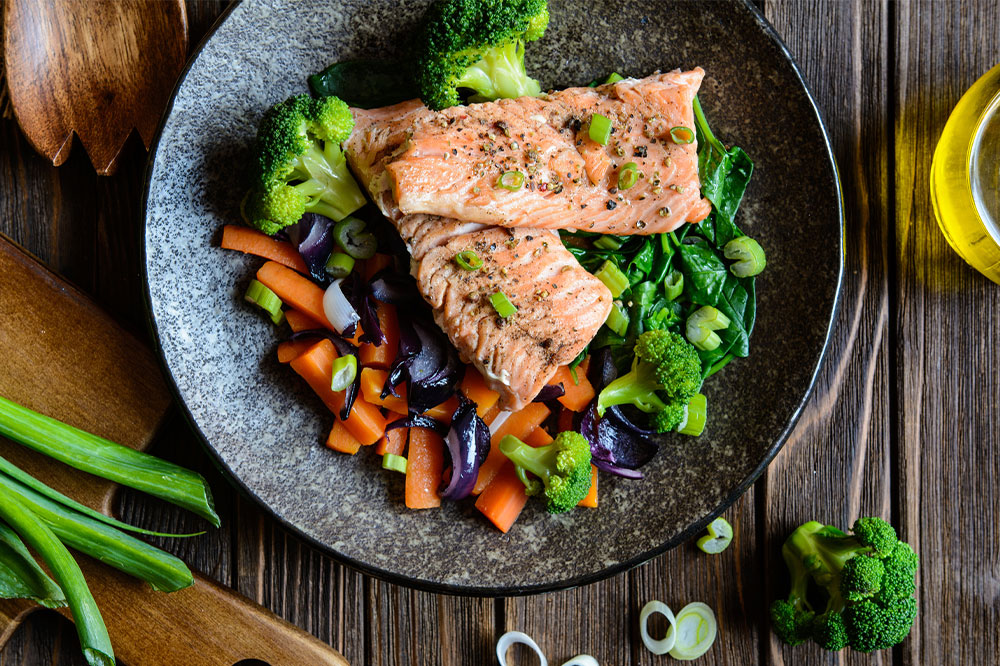
Reduce red meat consumption and opt for healthier protein sources - Limiting red meat intake has been linked to decreased cancer risks. Instead, focus on consuming fish such as salmon and mackerel, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, lean poultry, low-fat dairy products, eggs, and plant-based proteins like soy and tofu. These options provide essential amino acids without the adverse effects associated with red and processed meats.
Avoid charred and heavily processed foods - Cooking methods influence the formation of potentially carcinogenic compounds. Grilling or frying at high temperatures can produce heterocyclic amines and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which may increase cancer risk. Prioritize cooking techniques like baking, steaming, poaching, or broiling at moderate temperatures. Additionally, reduce consumption of cured, smoked, or heavily processed meats such as bacon, sausages, and deli meats, which contain preservatives and additives that may negatively impact health.
Limit dietary fats and emphasize healthy fats - Reducing saturated fats found in animal products and trans fats present in hydrogenated oils used in baked goods is advisable. Instead, emphasize the intake of omega-3 fatty acids, found abundantly in fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. These healthy fats have anti-inflammatory properties and support cardiovascular health, which is vital during and after cancer treatment.
Overall, adopting an anti-inflammatory, nutrient-rich diet tailored to the specific needs of GIST patients can significantly support their treatment journey. Consulting with healthcare professionals and dietitians to develop personalized nutrition plans ensures that dietary choices complement medical interventions, optimize recovery, and promote long-term health and well-being.





