Comprehensive Guide to Alleviating Chronic Lower Back Pain
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies to alleviate chronic lower back pain, including rest, heat and cold therapy, medical interventions, and exercise. Learn how to manage pain, promote recovery, and improve mobility through a combination of professional treatment and daily care. Whether dealing with acute or chronic discomfort, these evidence-based methods can help you regain comfort and strength in your back.

Effective Strategies to Alleviate Chronic Lower Back Pain
Lower back pain, medically known as lumbago, is a prevalent condition affecting millions worldwide. It involves discomfort or pain in the lumbar region, where the spine connects with various muscles, ligaments, nerves, and bones that work collectively to support the upper body. The lumbar spine encompasses vertebrae from L1 to L5, which play a crucial role in mobility, flexibility, and load-bearing functions. Muscles surrounding these vertebrae facilitate hip movement, rotation, and stability.
The lumbar nerves serve vital functions, supporting limb muscles and enabling movement. However, strain, injury, or prolonged poor posture can lead to nerve compression, inflammation, and muscle tension, significantly impairing daily routines. Pain intensity varies from dull, persistent aches to sharp, stabbing sensations, making simple activities like standing, bending, and twisting uncomfortable or even impossible. While occasional episodes of acute pain often resolve on their own with rest, severe or ongoing discomfort requires targeted treatment strategies to prevent worsening and promote recovery.
Effective Methods to Manage and Reduce Lower Back Pain
If you are experiencing persistent lower back soreness, it’s essential to adopt a comprehensive approach that combines home remedies, physical therapy, and, when necessary, medical interventions. Below are proven strategies to alleviate lower back pain and improve quality of life:
1. Rest and Activity Modification
Rest is a fundamental component in managing acute lower back pain. During severe episodes, avoiding strenuous activities allows muscles, ligaments, and tissues to recover without further strain. It’s important to strike a balance—remaining immobile for too long can lead to stiffness and weakness, while too much activity might worsen inflammation. Gentle movements and avoiding heavy lifting or twisting can facilitate healing. Short periods of rest combined with gradual resumption of gentle activity are typically recommended.
2. Application of Heat and Cold Therapy
Using heat and cold packs is a time-tested method to reduce pain and inflammation. Applying heat, such as heated pads, warm baths, or heat wraps, enhances blood circulation, supplies oxygen and nutrients to damaged tissues, relaxes tense muscles, and relieves stiffness. Cold therapy, on the other hand, constricts blood vessels, diminishes swelling, and numbs nerve endings, reducing pain and spasms. Alternating between heat and cold provides maximum relief—apply heat before engaging in activity to loosen muscles, and cold afterward to control inflammation. Proper usage typically involves applying each for 15-20 minutes with a soft cloth in between.
3. Medical Treatments and Interventions
When conservative measures do not suffice, medical interventions can significantly relieve symptoms. Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial to determine the appropriate therapy based on the severity and underlying cause of the pain. Common medical options include:
Epidural Steroid Injections: Targeted injections deliver corticosteroids near affected nerve roots, reducing inflammation and providing temporary relief from nerve-related pain.
Muscle Relaxants: Prescription medications help diminish muscle spasms and alleviate tightness that contribute to pain.
Narcotic Analgesics: In severe cases, opioids may be prescribed for short-term pain management, under strict medical oversight.
Supportive Devices: Back braces or orthotics stabilize the lumbar region, preventing further injury and aiding recovery, particularly when combined with physical therapy.
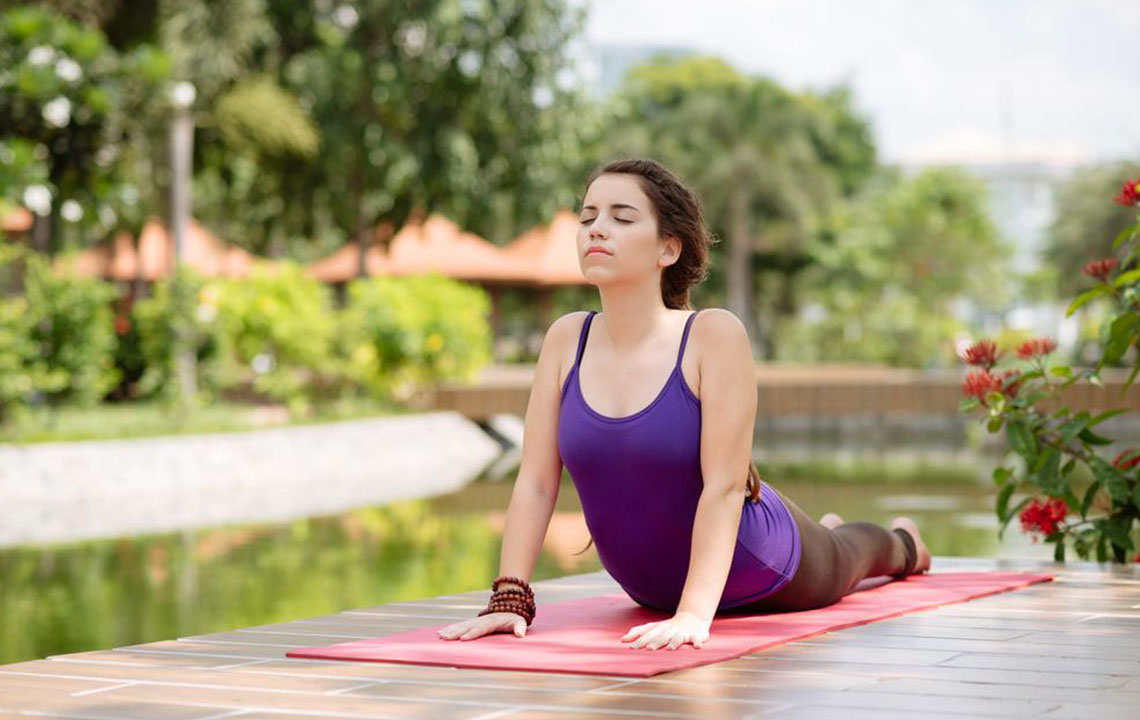
4. Incorporating Exercise and Physical Therapy
Long-term management of lower back pain involves maintaining strength, flexibility, and stability through tailored exercises. Physical therapy, guided by trained specialists, often includes stretching, strengthening, and postural correction exercises. Regular activity boosts blood flow to tissues, facilitates healing, and releases natural painkillers, called endorphins. Key exercise routines include:
Stretching Exercises: Focus on the hips, hamstrings, and lower back muscles to improve flexibility and reduce tightness, which can pull on the spine.
Core Strengthening: Strengthening abdominal, gluteal, and hip muscles provides essential support to the lumbar spine, distribution of load, and reduction of strain during daily movements.
It is advisable to start any exercise program under medical supervision to ensure safety and effectiveness. Before beginning any medication or therapy, consult your healthcare provider for a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific condition.Managing lower back pain is an ongoing process that combines lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and preventive exercises. Adherence to recommended strategies can lead to pain relief, improved mobility, and enhanced quality of life, helping you regain control over your daily activities and function.