Effective Dietary Strategies to Relieve Constipation: Foods to Embrace and Avoid
Discover effective dietary strategies to combat constipation, including foods to incorporate like prunes, apples, oats, and chia seeds, along with foods to avoid such as processed meats, fried foods, and high-fat dairy. Learn how proper hydration and lifestyle changes can further enhance digestive health. This comprehensive guide offers practical tips for maintaining regular bowel movements and reducing discomfort naturally.

Comprehensive Dietary Approaches for Managing Constipation
Constipation is a common gastrointestinal issue characterized by infrequent, hard, or difficult-to-pass bowel movements. It affects a significant portion of the population globally, leading to discomfort, bloating, and in some cases, more serious health complications if left unmanaged. While various factors contribute to constipation—including stress, medications, and underlying health conditions—dietary habits play a pivotal role in both causing and alleviating this condition. Understanding which foods to incorporate into your diet and which to avoid can greatly improve digestive health and overall well-being.
Key Foods to Include in Your Diet for Relief from Constipation
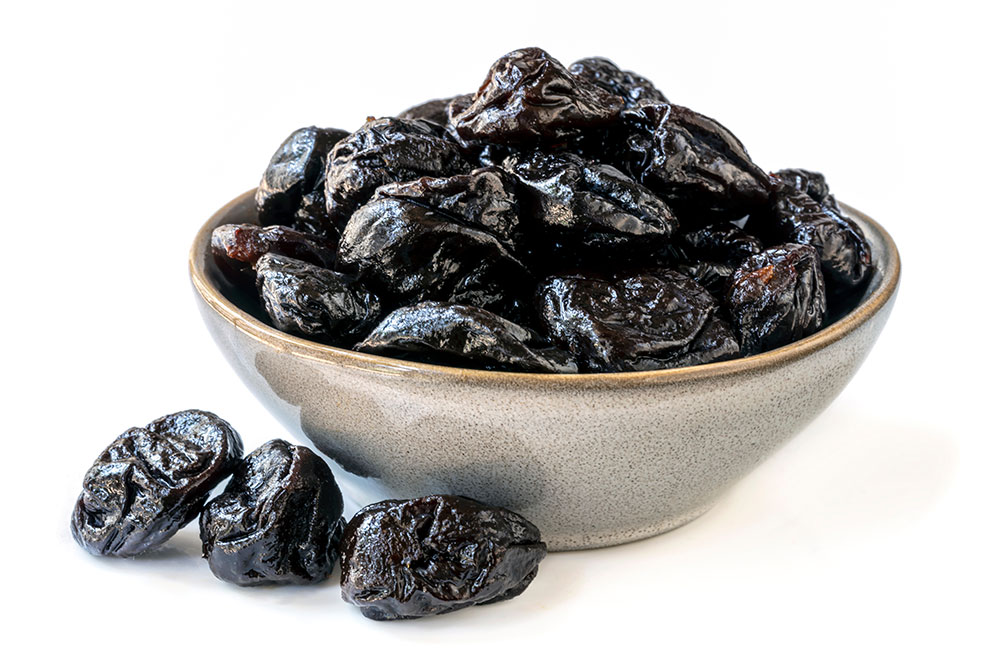
Prunes and Prune Juice
Prunes are widely recognized for their natural laxative properties. Their high fiber content, particularly soluble fiber, works by increasing stool volume and facilitating smoother bowel movements. Additionally, prunes contain sorbitol—a sugar alcohol with mild laxative effects—that helps soften stools and stimulates intestinal muscles. Consuming a handful of prunes daily or drinking a glass of fresh prune juice can restore regularity and reduce symptoms of constipation. For many, incorporating prunes into breakfast or snacks offers an easy and effective solution.
Fruits Rich in Insoluble Fiber: Apples and Pears
Fruits such as apples, pears, and berries are excellent sources of insoluble fiber, which adds bulk to stool and accelerates its movement through the digestive tract. Eating raw, whole apples with the skin increases water content in the colon, softening stool and promoting regularity. Including these fruits in your daily diet can enhance digestion, prevent stool hardening, and support healthy bowel habits. Moreover, apples contain additional antioxidants and vitamins that contribute to overall health.
Whole Grains: Oats and Brown Rice
Switching from refined grains to whole grains can significantly improve digestive health. Oats are rich in soluble fiber, which forms a gel-like substance in the gut, retaining water and softening stool. This process facilitates easier evacuation. Similarly, replacing white bread and white rice with oats, brown rice, or other whole grains increases fiber intake and supports gut motility. Regular consumption of oats can also help maintain steady blood sugar levels and provide sustained energy throughout the day.
Chia Seeds and Flaxseeds
Chia seeds are a powerhouse of dietary fiber, containing both soluble and insoluble types. When soaked in water or added to foods like yogurt or smoothies, chia seeds absorb liquid, forming a gel that adds bulk and softness to stool. This action stimulates bowel movements and alleviates constipation. Flaxseeds, similarly rich in fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and lignans, can also promote digestive health when ground and incorporated into meals. Including these seeds regularly can facilitate smoother digestion and improve gut function.
Hydration: Drinking Plenty of Water
Beyond dietary choices, maintaining adequate hydration is crucial when managing constipation. Water helps fiber do its job effectively by softening stool and making it easier to pass. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water daily, and increase intake during hot weather or physical activity. Proper hydration combined with fiber-rich foods enhances bowel motility and prevents stool hardening.
Foods to Limit or Avoid for Better Digestive Health
High-Fat Dairy Products
While dairy can be a nutritious part of the diet, certain high-fat products like full-fat milk, cheese, and ice cream may worsen constipation in some individuals. These foods tend to be low in fiber and can slow digestion due to their high fat content. Reducing or eliminating dairy, especially in cases of lactose intolerance or sensitivities, can help improve bowel movements and reduce bloating.
Red and Processed Meats
Red meats such as beef, pork, and lamb are devoid of dietary fiber and often contain saturated fats that can hinder digestion. Consuming large quantities of red meat may lead to slower gastrointestinal transit and harder stools. Replacing red meat with plant-based protein sources like legumes, nuts, and seeds can promote better bowel health and offer additional nutritional benefits.
Fried and Greasy Foods
Deep-fried foods—including French fries, fried chicken, and onion rings—are rich in trans fats and greasy oils. These foods can slow down the digestive process, cause inflammation, and promote stool hardening. Eliminating fried foods from your diet can significantly improve gut motility, reduce bloating, and support overall digestive health.
Limit processed and sugary foods
Highly processed snacks, sweets, and baked goods often lack fiber and contain additives or artificial ingredients that irritate the gastrointestinal tract. Excessive consumption of sugary foods can disrupt gut flora balance, leading to digestion issues. Focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods from natural sources can help maintain healthy bowel movements.
Medications and Supplements
In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe medications or supplements to help manage constipation. Options like fiber supplements (e.g., FiberCon), stool softeners, or laxatives may be recommended based on severity and individual health status. It is essential to follow medical advice and not rely solely on medication, but rather combine it with dietary and lifestyle modifications for optimal results.