Comprehensive Guide to Relieving Lower Back Pain Effectively
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for alleviating lower back pain, including self-care techniques, physical therapy options, and medical interventions. It emphasizes the importance of proper diagnosis, balance between rest and activity, and targeted exercises to promote healing and prevent chronic discomfort. Learn how heat and cold therapies can improve recovery, and discover when to seek professional medical support for persistent pain. Suitable for those experiencing acute or chronic lower back discomfort, this article offers practical advice for improving mobility and quality of life.

Comprehensive Strategies for Alleviating Lower Back Pain
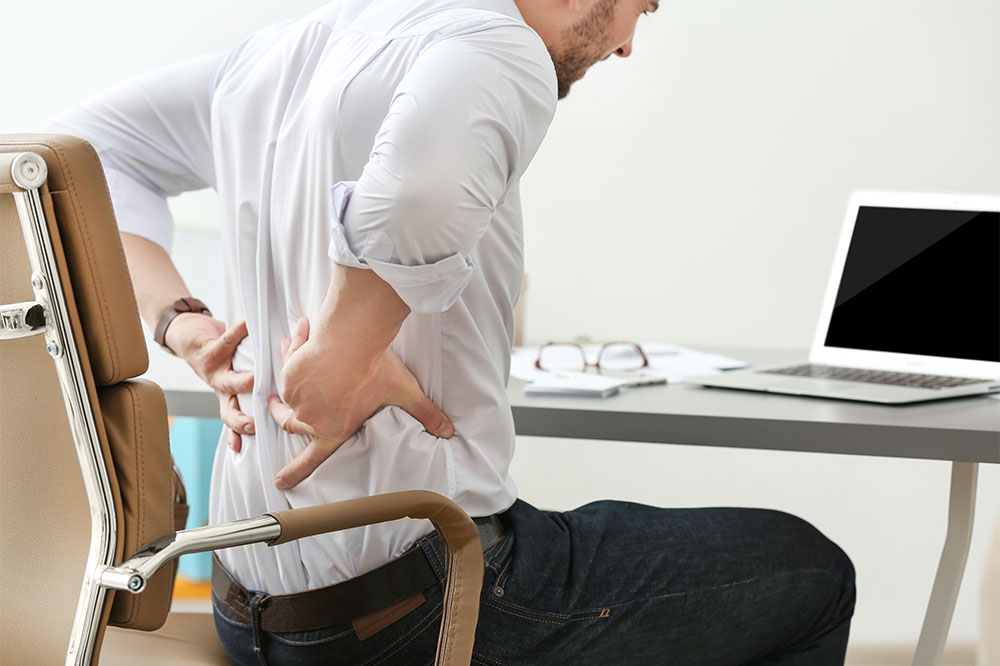
Lower back pain, medically known as lumbago, is a prevalent condition affecting a significant portion of the population at some point in their lives. It involves discomfort originating from the muscles, nerves, or bones located in the lumbar region of the spine, which spans from the lower rib cage to the top of the pelvis. The lumbar spine plays a critical role in supporting the weight of the upper body and facilitating a wide range of movements, including bending, twisting, and lifting. This region comprises vertebrae L1 through L5, interconnected by joints, ligaments, and muscles that work in harmony to provide stability and mobility. The surrounding musculature, especially those around the vertebrae, contributes to hip flexibility and rotation, while also facilitating communication with the nervous system to control limb movement. Injuries, strains, or degenerative changes in this area can impair normal function, leading to pain that varies from a dull ache to sharp, stabbing sensations, which can significantly limit daily activities and decrease overall quality of life.
Symptoms associated with lower back pain often include persistent aches, stiffness, and sometimes sudden, intense sharp pains that can occur during movement or even at rest. These symptoms can temporarily impair simple activities such as standing, bending, or lifting objects, and may worsen with prolonged inactivity or improper movement. While many instances of acute lower back pain resolve on their own within a few days to weeks, stubborn or recurrent pain warrants targeted management strategies to prevent progression to chronic conditions. Chronic lower back discomfort, which persists beyond six weeks, requires a comprehensive approach that combines lifestyle modifications, therapeutic interventions, and sometimes medical treatments for effective relief and improved mobility.
Effective Methods to Manage and Alleviate Lower Back Pain
Dealing with lower back pain can be challenging, but employing a combination of proper care techniques can significantly reduce discomfort and promote healing. Below are some of the most effective strategies:
Rest and Activity Balance
Initially, avoiding strenuous activities that exacerbate pain is crucial. Gentle rest helps muscles relax and recover, but prolonged inactivity can weaken muscles and delay healing. It is vital to strike a balance by allowing adequate rest without developing a sedentary lifestyle. Short periods of rest interspersed with gentle movement support recovery, but consult healthcare providers to determine suitable activity levels based on the severity of your condition.
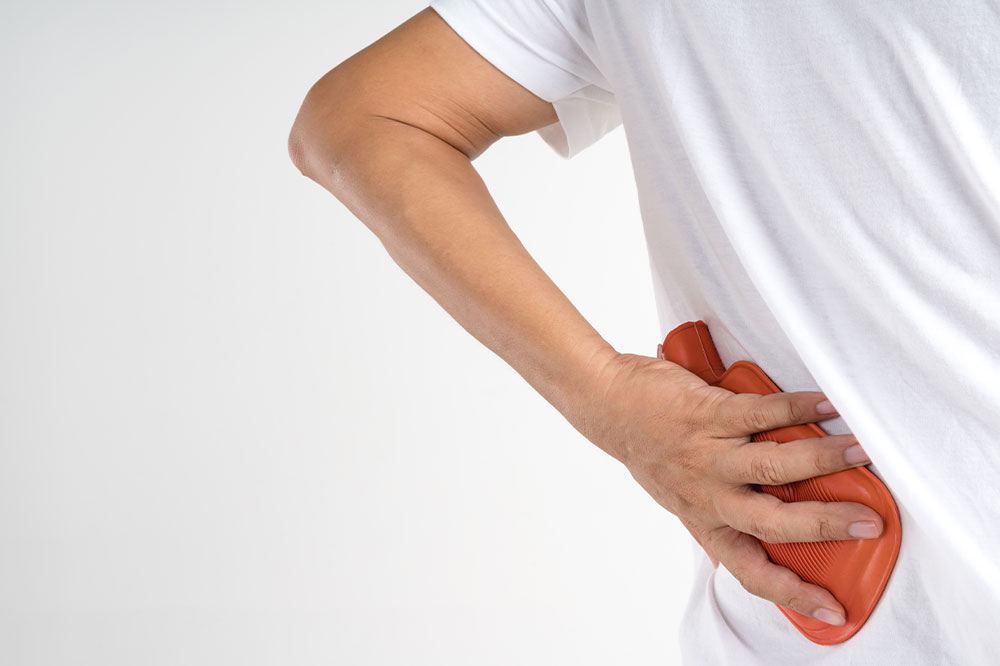
Application of Heat and Cold Therapy
Thermal therapies are cornerstone treatments for lower back pain relief. Applying heat, such as via hot water bottles, electric heating pads, or warm baths, increases blood circulation in the affected area, delivering vital nutrients and oxygen that facilitate tissue repair. Heat treatment also relaxes tense muscles, easing stiffness and reducing pain. Conversely, cold therapy using ice packs or cold wraps helps diminish inflammation and swelling that often accompany injuries. Cold numbness can also alleviate nerve pain and spasms. Alternating between heat and cold can optimize relief, decrease muscle stiffness, and promote faster recovery.
Medical Interventions for Persistent Pain
When pain persists despite self-care efforts, medical treatments may be necessary. These interventions aim to reduce inflammation, relieve nerve compression, and improve function. Common medical options include:
Intradural Steroid Injections - Administered directly into the epidural space around the spinal cord, these injections deliver corticosteroids that reduce nerve inflammation temporarily. They are often performed under imaging guidance, such as fluoroscopy, to ensure precise placement.
Muscle Relaxants - Prescribed medications that alleviate muscle spasms and reduce tightness, helping improve mobility and decrease pain levels.
Narcotic Painkillers - Short-term use of opioids can be effective for severe pain, but they require careful monitoring due to potential dependence and side effects.
Support Braces and Orthopedic Devices - Wearing lumbar braces or supports can stabilize the spine, reduce load on injured structures, and facilitate healing, especially during physical activity or rehabilitation.
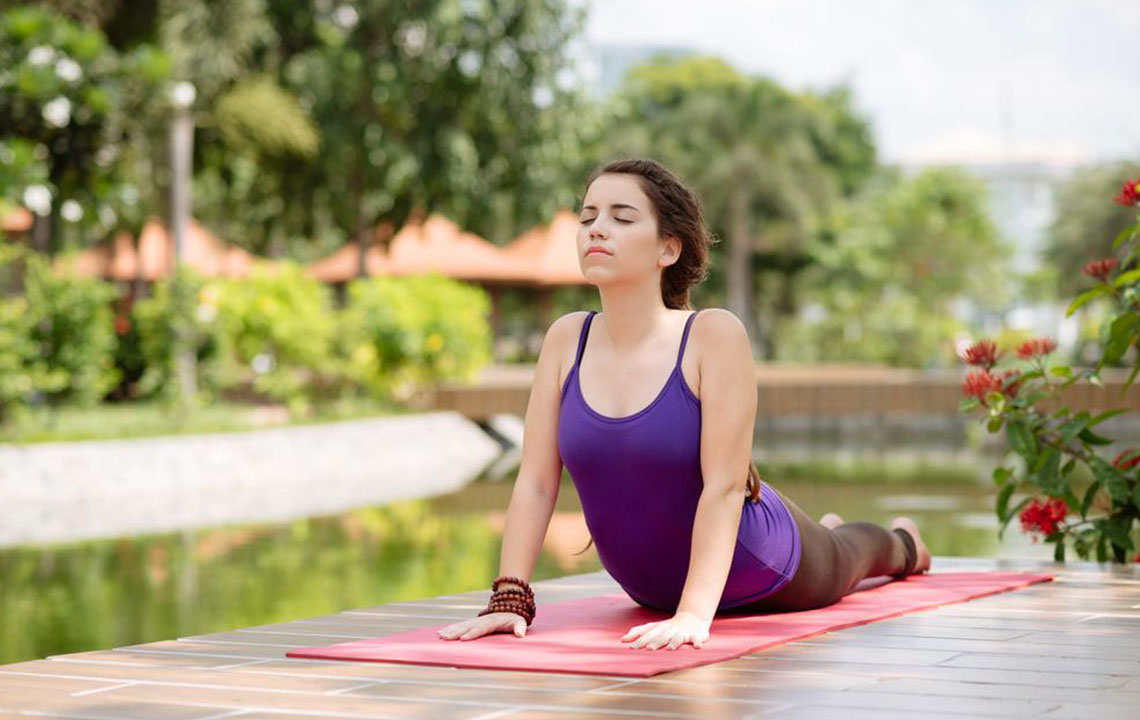
Incorporating Physical Activity and Exercise
Engaging in regular, targeted physical activity is vital in managing ongoing lower back pain. Exercise stimulates the release of endorphins, natural pain-relieving hormones, and helps improve flexibility, strength, and posture. The following exercises are particularly beneficial:
Stretching Exercises - Gentle stretching of the hips, hamstrings, and lower back can reduce muscle stiffness, improve range of motion, and decrease pressure on the lumbar area. Techniques such as hamstring stretches, pelvic tilts, and lower-back rotations are recommended.
Core Strengthening Movements - Building strength in the abdominal, pelvic, and hip muscles creates a supportive girdle for the lower spine, significantly reducing strain and the likelihood of injury. Exercises like planks, bridges, and abdominal curls are effective but should be performed under professional guidance to prevent exacerbating pain.
Always consult with healthcare professionals before initiating any new exercise or medication plan for lower back pain. Proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plans are key for effective management and long-term relief.